Patrick Cardinal
Multi-Target Backdoor Attacks Against Speaker Recognition
Aug 13, 2025Abstract:In this work, we propose a multi-target backdoor attack against speaker identification using position-independent clicking sounds as triggers. Unlike previous single-target approaches, our method targets up to 50 speakers simultaneously, achieving success rates of up to 95.04%. To simulate more realistic attack conditions, we vary the signal-to-noise ratio between speech and trigger, demonstrating a trade-off between stealth and effectiveness. We further extend the attack to the speaker verification task by selecting the most similar training speaker - based on cosine similarity - as a proxy target. The attack is most effective when target and enrolled speaker pairs are highly similar, reaching success rates of up to 90% in such cases.
Automatic Proficiency Assessment in L2 English Learners
May 05, 2025Abstract:Second language proficiency (L2) in English is usually perceptually evaluated by English teachers or expert evaluators, with the inherent intra- and inter-rater variability. This paper explores deep learning techniques for comprehensive L2 proficiency assessment, addressing both the speech signal and its correspondent transcription. We analyze spoken proficiency classification prediction using diverse architectures, including 2D CNN, frequency-based CNN, ResNet, and a pretrained wav2vec 2.0 model. Additionally, we examine text-based proficiency assessment by fine-tuning a BERT language model within resource constraints. Finally, we tackle the complex task of spontaneous dialogue assessment, managing long-form audio and speaker interactions through separate applications of wav2vec 2.0 and BERT models. Results from experiments on EFCamDat and ANGLISH datasets and a private dataset highlight the potential of deep learning, especially the pretrained wav2vec 2.0 model, for robust automated L2 proficiency evaluation.
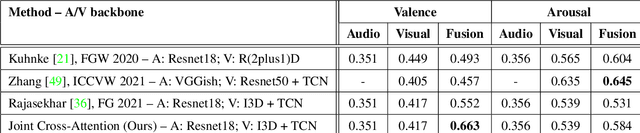
Recursive Joint Attention for Audio-Visual Fusion in Regression based Emotion Recognition
Apr 17, 2023Abstract:In video-based emotion recognition (ER), it is important to effectively leverage the complementary relationship among audio (A) and visual (V) modalities, while retaining the intra-modal characteristics of individual modalities. In this paper, a recursive joint attention model is proposed along with long short-term memory (LSTM) modules for the fusion of vocal and facial expressions in regression-based ER. Specifically, we investigated the possibility of exploiting the complementary nature of A and V modalities using a joint cross-attention model in a recursive fashion with LSTMs to capture the intra-modal temporal dependencies within the same modalities as well as among the A-V feature representations. By integrating LSTMs with recursive joint cross-attention, our model can efficiently leverage both intra- and inter-modal relationships for the fusion of A and V modalities. The results of extensive experiments performed on the challenging Affwild2 and Fatigue (private) datasets indicate that the proposed A-V fusion model can significantly outperform state-of-art-methods.
Audio-Visual Fusion for Emotion Recognition in the Valence-Arousal Space Using Joint Cross-Attention
Sep 19, 2022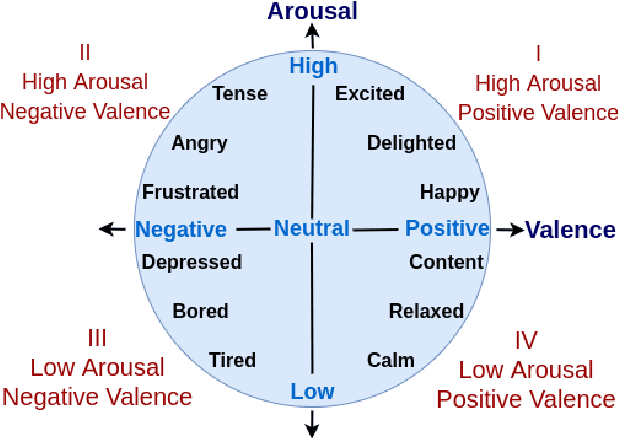
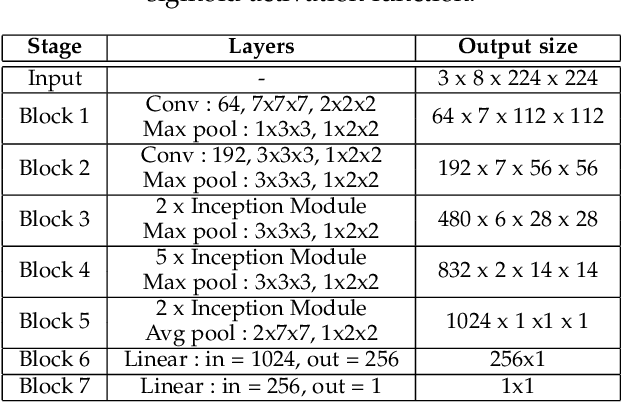
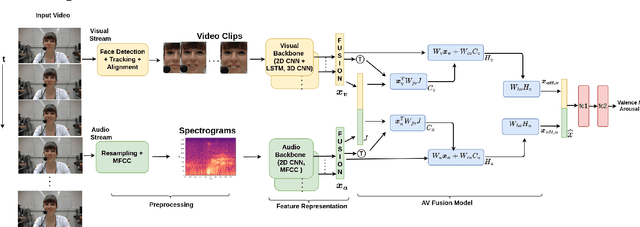
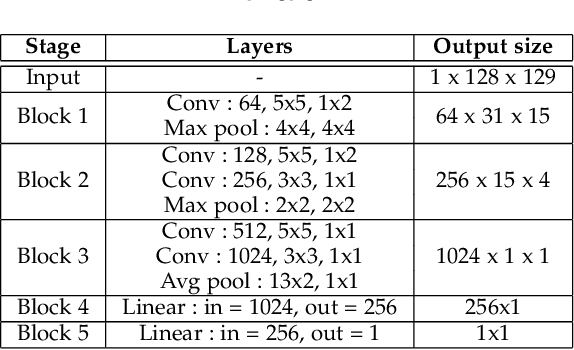
Abstract:Automatic emotion recognition (ER) has recently gained lot of interest due to its potential in many real-world applications. In this context, multimodal approaches have been shown to improve performance (over unimodal approaches) by combining diverse and complementary sources of information, providing some robustness to noisy and missing modalities. In this paper, we focus on dimensional ER based on the fusion of facial and vocal modalities extracted from videos, where complementary audio-visual (A-V) relationships are explored to predict an individual's emotional states in valence-arousal space. Most state-of-the-art fusion techniques rely on recurrent networks or conventional attention mechanisms that do not effectively leverage the complementary nature of A-V modalities. To address this problem, we introduce a joint cross-attentional model for A-V fusion that extracts the salient features across A-V modalities, that allows to effectively leverage the inter-modal relationships, while retaining the intra-modal relationships. In particular, it computes the cross-attention weights based on correlation between the joint feature representation and that of the individual modalities. By deploying the joint A-V feature representation into the cross-attention module, it helps to simultaneously leverage both the intra and inter modal relationships, thereby significantly improving the performance of the system over the vanilla cross-attention module. The effectiveness of our proposed approach is validated experimentally on challenging videos from the RECOLA and AffWild2 datasets. Results indicate that our joint cross-attentional A-V fusion model provides a cost-effective solution that can outperform state-of-the-art approaches, even when the modalities are noisy or absent.
RSD-GAN: Regularized Sobolev Defense GAN Against Speech-to-Text Adversarial Attacks
Jul 14, 2022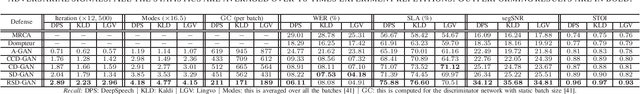
Abstract:This paper introduces a new synthesis-based defense algorithm for counteracting with a varieties of adversarial attacks developed for challenging the performance of the cutting-edge speech-to-text transcription systems. Our algorithm implements a Sobolev-based GAN and proposes a novel regularizer for effectively controlling over the functionality of the entire generative model, particularly the discriminator network during training. Our achieved results upon carrying out numerous experiments on the victim DeepSpeech, Kaldi, and Lingvo speech transcription systems corroborate the remarkable performance of our defense approach against a comprehensive range of targeted and non-targeted adversarial attacks.
RCC-GAN: Regularized Compound Conditional GAN for Large-Scale Tabular Data Synthesis
May 24, 2022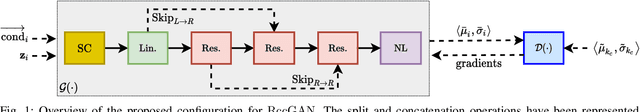
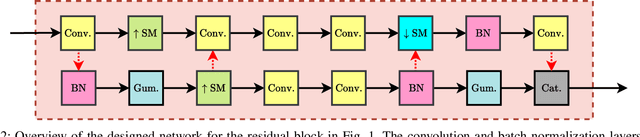
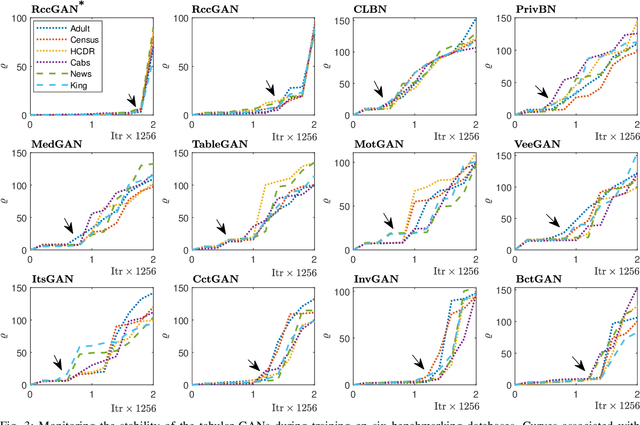
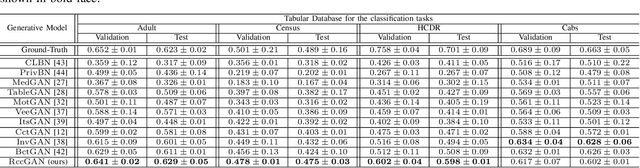
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel generative adversarial network (GAN) for synthesizing large-scale tabular databases which contain various features such as continuous, discrete, and binary. Technically, our GAN belongs to the category of class-conditioned generative models with a predefined conditional vector. However, we propose a new formulation for deriving such a vector incorporating both binary and discrete features simultaneously. We refer to this noble definition as compound conditional vector and employ it for training the generator network. The core architecture of this network is a three-layered deep residual neural network with skip connections. For improving the stability of such complex architecture, we present a regularization scheme towards limiting unprecedented variations on its weight vectors during training. This regularization approach is quite compatible with the nature of adversarial training and it is not computationally prohibitive in runtime. Furthermore, we constantly monitor the variation of the weight vectors for identifying any potential instabilities or irregularities to measure the strength of our proposed regularizer. Toward this end, we also develop a new metric for tracking sudden perturbation on the weight vectors using the singular value decomposition theory. Finally, we evaluate the performance of our proposed synthesis approach on six benchmarking tabular databases, namely Adult, Census, HCDR, Cabs, News, and King. The achieved results corroborate that for the majority of the cases, our proposed RccGAN outperforms other conventional and modern generative models in terms of accuracy, stability, and reliability.
Named Entity Recognition for Audio De-Identification
Apr 26, 2022

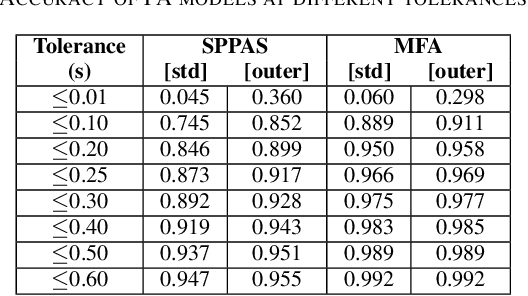
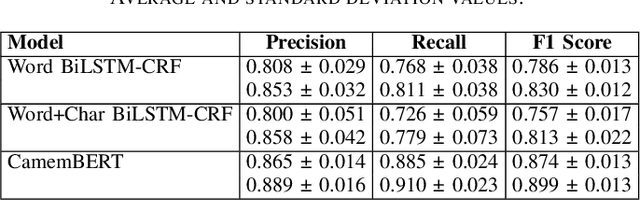
Abstract:Data anonymization is often a task carried out by humans. Automating it would reduce the cost and time required to complete this task. This paper presents a pipeline to automate the anonymization of audio data in French. We propose a pipeline, which takes audio files with their transcriptions and removes the named entities (NEs) present in the audio. Our pipeline is made up of a forced aligner, which aligns words in an audio transcript with speech and a model that performs named entity recognition (NER). Then, the audio segments that correspond to NEs are substituted with silence to anonymize audio. We compared forced aligners and NER models to find the best ones for our scenario. We evaluated our pipeline on a small hand-annotated dataset, achieving an F1 score of 0.769. This result shows that automating this task is feasible.
From Environmental Sound Representation to Robustness of 2D CNN Models Against Adversarial Attacks
Apr 14, 2022
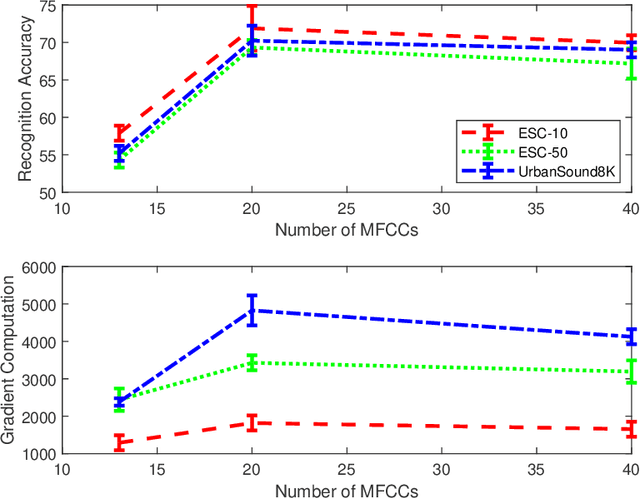
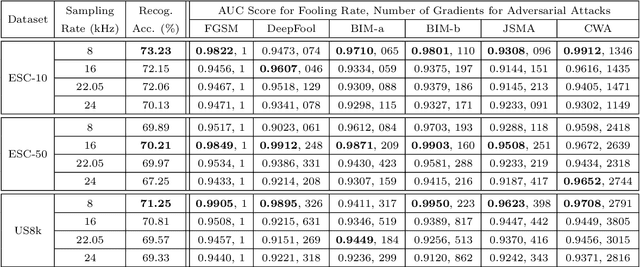
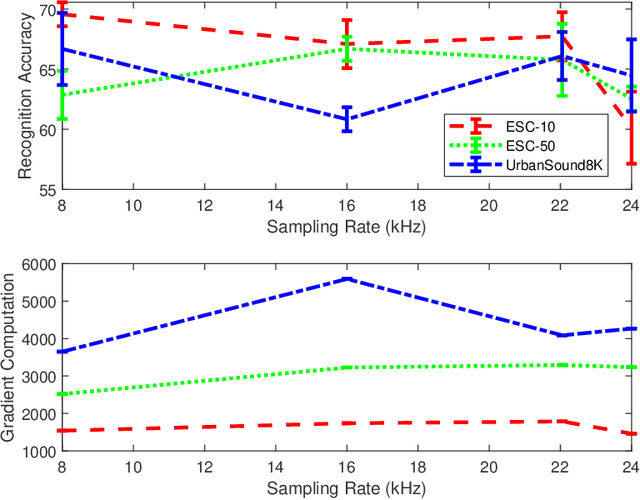
Abstract:This paper investigates the impact of different standard environmental sound representations (spectrograms) on the recognition performance and adversarial attack robustness of a victim residual convolutional neural network, namely ResNet-18. Our main motivation for focusing on such a front-end classifier rather than other complex architectures is balancing recognition accuracy and the total number of training parameters. Herein, we measure the impact of different settings required for generating more informative Mel-frequency cepstral coefficient (MFCC), short-time Fourier transform (STFT), and discrete wavelet transform (DWT) representations on our front-end model. This measurement involves comparing the classification performance over the adversarial robustness. We demonstrate an inverse relationship between recognition accuracy and model robustness against six benchmarking attack algorithms on the balance of average budgets allocated by the adversary and the attack cost. Moreover, our experimental results have shown that while the ResNet-18 model trained on DWT spectrograms achieves a high recognition accuracy, attacking this model is relatively more costly for the adversary than other 2D representations. We also report some results on different convolutional neural network architectures such as ResNet-34, ResNet-56, AlexNet, and GoogLeNet, SB-CNN, and LSTM-based.
A Joint Cross-Attention Model for Audio-Visual Fusion in Dimensional Emotion Recognition
Apr 04, 2022
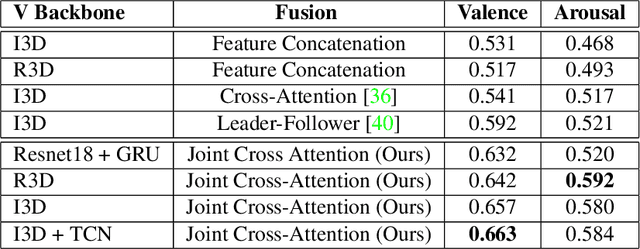
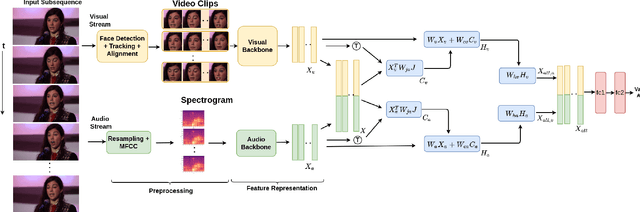
Abstract:Multimodal emotion recognition has recently gained much attention since it can leverage diverse and complementary relationships over multiple modalities (e.g., audio, visual, biosignals, etc.), and can provide some robustness to noisy modalities. Most state-of-the-art methods for audio-visual (A-V) fusion rely on recurrent networks or conventional attention mechanisms that do not effectively leverage the complementary nature of A-V modalities. In this paper, we focus on dimensional emotion recognition based on the fusion of facial and vocal modalities extracted from videos. Specifically, we propose a joint cross-attention model that relies on the complementary relationships to extract the salient features across A-V modalities, allowing for accurate prediction of continuous values of valence and arousal. The proposed fusion model efficiently leverages the inter-modal relationships, while reducing the heterogeneity between the features. In particular, it computes the cross-attention weights based on correlation between the combined feature representation and individual modalities. By deploying the combined A-V feature representation into the cross-attention module, the performance of our fusion module improves significantly over the vanilla cross-attention module. Experimental results on validation-set videos from the AffWild2 dataset indicate that our proposed A-V fusion model provides a cost-effective solution that can outperform state-of-the-art approaches. The code is available on GitHub: https://github.com/praveena2j/JointCrossAttentional-AV-Fusion.
Bi-Discriminator Class-Conditional Tabular GAN
Dec 02, 2021
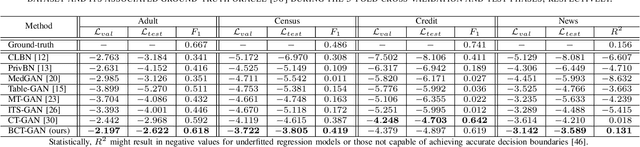
Abstract:This paper introduces a bi-discriminator GAN for synthesizing tabular datasets containing continuous, binary, and discrete columns. Our proposed approach employs an adapted preprocessing scheme and a novel conditional term for the generator network to more effectively capture the input sample distributions. Additionally, we implement straightforward yet effective architectures for discriminator networks aiming at providing more discriminative gradient information to the generator. Our experimental results on four benchmarking public datasets corroborates the superior performance of our GAN both in terms of likelihood fitness metric and machine learning efficacy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge