Mohammad Esmaeilpour
RSD-GAN: Regularized Sobolev Defense GAN Against Speech-to-Text Adversarial Attacks
Jul 14, 2022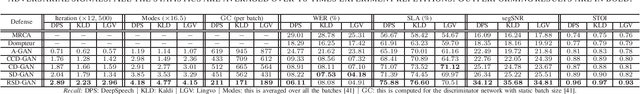
Abstract:This paper introduces a new synthesis-based defense algorithm for counteracting with a varieties of adversarial attacks developed for challenging the performance of the cutting-edge speech-to-text transcription systems. Our algorithm implements a Sobolev-based GAN and proposes a novel regularizer for effectively controlling over the functionality of the entire generative model, particularly the discriminator network during training. Our achieved results upon carrying out numerous experiments on the victim DeepSpeech, Kaldi, and Lingvo speech transcription systems corroborate the remarkable performance of our defense approach against a comprehensive range of targeted and non-targeted adversarial attacks.
RCC-GAN: Regularized Compound Conditional GAN for Large-Scale Tabular Data Synthesis
May 24, 2022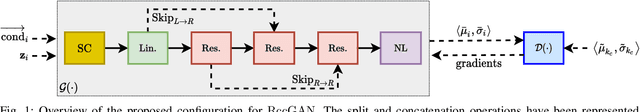
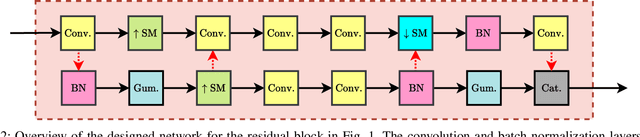
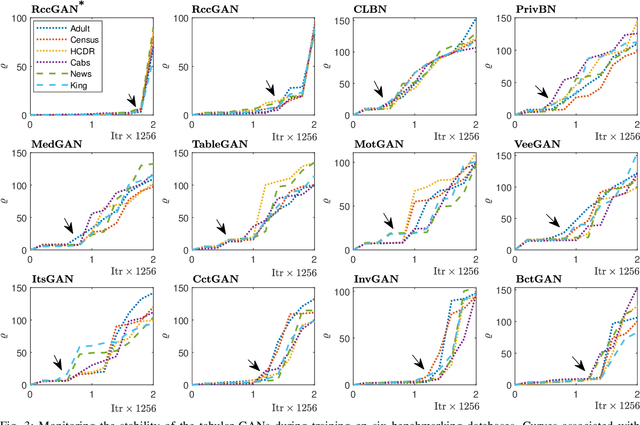
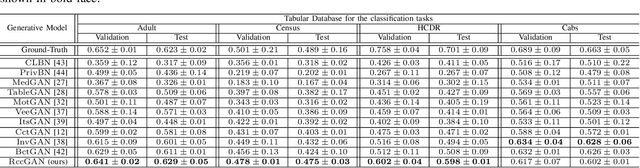
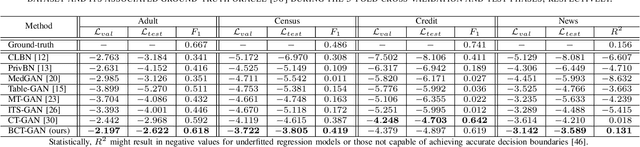
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel generative adversarial network (GAN) for synthesizing large-scale tabular databases which contain various features such as continuous, discrete, and binary. Technically, our GAN belongs to the category of class-conditioned generative models with a predefined conditional vector. However, we propose a new formulation for deriving such a vector incorporating both binary and discrete features simultaneously. We refer to this noble definition as compound conditional vector and employ it for training the generator network. The core architecture of this network is a three-layered deep residual neural network with skip connections. For improving the stability of such complex architecture, we present a regularization scheme towards limiting unprecedented variations on its weight vectors during training. This regularization approach is quite compatible with the nature of adversarial training and it is not computationally prohibitive in runtime. Furthermore, we constantly monitor the variation of the weight vectors for identifying any potential instabilities or irregularities to measure the strength of our proposed regularizer. Toward this end, we also develop a new metric for tracking sudden perturbation on the weight vectors using the singular value decomposition theory. Finally, we evaluate the performance of our proposed synthesis approach on six benchmarking tabular databases, namely Adult, Census, HCDR, Cabs, News, and King. The achieved results corroborate that for the majority of the cases, our proposed RccGAN outperforms other conventional and modern generative models in terms of accuracy, stability, and reliability.
From Environmental Sound Representation to Robustness of 2D CNN Models Against Adversarial Attacks
Apr 14, 2022
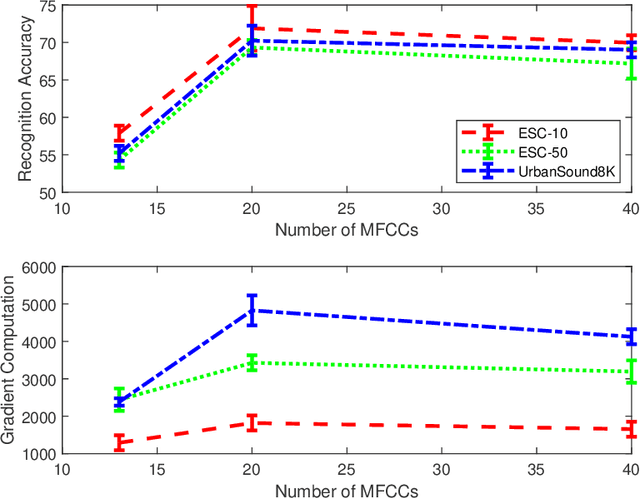
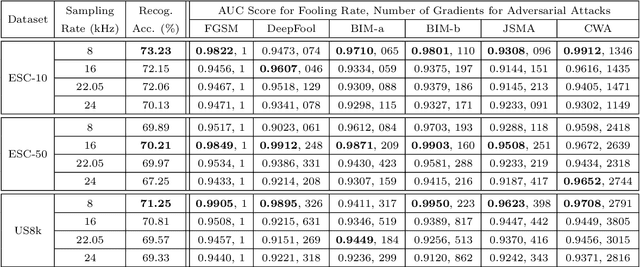
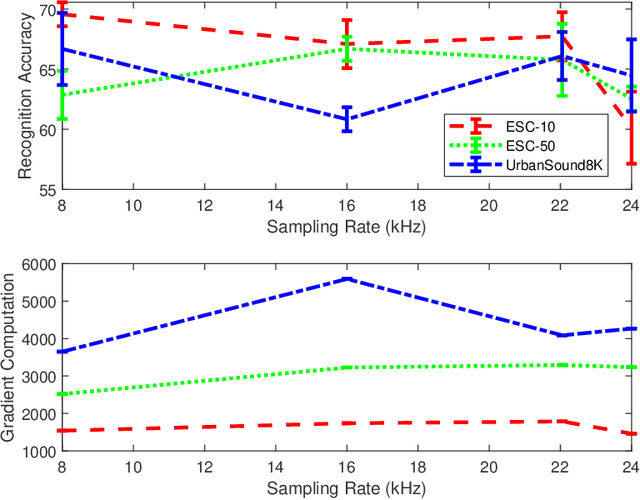
Abstract:This paper investigates the impact of different standard environmental sound representations (spectrograms) on the recognition performance and adversarial attack robustness of a victim residual convolutional neural network, namely ResNet-18. Our main motivation for focusing on such a front-end classifier rather than other complex architectures is balancing recognition accuracy and the total number of training parameters. Herein, we measure the impact of different settings required for generating more informative Mel-frequency cepstral coefficient (MFCC), short-time Fourier transform (STFT), and discrete wavelet transform (DWT) representations on our front-end model. This measurement involves comparing the classification performance over the adversarial robustness. We demonstrate an inverse relationship between recognition accuracy and model robustness against six benchmarking attack algorithms on the balance of average budgets allocated by the adversary and the attack cost. Moreover, our experimental results have shown that while the ResNet-18 model trained on DWT spectrograms achieves a high recognition accuracy, attacking this model is relatively more costly for the adversary than other 2D representations. We also report some results on different convolutional neural network architectures such as ResNet-34, ResNet-56, AlexNet, and GoogLeNet, SB-CNN, and LSTM-based.
Bi-Discriminator Class-Conditional Tabular GAN
Dec 02, 2021
Abstract:This paper introduces a bi-discriminator GAN for synthesizing tabular datasets containing continuous, binary, and discrete columns. Our proposed approach employs an adapted preprocessing scheme and a novel conditional term for the generator network to more effectively capture the input sample distributions. Additionally, we implement straightforward yet effective architectures for discriminator networks aiming at providing more discriminative gradient information to the generator. Our experimental results on four benchmarking public datasets corroborates the superior performance of our GAN both in terms of likelihood fitness metric and machine learning efficacy.
Cyclic Defense GAN Against Speech Adversarial Attacks
Mar 26, 2021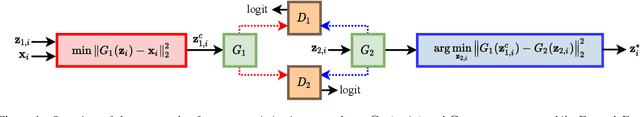
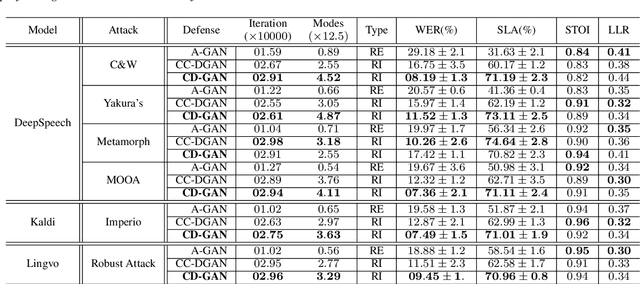
Abstract:This paper proposes a new defense approach for counteracting with state-of-the-art white and black-box adversarial attack algorithms. Our approach fits in the category of implicit reactive defense algorithms since it does not directly manipulate the potentially malicious input signals. Instead, it reconstructs a similar signal with a synthesized spectrogram using a cyclic generative adversarial network. This cyclic framework helps to yield a stable generative model. Finally, we feed the reconstructed signal into the speech-to-text model for transcription. The conducted experiments on targeted and non-targeted adversarial attacks developed for attacking DeepSpeech, Kaldi, and Lingvo models demonstrate the proposed defense's effectiveness in adverse scenarios.
Towards Robust Speech-to-Text Adversarial Attack
Mar 15, 2021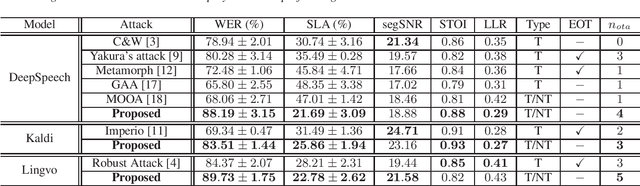
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel adversarial algorithm for attacking the state-of-the-art speech-to-text systems, namely DeepSpeech, Kaldi, and Lingvo. Our approach is based on developing an extension for the conventional distortion condition of the adversarial optimization formulation using the Cram\`er integral probability metric. Minimizing over this metric, which measures the discrepancies between original and adversarial samples' distributions, contributes to crafting signals very close to the subspace of legitimate speech recordings. This helps to yield more robust adversarial signals against playback over-the-air without employing neither costly expectation over transformation operations nor static room impulse response simulations. Our approach outperforms other targeted and non-targeted algorithms in terms of word error rate and sentence-level-accuracy with competitive performance on the crafted adversarial signals' quality. Compared to seven other strong white and black-box adversarial attacks, our proposed approach is considerably more resilient against multiple consecutive playbacks over-the-air, corroborating its higher robustness in noisy environments.
Multi-Discriminator Sobolev Defense-GAN Against Adversarial Attacks for End-to-End Speech Systems
Mar 15, 2021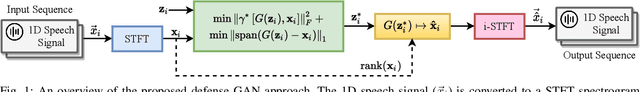
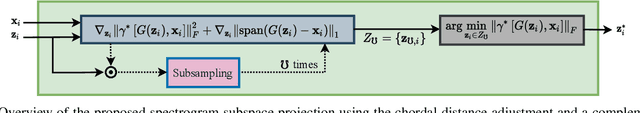
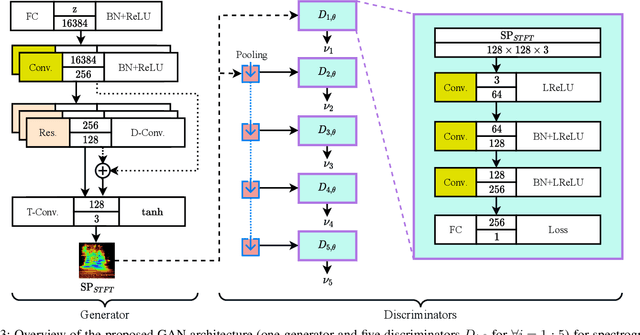
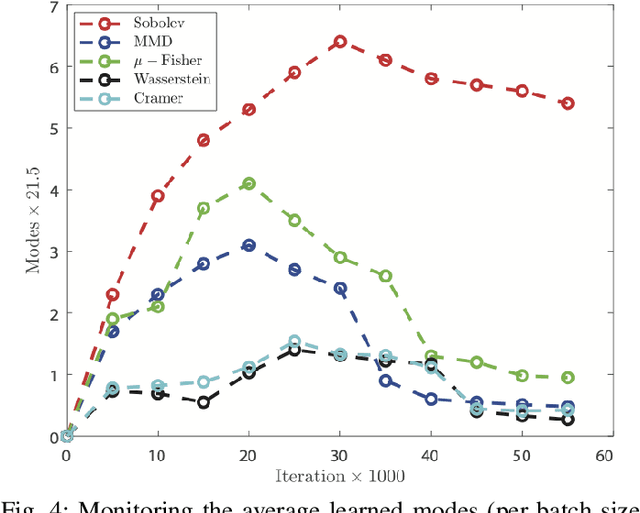
Abstract:This paper introduces a defense approach against end-to-end adversarial attacks developed for cutting-edge speech-to-text systems. The proposed defense algorithm has four major steps. First, we represent speech signals with 2D spectrograms using the short-time Fourier transform. Second, we iteratively find a safe vector using a spectrogram subspace projection operation. This operation minimizes the chordal distance adjustment between spectrograms with an additional regularization term. Third, we synthesize a spectrogram with such a safe vector using a novel GAN architecture trained with Sobolev integral probability metric. To improve the model's performance in terms of stability and the total number of learned modes, we impose an additional constraint on the generator network. Finally, we reconstruct the signal from the synthesized spectrogram and the Griffin-Lim phase approximation technique. We evaluate the proposed defense approach against six strong white and black-box adversarial attacks benchmarked on DeepSpeech, Kaldi, and Lingvo models. Our experimental results show that our algorithm outperforms other state-of-the-art defense algorithms both in terms of accuracy and signal quality.
Class-Conditional Defense GAN Against End-to-End Speech Attacks
Oct 22, 2020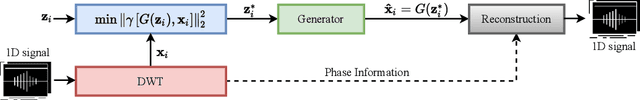
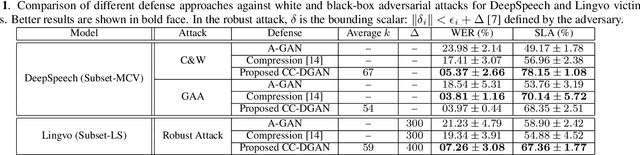
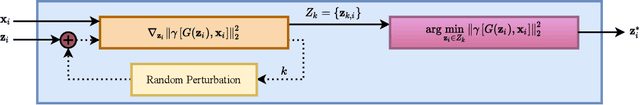
Abstract:In this paper we propose a novel defense approach against end-to-end adversarial attacks developed to fool advanced speech-to-text systems such as DeepSpeech and Lingvo. Unlike conventional defense approaches, the proposed approach does not directly employ low-level transformations such as autoencoding a given input signal aiming at removing potential adversarial perturbation. Instead of that, we find an optimal input vector for a class conditional generative adversarial network through minimizing the relative chordal distance adjustment between a given test input and the generator network. Then, we reconstruct the 1D signal from the synthesized spectrogram and the original phase information derived from the given input signal. Hence, this reconstruction does not add any extra noise to the signal and according to our experimental results, our defense-GAN considerably outperforms conventional defense algorithms both in terms of word error rate and sentence level recognition accuracy.
Conditioning Trick for Training Stable GANs
Oct 12, 2020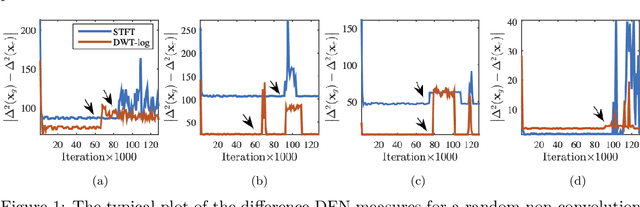
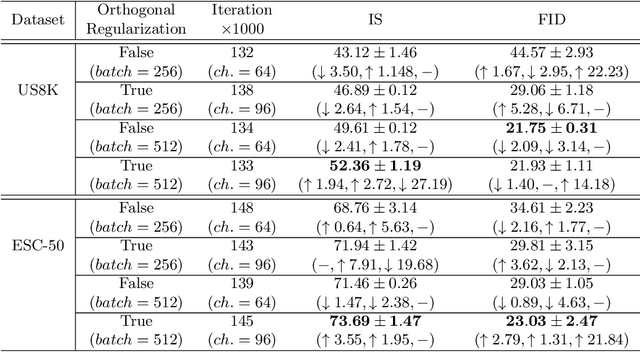
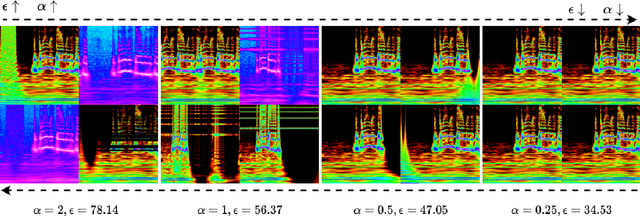
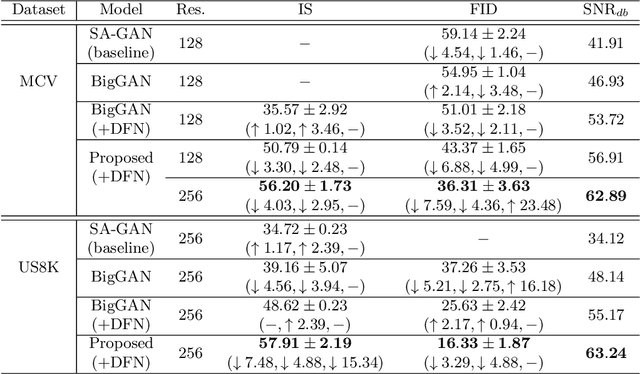
Abstract:In this paper we propose a conditioning trick, called difference departure from normality, applied on the generator network in response to instability issues during GAN training. We force the generator to get closer to the departure from normality function of real samples computed in the spectral domain of Schur decomposition. This binding makes the generator amenable to truncation and does not limit exploring all the possible modes. We slightly modify the BigGAN architecture incorporating residual network for synthesizing 2D representations of audio signals which enables reconstructing high quality sounds with some preserved phase information. Additionally, the proposed conditional training scenario makes a trade-off between fidelity and variety for the generated spectrograms. The experimental results on UrbanSound8k and ESC-50 environmental sound datasets and the Mozilla common voice dataset have shown that the proposed GAN configuration with the conditioning trick remarkably outperforms baseline architectures, according to three objective metrics: inception score, Frechet inception distance, and signal-to-noise ratio.
Adversarially Training for Audio Classifiers
Aug 26, 2020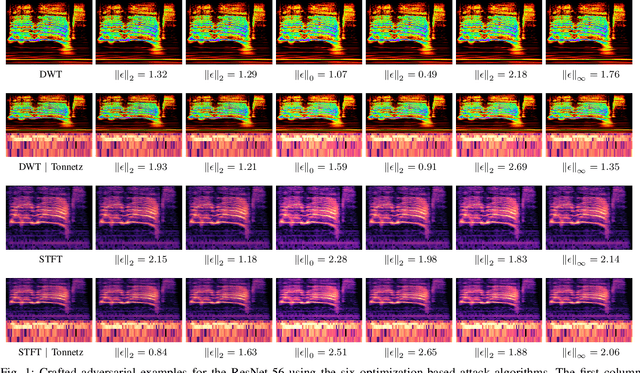
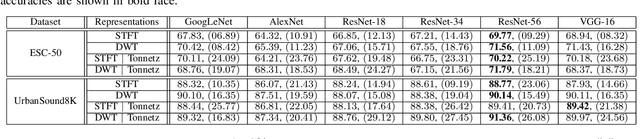
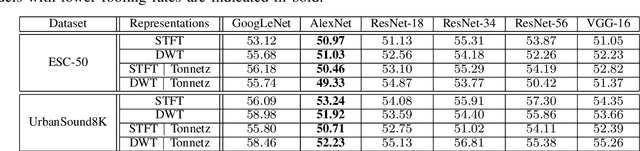
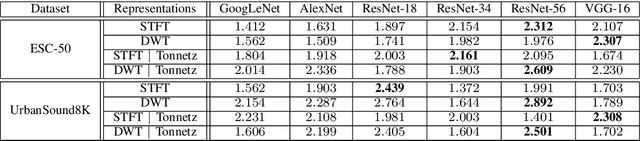
Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the potential effect of the adversarially training on the robustness of six advanced deep neural networks against a variety of targeted and non-targeted adversarial attacks. We firstly show that, the ResNet-56 model trained on the 2D representation of the discrete wavelet transform appended with the tonnetz chromagram outperforms other models in terms of recognition accuracy. Then we demonstrate the positive impact of adversarially training on this model as well as other deep architectures against six types of attack algorithms (white and black-box) with the cost of the reduced recognition accuracy and limited adversarial perturbation. We run our experiments on two benchmarking environmental sound datasets and show that without any imposed limitations on the budget allocations for the adversary, the fooling rate of the adversarially trained models can exceed 90\%. In other words, adversarial attacks exist in any scales, but they might require higher adversarial perturbations compared to non-adversarially trained models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge