Paisan Ruamviboonsuk
APTOS-2024 challenge report: Generation of synthetic 3D OCT images from fundus photographs
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) provides high-resolution, 3D, and non-invasive visualization of retinal layers in vivo, serving as a critical tool for lesion localization and disease diagnosis. However, its widespread adoption is limited by equipment costs and the need for specialized operators. In comparison, 2D color fundus photography offers faster acquisition and greater accessibility with less dependence on expensive devices. Although generative artificial intelligence has demonstrated promising results in medical image synthesis, translating 2D fundus images into 3D OCT images presents unique challenges due to inherent differences in data dimensionality and biological information between modalities. To advance generative models in the fundus-to-3D-OCT setting, the Asia Pacific Tele-Ophthalmology Society (APTOS-2024) organized a challenge titled Artificial Intelligence-based OCT Generation from Fundus Images. This paper details the challenge framework (referred to as APTOS-2024 Challenge), including: the benchmark dataset, evaluation methodology featuring two fidelity metrics-image-based distance (pixel-level OCT B-scan similarity) and video-based distance (semantic-level volumetric consistency), and analysis of top-performing solutions. The challenge attracted 342 participating teams, with 42 preliminary submissions and 9 finalists. Leading methodologies incorporated innovations in hybrid data preprocessing or augmentation (cross-modality collaborative paradigms), pre-training on external ophthalmic imaging datasets, integration of vision foundation models, and model architecture improvement. The APTOS-2024 Challenge is the first benchmark demonstrating the feasibility of fundus-to-3D-OCT synthesis as a potential solution for improving ophthalmic care accessibility in under-resourced healthcare settings, while helping to expedite medical research and clinical applications.
Predicting Diabetic Macular Edema Treatment Responses Using OCT: Dataset and Methods of APTOS Competition
May 09, 2025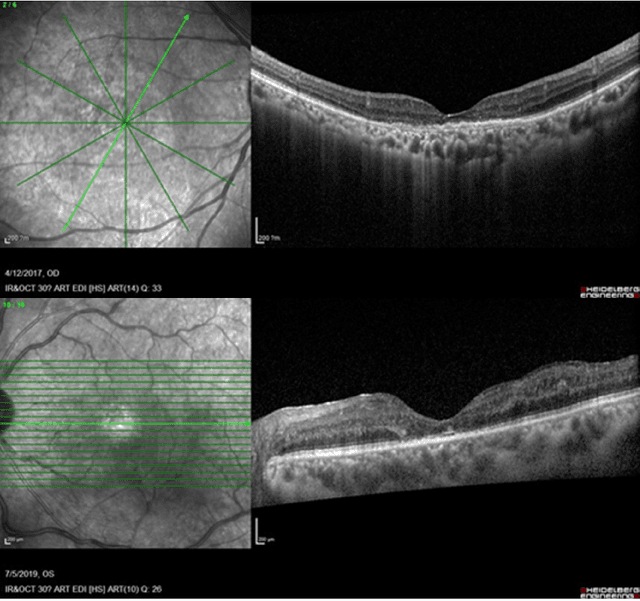
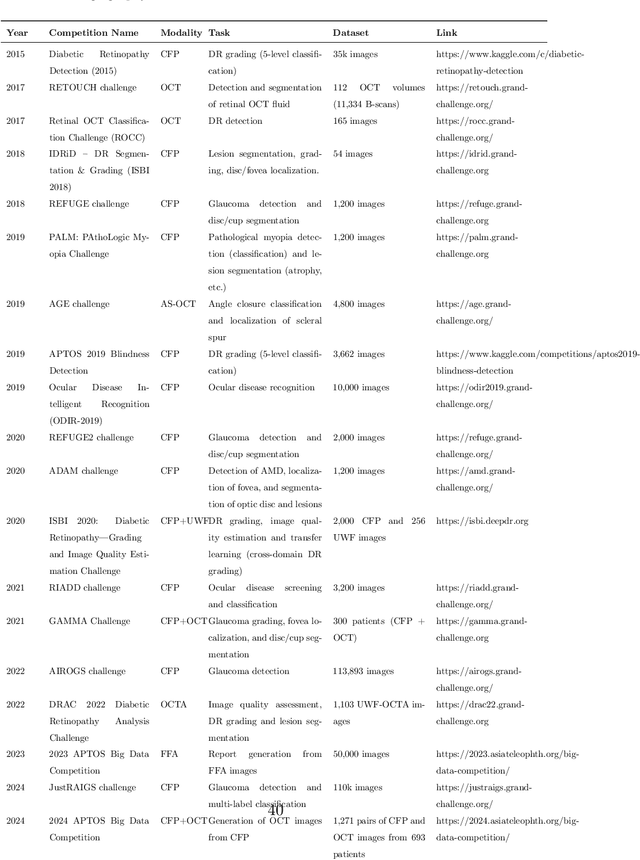
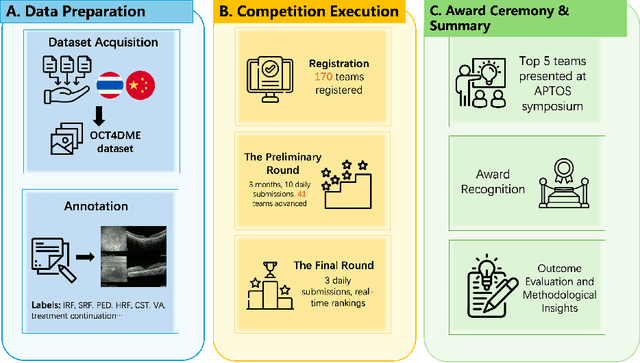

Abstract:Diabetic macular edema (DME) significantly contributes to visual impairment in diabetic patients. Treatment responses to intravitreal therapies vary, highlighting the need for patient stratification to predict therapeutic benefits and enable personalized strategies. To our knowledge, this study is the first to explore pre-treatment stratification for predicting DME treatment responses. To advance this research, we organized the 2nd Asia-Pacific Tele-Ophthalmology Society (APTOS) Big Data Competition in 2021. The competition focused on improving predictive accuracy for anti-VEGF therapy responses using ophthalmic OCT images. We provided a dataset containing tens of thousands of OCT images from 2,000 patients with labels across four sub-tasks. This paper details the competition's structure, dataset, leading methods, and evaluation metrics. The competition attracted strong scientific community participation, with 170 teams initially registering and 41 reaching the final round. The top-performing team achieved an AUC of 80.06%, highlighting the potential of AI in personalized DME treatment and clinical decision-making.
Predicting Risk of Developing Diabetic Retinopathy using Deep Learning
Aug 10, 2020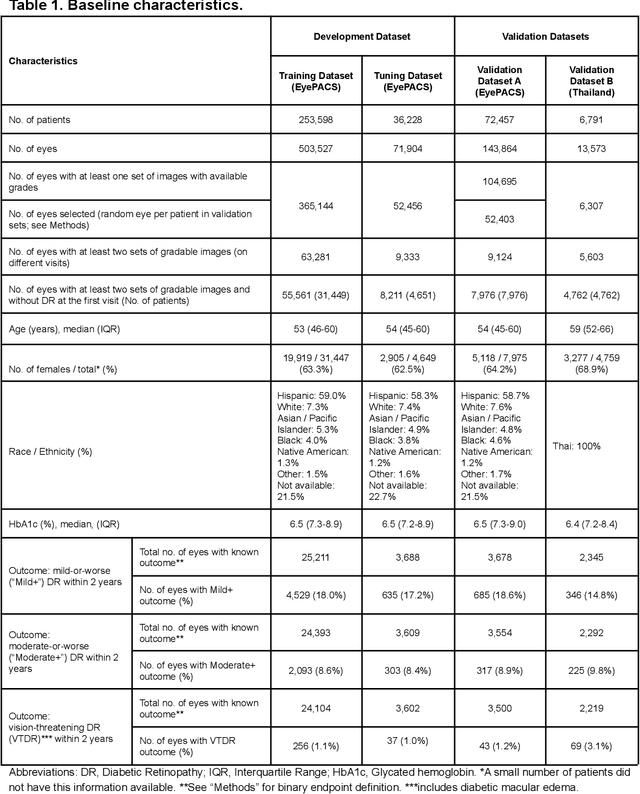

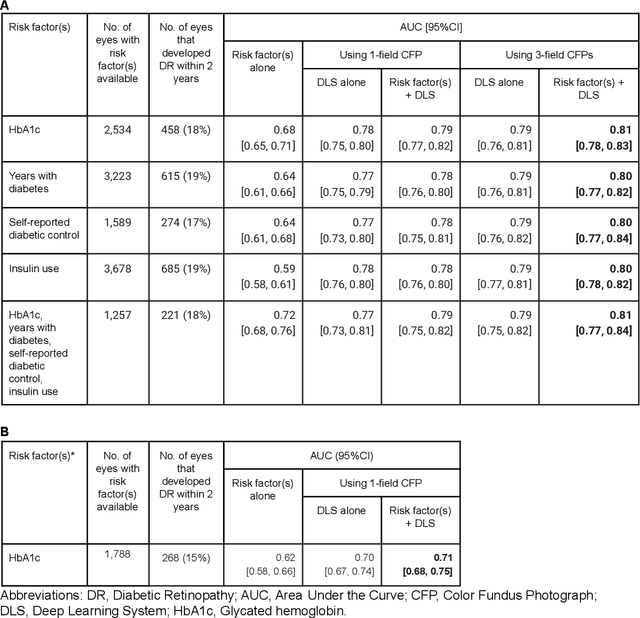

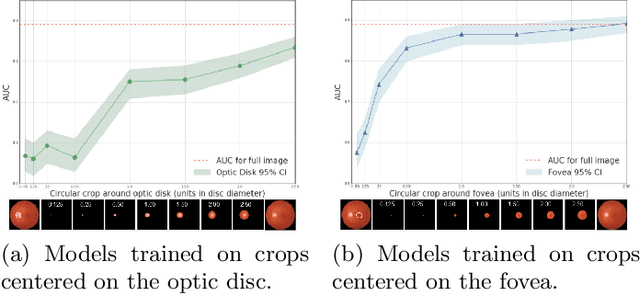
Abstract:Diabetic retinopathy (DR) screening is instrumental in preventing blindness, but faces a scaling challenge as the number of diabetic patients rises. Risk stratification for the development of DR may help optimize screening intervals to reduce costs while improving vision-related outcomes. We created and validated two versions of a deep learning system (DLS) to predict the development of mild-or-worse ("Mild+") DR in diabetic patients undergoing DR screening. The two versions used either three-fields or a single field of color fundus photographs (CFPs) as input. The training set was derived from 575,431 eyes, of which 28,899 had known 2-year outcome, and the remaining were used to augment the training process via multi-task learning. Validation was performed on both an internal validation set (set A; 7,976 eyes; 3,678 with known outcome) and an external validation set (set B; 4,762 eyes; 2,345 with known outcome). For predicting 2-year development of DR, the 3-field DLS had an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.79 (95%CI, 0.78-0.81) on validation set A. On validation set B (which contained only a single field), the 1-field DLS's AUC was 0.70 (95%CI, 0.67-0.74). The DLS was prognostic even after adjusting for available risk factors (p<0.001). When added to the risk factors, the 3-field DLS improved the AUC from 0.72 (95%CI, 0.68-0.76) to 0.81 (95%CI, 0.77-0.84) in validation set A, and the 1-field DLS improved the AUC from 0.62 (95%CI, 0.58-0.66) to 0.71 (95%CI, 0.68-0.75) in validation set B. The DLSs in this study identified prognostic information for DR development from CFPs. This information is independent of and more informative than the available risk factors.
Scientific Discovery by Generating Counterfactuals using Image Translation
Jul 10, 2020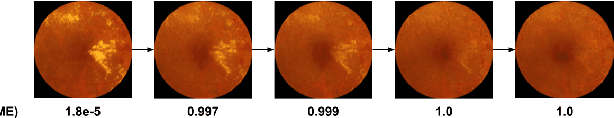
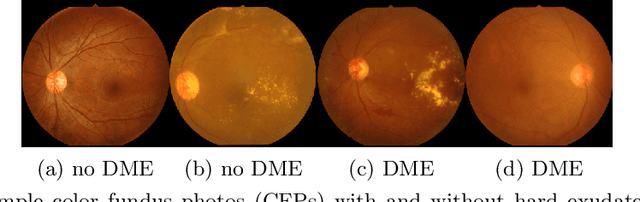
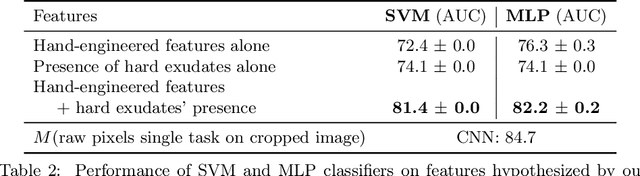
Abstract:Model explanation techniques play a critical role in understanding the source of a model's performance and making its decisions transparent. Here we investigate if explanation techniques can also be used as a mechanism for scientific discovery. We make three contributions: first, we propose a framework to convert predictions from explanation techniques to a mechanism of discovery. Second, we show how generative models in combination with black-box predictors can be used to generate hypotheses (without human priors) that can be critically examined. Third, with these techniques we study classification models for retinal images predicting Diabetic Macular Edema (DME), where recent work showed that a CNN trained on these images is likely learning novel features in the image. We demonstrate that the proposed framework is able to explain the underlying scientific mechanism, thus bridging the gap between the model's performance and human understanding.
* Accepted at MICCAI 2020. This version combines camera-ready and supplement
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge