Pablo Gómez
MCTED: A Machine-Learning-Ready Dataset for Digital Elevation Model Generation From Mars Imagery
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:This work presents a new dataset for the Martian digital elevation model prediction task, ready for machine learning applications called MCTED. The dataset has been generated using a comprehensive pipeline designed to process high-resolution Mars orthoimage and DEM pairs from Day et al., yielding a dataset consisting of 80,898 data samples. The source images are data gathered by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter using the CTX instrument, providing a very diverse and comprehensive coverage of the Martian surface. Given the complexity of the processing pipelines used in large-scale DEMs, there are often artefacts and missing data points in the original data, for which we developed tools to solve or mitigate their impact. We divide the processed samples into training and validation splits, ensuring samples in both splits cover no mutual areas to avoid data leakage. Every sample in the dataset is represented by the optical image patch, DEM patch, and two mask patches, indicating values that were originally missing or were altered by us. This allows future users of the dataset to handle altered elevation regions as they please. We provide statistical insights of the generated dataset, including the spatial distribution of samples, the distributions of elevation values, slopes and more. Finally, we train a small U-Net architecture on the MCTED dataset and compare its performance to a monocular depth estimation foundation model, DepthAnythingV2, on the task of elevation prediction. We find that even a very small architecture trained on this dataset specifically, beats a zero-shot performance of a depth estimation foundation model like DepthAnythingV2. We make the dataset and code used for its generation completely open source in public repositories.
AnomalyMatch: Discovering Rare Objects of Interest with Semi-supervised and Active Learning
May 06, 2025Abstract:Anomaly detection in large datasets is essential in fields such as astronomy and computer vision; however, supervised methods typically require extensive anomaly labelling, which is often impractical. We present AnomalyMatch, an anomaly detection framework combining the semi-supervised FixMatch algorithm using EfficientNet classifiers with active learning. By treating anomaly detection as a semi-supervised binary classification problem, we efficiently utilise limited labelled and abundant unlabelled images. We allow iterative model refinement in a user interface for expert verification of high-confidence anomalies and correction of false positives. Built for astronomical data, AnomalyMatch generalises readily to other domains facing similar data challenges. Evaluations on the GalaxyMNIST astronomical dataset and the miniImageNet natural-image benchmark under severe class imbalance (1% anomalies for miniImageNet) display strong performance: starting from five to ten labelled anomalies and after three active learning cycles, we achieve an average AUROC of 0.95 (miniImageNet) and 0.86 (GalaxyMNIST), with respective AUPRC of 0.77 and 0.71. After active learning cycles, anomalies are ranked with 71% (miniImageNet) to 93% precision in the 1% of the highest-ranked images. AnomalyMatch is tailored for large-scale applications, efficiently processing predictions for 100 million images within three days on a single GPU. Integrated into ESAs Datalabs platform, AnomalyMatch facilitates targeted discovery of scientifically valuable anomalies in vast astronomical datasets. Our results underscore the exceptional utility and scalability of this approach for anomaly discovery, highlighting the value of specialised approaches for domains characterised by severe label scarcity.
Rapid Distributed Fine-tuning of a Segmentation Model Onboard Satellites
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:Segmentation of Earth observation (EO) satellite data is critical for natural hazard analysis and disaster response. However, processing EO data at ground stations introduces delays due to data transmission bottlenecks and communication windows. Using segmentation models capable of near-real-time data analysis onboard satellites can therefore improve response times. This study presents a proof-of-concept using MobileSAM, a lightweight, pre-trained segmentation model, onboard Unibap iX10-100 satellite hardware. We demonstrate the segmentation of water bodies from Sentinel-2 satellite imagery and integrate MobileSAM with PASEOS, an open-source Python module that simulates satellite operations. This integration allows us to evaluate MobileSAM's performance under simulated conditions of a satellite constellation. Our research investigates the potential of fine-tuning MobileSAM in a decentralised way onboard multiple satellites in rapid response to a disaster. Our findings show that MobileSAM can be rapidly fine-tuned and benefits from decentralised learning, considering the constraints imposed by the simulated orbital environment. We observe improvements in segmentation performance with minimal training data and fast fine-tuning when satellites frequently communicate model updates. This study contributes to the field of onboard AI by emphasising the benefits of decentralised learning and fine-tuning pre-trained models for rapid response scenarios. Our work builds on recent related research at a critical time; as extreme weather events increase in frequency and magnitude, rapid response with onboard data analysis is essential.
Machine learning-driven Anomaly Detection and Forecasting for Euclid Space Telescope Operations
Nov 08, 2024
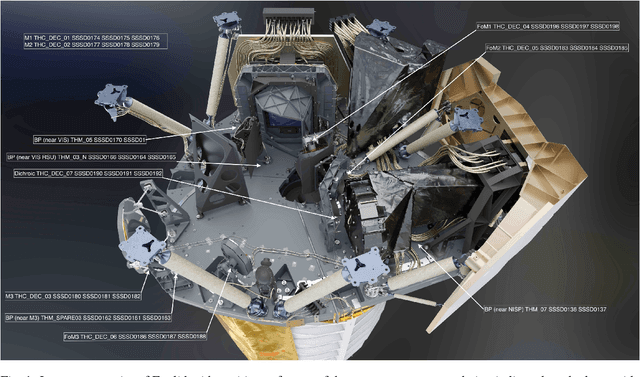
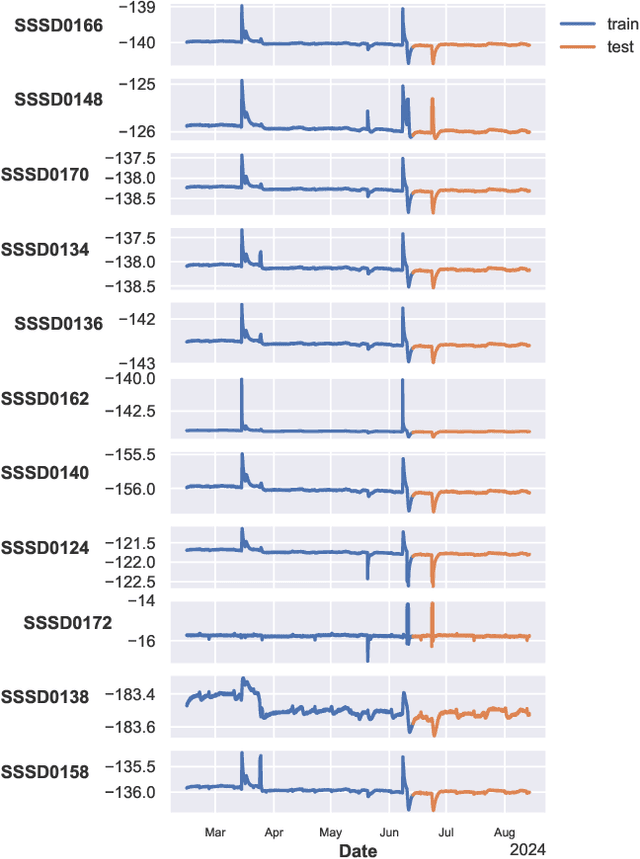
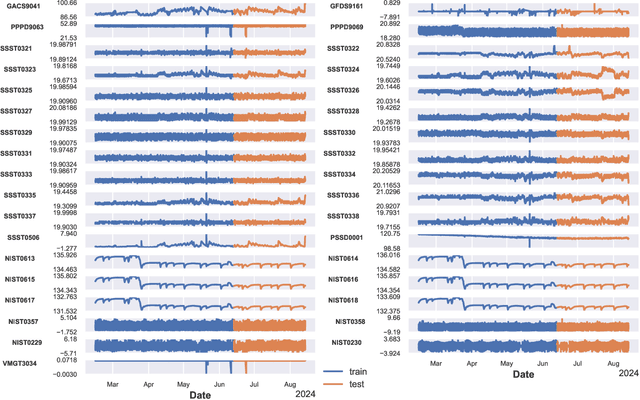
Abstract:State-of-the-art space science missions increasingly rely on automation due to spacecraft complexity and the costs of human oversight. The high volume of data, including scientific and telemetry data, makes manual inspection challenging. Machine learning offers significant potential to meet these demands. The Euclid space telescope, in its survey phase since February 2024, exemplifies this shift. Euclid's success depends on accurate monitoring and interpretation of housekeeping telemetry and science-derived data. Thousands of telemetry parameters, monitored as time series, may or may not impact the quality of scientific data. These parameters have complex interdependencies, often due to physical relationships (e.g., proximity of temperature sensors). Optimising science operations requires careful anomaly detection and identification of hidden parameter states. Moreover, understanding the interactions between known anomalies and physical quantities is crucial yet complex, as related parameters may display anomalies with varied timing and intensity. We address these challenges by analysing temperature anomalies in Euclid's telemetry from February to August 2024, focusing on eleven temperature parameters and 35 covariates. We use a predictive XGBoost model to forecast temperatures based on historical values, detecting anomalies as deviations from predictions. A second XGBoost model predicts anomalies from covariates, capturing their relationships to temperature anomalies. We identify the top three anomalies per parameter and analyse their interactions with covariates using SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanations), enabling rapid, automated analysis of complex parameter relationships. Our method demonstrates how machine learning can enhance telemetry monitoring, offering scalable solutions for other missions with similar data challenges.
XAMI -- A Benchmark Dataset for Artefact Detection in XMM-Newton Optical Images
Jun 25, 2024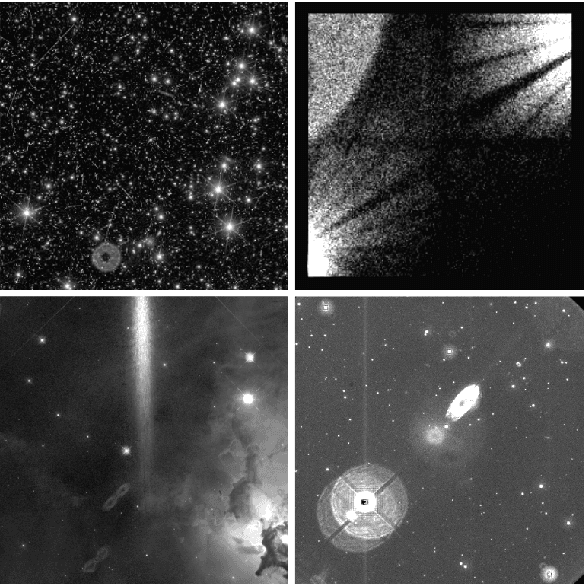
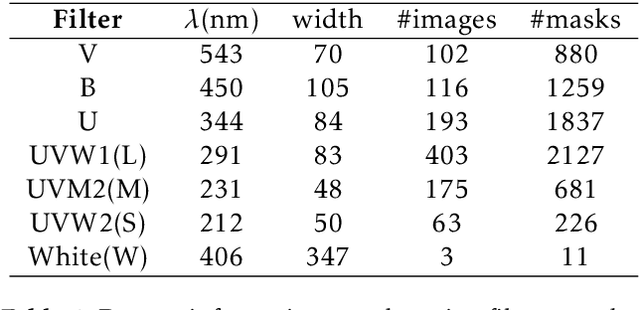
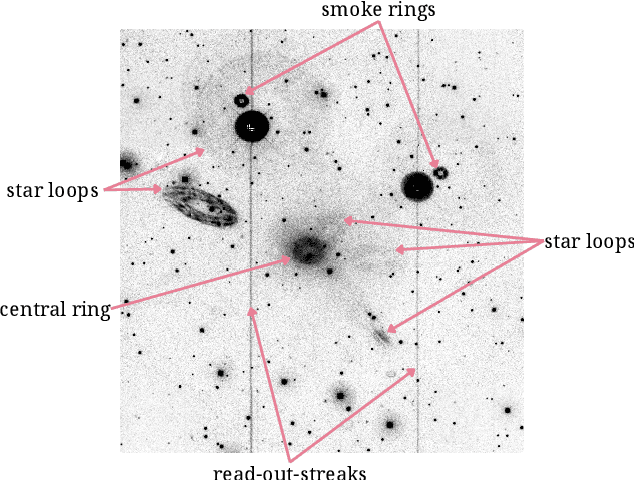
Abstract:Reflected or scattered light produce artefacts in astronomical observations that can negatively impact the scientific study. Hence, automated detection of these artefacts is highly beneficial, especially with the increasing amounts of data gathered. Machine learning methods are well-suited to this problem, but currently there is a lack of annotated data to train such approaches to detect artefacts in astronomical observations. In this work, we present a dataset of images from the XMM-Newton space telescope Optical Monitoring camera showing different types of artefacts. We hand-annotated a sample of 1000 images with artefacts which we use to train automated ML methods. We further demonstrate techniques tailored for accurate detection and masking of artefacts using instance segmentation. We adopt a hybrid approach, combining knowledge from both convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and transformer-based models and use their advantages in segmentation. The presented method and dataset will advance artefact detection in astronomical observations by providing a reproducible baseline. All code and data are made available (https://github.com/ESA-Datalabs/XAMI-model and https://github.com/ESA-Datalabs/XAMI-dataset).
Delving into the Utilisation of ChatGPT in Scientific Publications in Astronomy
Jun 25, 2024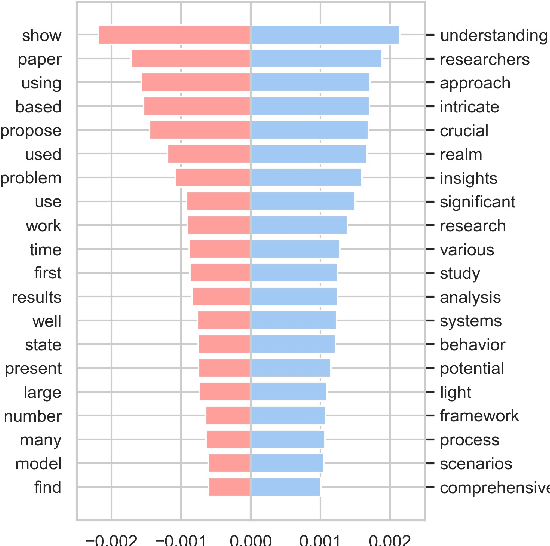
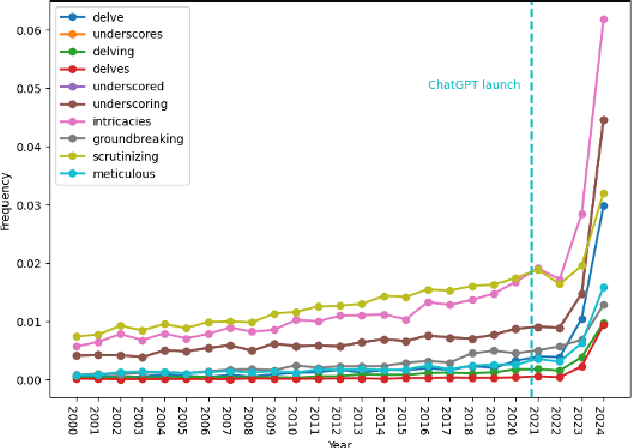
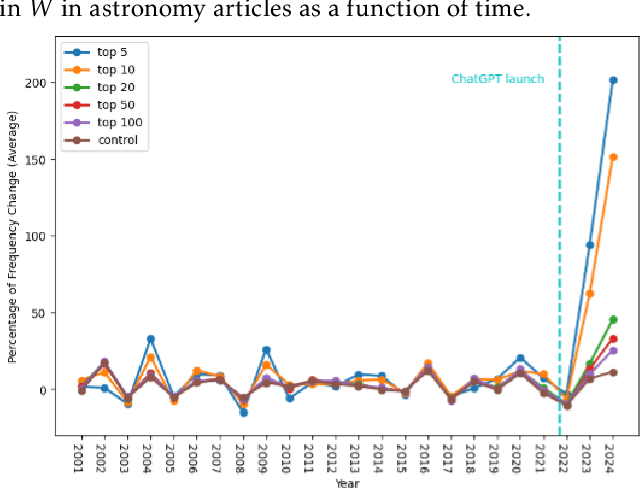
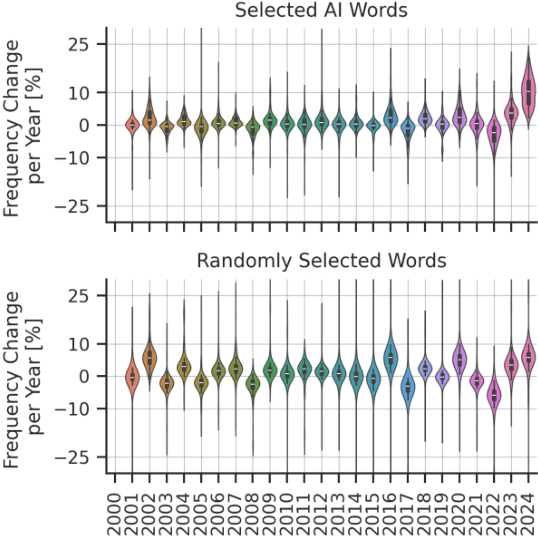
Abstract:Rapid progress in the capabilities of machine learning approaches in natural language processing has culminated in the rise of large language models over the last two years. Recent works have shown unprecedented adoption of these for academic writing, especially in some fields, but their pervasiveness in astronomy has not been studied sufficiently. To remedy this, we extract words that ChatGPT uses more often than humans when generating academic text and search a total of 1 million articles for them. This way, we assess the frequency of word occurrence in published works in astronomy tracked by the NASA Astrophysics Data System since 2000. We then perform a statistical analysis of the occurrences. We identify a list of words favoured by ChatGPT and find a statistically significant increase for these words against a control group in 2024, which matches the trend in other disciplines. These results suggest a widespread adoption of these models in the writing of astronomy papers. We encourage organisations, publishers, and researchers to work together to identify ethical and pragmatic guidelines to maximise the benefits of these systems while maintaining scientific rigour.
Machine learning-based identification of Gaia astrometric exoplanet orbits
Apr 14, 2024Abstract:The third Gaia data release (DR3) contains $\sim$170 000 astrometric orbit solutions of two-body systems located within $\sim$500 pc of the Sun. Determining component masses in these systems, in particular of stars hosting exoplanets, usually hinges on incorporating complementary observations in addition to the astrometry, e.g. spectroscopy and radial velocities. Several DR3 two-body systems with exoplanet, brown-dwarf, stellar, and black-hole components have been confirmed in this way. We developed an alternative machine learning approach that uses only the DR3 orbital solutions with the aim of identifying the best candidates for exoplanets and brown-dwarf companions. Based on confirmed substellar companions in the literature, we use semi-supervised anomaly detection methods in combination with extreme gradient boosting and random forest classifiers to determine likely low-mass outliers in the population of non-single sources. We employ and study feature importance to investigate the method's plausibility and produced a list of 22 best candidates of which four are exoplanet candidates and another five are either very-massive brown dwarfs or very-low mass stars. Three candidates, including one initial exoplanet candidate, correspond to false-positive solutions where longer-period binary star motion was fitted with a biased shorter-period orbit. We highlight nine candidates with brown-dwarf companions for preferential follow-up. One candidate companion around the Sun-like star G 15-6 could be confirmed as a genuine brown dwarf using external radial-velocity data. This new approach is a powerful complement to the traditional identification methods for substellar companions among Gaia astrometric orbits. It is particularly relevant in the context of Gaia DR4 and its expected exoplanet discovery yield.
Robust Wake-Up Word Detection by Two-stage Multi-resolution Ensembles
Oct 17, 2023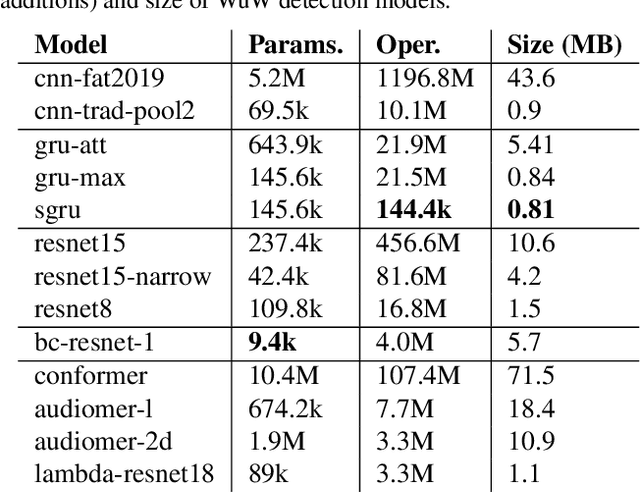
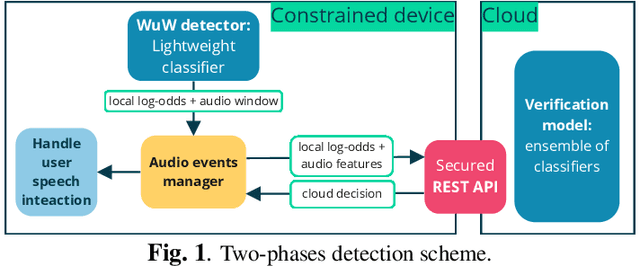
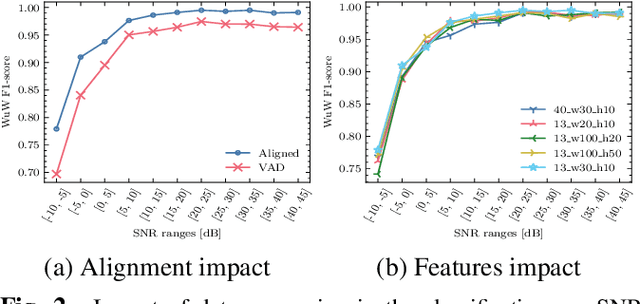
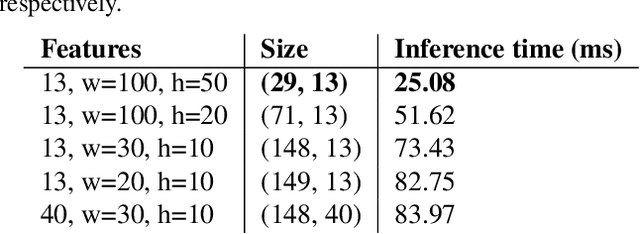
Abstract:Voice-based interfaces rely on a wake-up word mechanism to initiate communication with devices. However, achieving a robust, energy-efficient, and fast detection remains a challenge. This paper addresses these real production needs by enhancing data with temporal alignments and using detection based on two phases with multi-resolution. It employs two models: a lightweight on-device model for real-time processing of the audio stream and a verification model on the server-side, which is an ensemble of heterogeneous architectures that refine detection. This scheme allows the optimization of two operating points. To protect privacy, audio features are sent to the cloud instead of raw audio. The study investigated different parametric configurations for feature extraction to select one for on-device detection and another for the verification model. Furthermore, thirteen different audio classifiers were compared in terms of performance and inference time. The proposed ensemble outperforms our stronger classifier in every noise condition.
Investigation of the Robustness of Neural Density Fields
May 31, 2023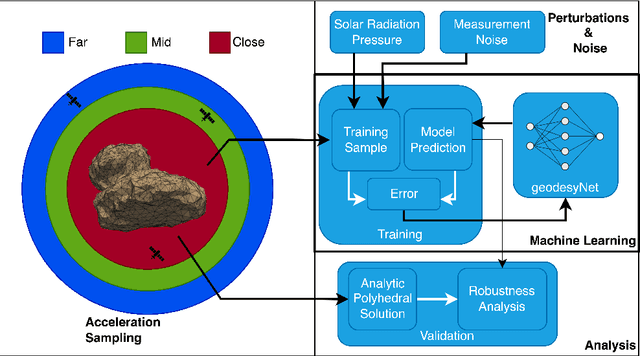
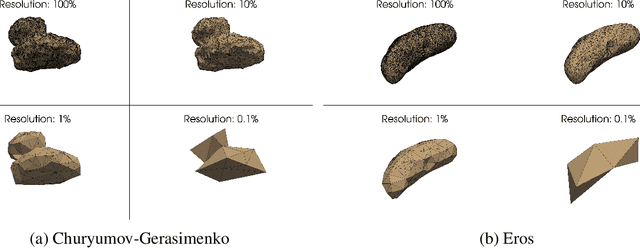
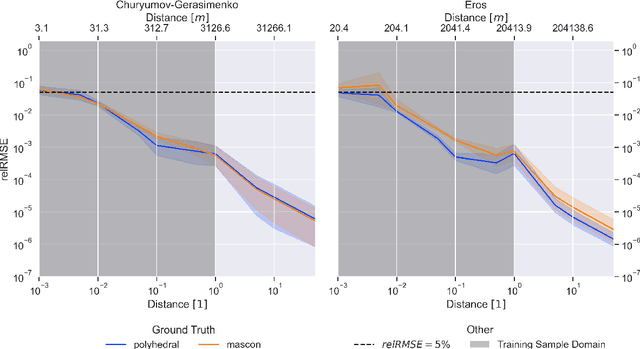
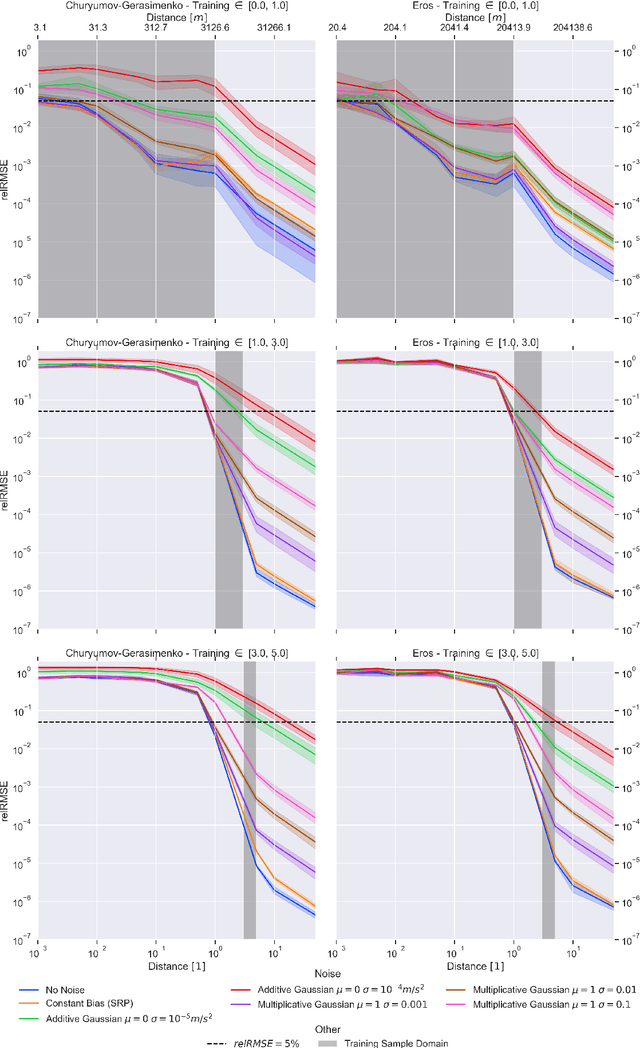
Abstract:Recent advances in modeling density distributions, so-called neural density fields, can accurately describe the density distribution of celestial bodies without, e.g., requiring a shape model - properties of great advantage when designing trajectories close to these bodies. Previous work introduced this approach, but several open questions remained. This work investigates neural density fields and their relative errors in the context of robustness to external factors like noise or constraints during training, like the maximal available gravity signal strength due to a certain distance exemplified for 433 Eros and 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. It is found that both models trained on a polyhedral and mascon ground truth perform similarly, indicating that the ground truth is not the accuracy bottleneck. The impact of solar radiation pressure on a typical probe affects training neglectable, with the relative error being of the same magnitude as without noise. However, limiting the precision of measurement data by applying Gaussian noise hurts the obtainable precision. Further, pretraining is shown as practical in order to speed up network training. Hence, this work demonstrates that training neural networks for the gravity inversion problem is appropriate as long as the gravity signal is distinguishable from noise. Code and results are available at https://github.com/gomezzz/geodesyNets
Selected Trends in Artificial Intelligence for Space Applications
Dec 17, 2022



Abstract:The development and adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies in space applications is growing quickly as the consensus increases on the potential benefits introduced. As more and more aerospace engineers are becoming aware of new trends in AI, traditional approaches are revisited to consider the applications of emerging AI technologies. Already at the time of writing, the scope of AI-related activities across academia, the aerospace industry and space agencies is so wide that an in-depth review would not fit in these pages. In this chapter we focus instead on two main emerging trends we believe capture the most relevant and exciting activities in the field: differentiable intelligence and on-board machine learning. Differentiable intelligence, in a nutshell, refers to works making extensive use of automatic differentiation frameworks to learn the parameters of machine learning or related models. Onboard machine learning considers the problem of moving inference, as well as learning, onboard. Within these fields, we discuss a few selected projects originating from the European Space Agency's (ESA) Advanced Concepts Team (ACT), giving priority to advanced topics going beyond the transposition of established AI techniques and practices to the space domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge