Pablo Castells
Toward Holistic Evaluation of Recommender Systems Powered by Generative Models
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:Recommender systems powered by generative models (Gen-RecSys) extend beyond classical item ranking by producing open-ended content, which simultaneously unlocks richer user experiences and introduces new risks. On one hand, these systems can enhance personalization and appeal through dynamic explanations and multi-turn dialogues. On the other hand, they might venture into unknown territory-hallucinating nonexistent items, amplifying bias, or leaking private information. Traditional accuracy metrics cannot fully capture these challenges, as they fail to measure factual correctness, content safety, or alignment with user intent. This paper makes two main contributions. First, we categorize the evaluation challenges of Gen-RecSys into two groups: (i) existing concerns that are exacerbated by generative outputs (e.g., bias, privacy) and (ii) entirely new risks (e.g., item hallucinations, contradictory explanations). Second, we propose a holistic evaluation approach that includes scenario-based assessments and multi-metric checks-incorporating relevance, factual grounding, bias detection, and policy compliance. Our goal is to provide a guiding framework so researchers and practitioners can thoroughly assess Gen-RecSys, ensuring effective personalization and responsible deployment.
Metamorphic Evaluation of ChatGPT as a Recommender System
Nov 18, 2024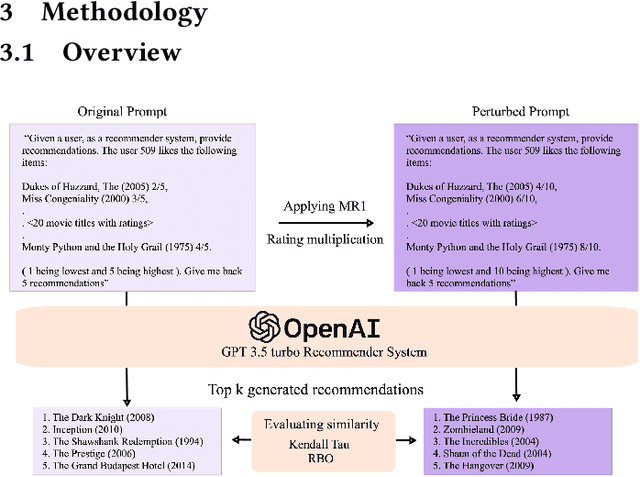
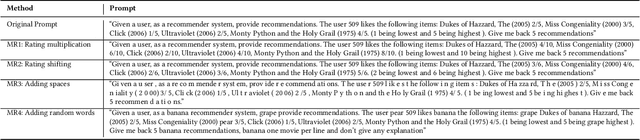
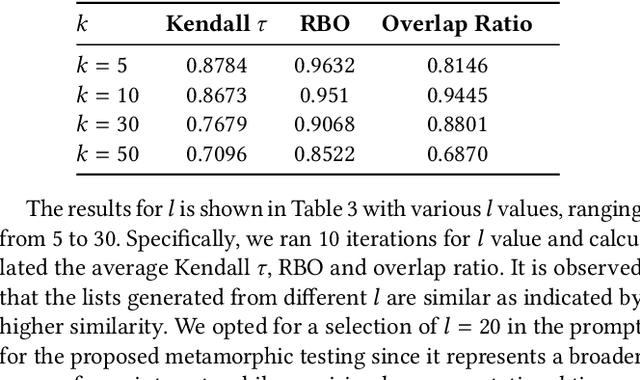
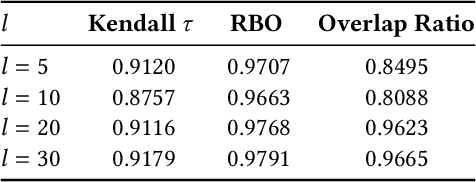
Abstract:With the rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, researchers have been working on how to utilize the LLMs for better recommendations. However, although LLMs exhibit black-box and probabilistic characteristics (meaning their internal working is not visible), the evaluation framework used for assessing these LLM-based recommender systems (RS) are the same as those used for traditional recommender systems. To address this gap, we introduce the metamorphic testing for the evaluation of GPT-based RS. This testing technique involves defining of metamorphic relations (MRs) between the inputs and checking if the relationship has been satisfied in the outputs. Specifically, we examined the MRs from both RS and LLMs perspectives, including rating multiplication/shifting in RS and adding spaces/randomness in the LLMs prompt via prompt perturbation. Similarity metrics (e.g. Kendall tau and Ranking Biased Overlap(RBO)) are deployed to measure whether the relationship has been satisfied in the outputs of MRs. The experiment results on MovieLens dataset with GPT3.5 show that lower similarity are obtained in terms of Kendall $\tau$ and RBO, which concludes that there is a need of a comprehensive evaluation of the LLM-based RS in addition to the existing evaluation metrics used for traditional recommender systems.
Impression-Aware Recommender Systems
Aug 15, 2023



Abstract:Novel data sources bring new opportunities to improve the quality of recommender systems. Impressions are a novel data source containing past recommendations (shown items) and traditional interactions. Researchers may use impressions to refine user preferences and overcome the current limitations in recommender systems research. The relevance and interest of impressions have increased over the years; hence, the need for a review of relevant work on this type of recommenders. We present a systematic literature review on recommender systems using impressions, focusing on three fundamental angles in research: recommenders, datasets, and evaluation methodologies. We provide three categorizations of papers describing recommenders using impressions, present each reviewed paper in detail, describe datasets with impressions, and analyze the existing evaluation methodologies. Lastly, we present open questions and future directions of interest, highlighting aspects missing in the literature that can be addressed in future works.
Recommender Systems: A Primer
Feb 06, 2023



Abstract:Personalized recommendations have become a common feature of modern online services, including most major e-commerce sites, media platforms and social networks. Today, due to their high practical relevance, research in the area of recommender systems is flourishing more than ever. However, with the new application scenarios of recommender systems that we observe today, constantly new challenges arise as well, both in terms of algorithmic requirements and with respect to the evaluation of such systems. In this paper, we first provide an overview of the traditional formulation of the recommendation problem. We then review the classical algorithmic paradigms for item retrieval and ranking and elaborate how such systems can be evaluated. Afterwards, we discuss a number of recent developments in recommender systems research, including research on session-based recommendation, biases in recommender systems, and questions regarding the impact and value of recommender systems in practice.
Human Preferences as Dueling Bandits
Apr 21, 2022
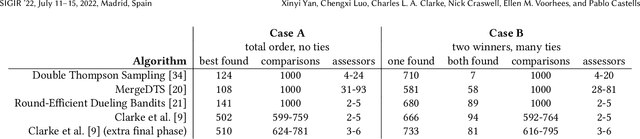
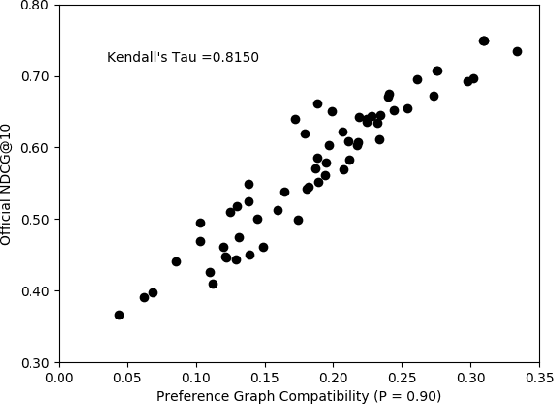
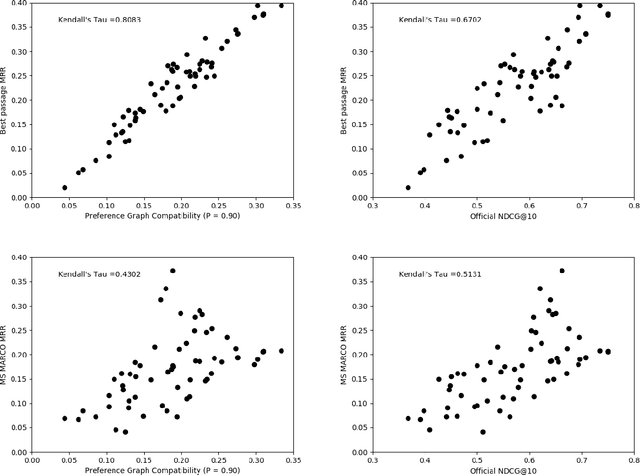
Abstract:The dramatic improvements in core information retrieval tasks engendered by neural rankers create a need for novel evaluation methods. If every ranker returns highly relevant items in the top ranks, it becomes difficult to recognize meaningful differences between them and to build reusable test collections. Several recent papers explore pairwise preference judgments as an alternative to traditional graded relevance assessments. Rather than viewing items one at a time, assessors view items side-by-side and indicate the one that provides the better response to a query, allowing fine-grained distinctions. If we employ preference judgments to identify the probably best items for each query, we can measure rankers by their ability to place these items as high as possible. We frame the problem of finding best items as a dueling bandits problem. While many papers explore dueling bandits for online ranker evaluation via interleaving, they have not been considered as a framework for offline evaluation via human preference judgments. We review the literature for possible solutions. For human preference judgments, any usable algorithm must tolerate ties, since two items may appear nearly equal to assessors, and it must minimize the number of judgments required for any specific pair, since each such comparison requires an independent assessor. Since the theoretical guarantees provided by most algorithms depend on assumptions that are not satisfied by human preference judgments, we simulate selected algorithms on representative test cases to provide insight into their practical utility. Based on these simulations, one algorithm stands out for its potential. Our simulations suggest modifications to further improve its performance. Using the modified algorithm, we collect over 10,000 preference judgments for submissions to the TREC 2021 Deep Learning Track, confirming its suitability.
Sudden Death: A New Way to Compare Recommendation Diversification
Jul 31, 2019
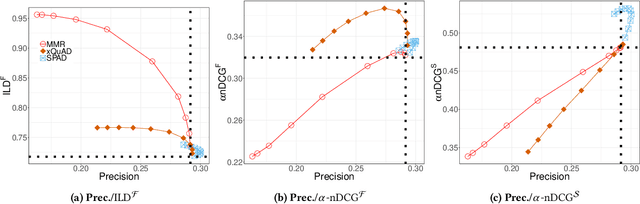

Abstract:This paper describes problems with the current way we compare the diversity of different recommendation lists in offline experiments. We illustrate the problems with a case study. We propose the Sudden Death score as a new and better way of making these comparisons.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge