Ning Huang
Pulmonary Vessel Segmentation based on Orthogonal Fused U-Net++ of Chest CT Images
Jul 03, 2021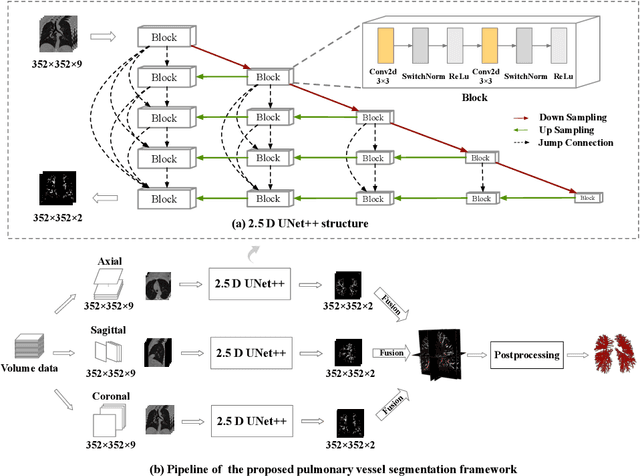
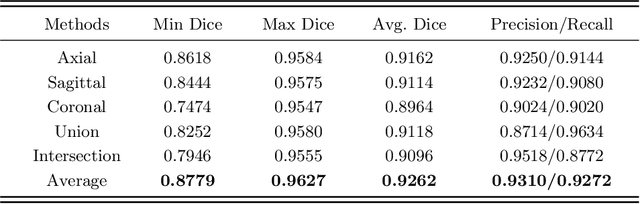
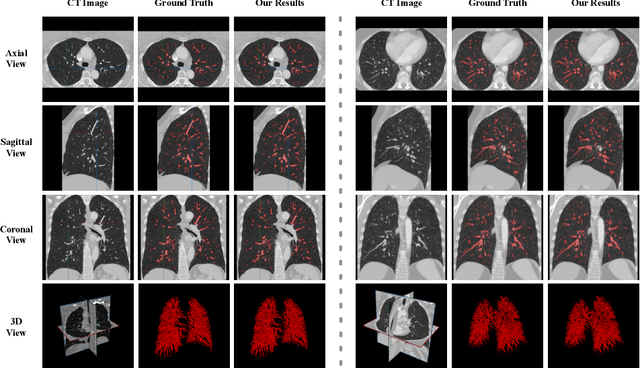
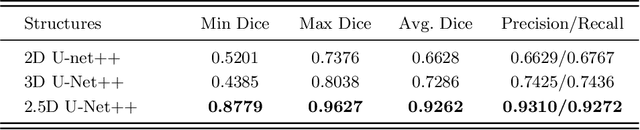
Abstract:Pulmonary vessel segmentation is important for clinical diagnosis of pulmonary diseases, while is also challenging due to the complicated structure. In this work, we present an effective framework and refinement process of pulmonary vessel segmentation from chest computed tomographic (CT) images. The key to our approach is a 2.5D segmentation network applied from three orthogonal axes, which presents a robust and fully automated pulmonary vessel segmentation result with lower network complexity and memory usage compared to 3D networks. The slice radius is introduced to convolve the adjacent information of the center slice and the multi-planar fusion optimizes the presentation of intra- and inter- slice features. Besides, the tree-like structure of the pulmonary vessel is extracted in the post-processing process, which is used for segmentation refining and pruning. In the evaluation experiments, three fusion methods are tested and the most promising one is compared with the state-of-the-art 2D and 3D structures on 300 cases of lung images randomly selected from LIDC dataset. Our method outperforms other network structures by a large margin and achieves by far the highest average DICE score of 0.9272 and precision of 0.9310, as per our knowledge from the pulmonary vessel segmentation models available in the literature.
Automatic Ischemic Stroke Lesion Segmentation from Computed Tomography Perfusion Images by Image Synthesis and Attention-Based Deep Neural Networks
Jul 07, 2020



Abstract:Ischemic stroke lesion segmentation from Computed Tomography Perfusion (CTP) images is important for accurate diagnosis of stroke in acute care units. However, it is challenged by low image contrast and resolution of the perfusion parameter maps, in addition to the complex appearance of the lesion. To deal with this problem, we propose a novel framework based on synthesized pseudo Diffusion-Weighted Imaging (DWI) from perfusion parameter maps to obtain better image quality for more accurate segmentation. Our framework consists of three components based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and is trained end-to-end. First, a feature extractor is used to obtain both a low-level and high-level compact representation of the raw spatiotemporal Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) images. Second, a pseudo DWI generator takes as input the concatenation of CTP perfusion parameter maps and our extracted features to obtain the synthesized pseudo DWI. To achieve better synthesis quality, we propose a hybrid loss function that pays more attention to lesion regions and encourages high-level contextual consistency. Finally, we segment the lesion region from the synthesized pseudo DWI, where the segmentation network is based on switchable normalization and channel calibration for better performance. Experimental results showed that our framework achieved the top performance on ISLES 2018 challenge and: 1) our method using synthesized pseudo DWI outperformed methods segmenting the lesion from perfusion parameter maps directly; 2) the feature extractor exploiting additional spatiotemporal CTA images led to better synthesized pseudo DWI quality and higher segmentation accuracy; and 3) the proposed loss functions and network structure improved the pseudo DWI synthesis and lesion segmentation performance.
Weakly Supervised Vessel Segmentation in X-ray Angiograms by Self-Paced Learning from Noisy Labels with Suggestive Annotation
May 27, 2020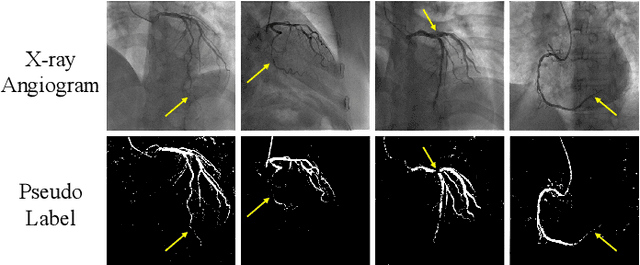
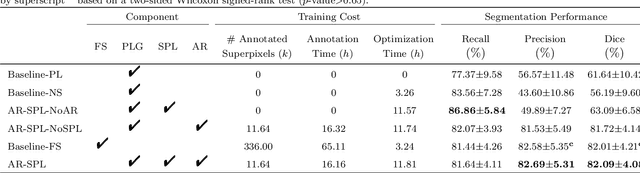
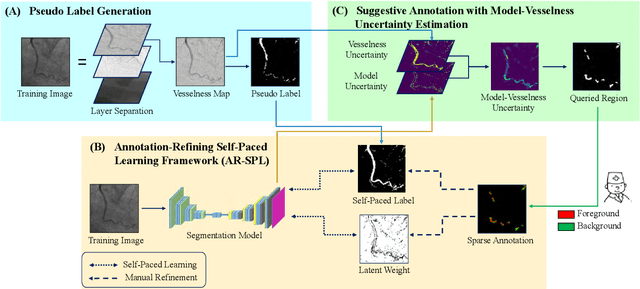
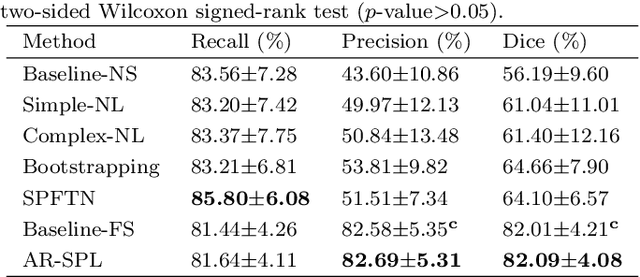
Abstract:The segmentation of coronary arteries in X-ray angiograms by convolutional neural networks (CNNs) is promising yet limited by the requirement of precisely annotating all pixels in a large number of training images, which is extremely labor-intensive especially for complex coronary trees. To alleviate the burden on the annotator, we propose a novel weakly supervised training framework that learns from noisy pseudo labels generated from automatic vessel enhancement, rather than accurate labels obtained by fully manual annotation. A typical self-paced learning scheme is used to make the training process robust against label noise while challenged by the systematic biases in pseudo labels, thus leading to the decreased performance of CNNs at test time. To solve this problem, we propose an annotation-refining self-paced learning framework (AR-SPL) to correct the potential errors using suggestive annotation. An elaborate model-vesselness uncertainty estimation is also proposed to enable the minimal annotation cost for suggestive annotation, based on not only the CNNs in training but also the geometric features of coronary arteries derived directly from raw data. Experiments show that our proposed framework achieves 1) comparable accuracy to fully supervised learning, which also significantly outperforms other weakly supervised learning frameworks; 2) largely reduced annotation cost, i.e., 75.18% of annotation time is saved, and only 3.46% of image regions are required to be annotated; and 3) an efficient intervention process, leading to superior performance with even fewer manual interactions.
A Global Benchmark of Algorithms for Segmenting Late Gadolinium-Enhanced Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
May 07, 2020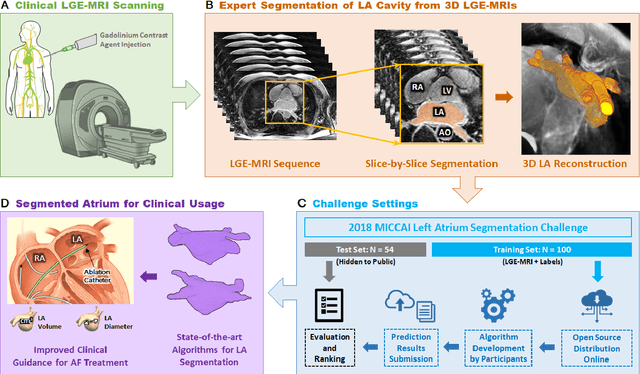
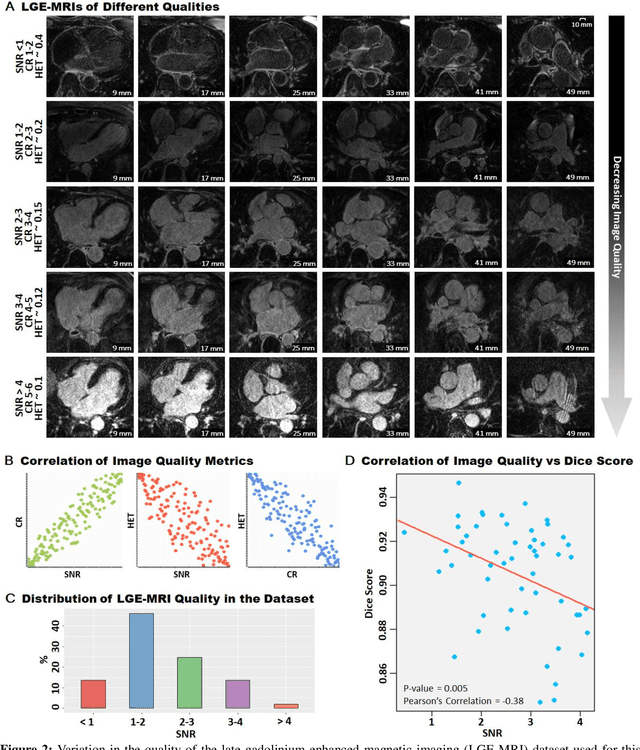
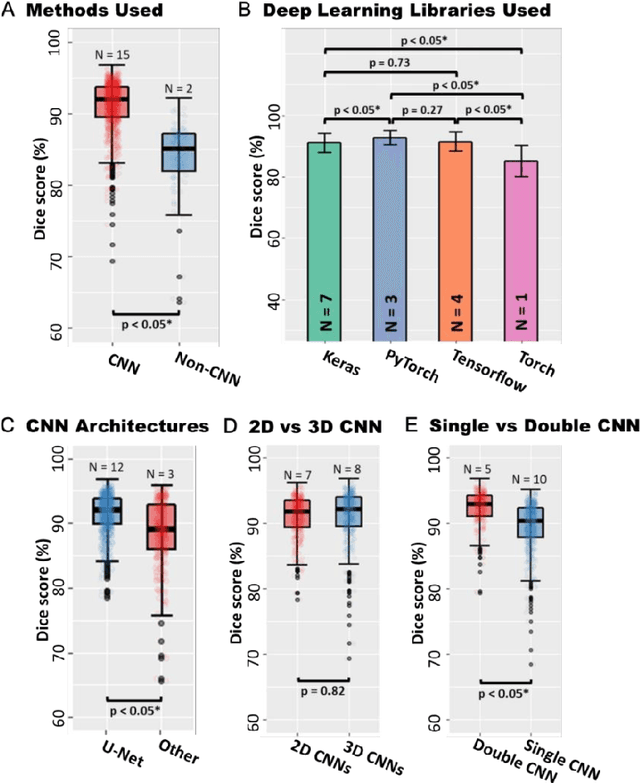
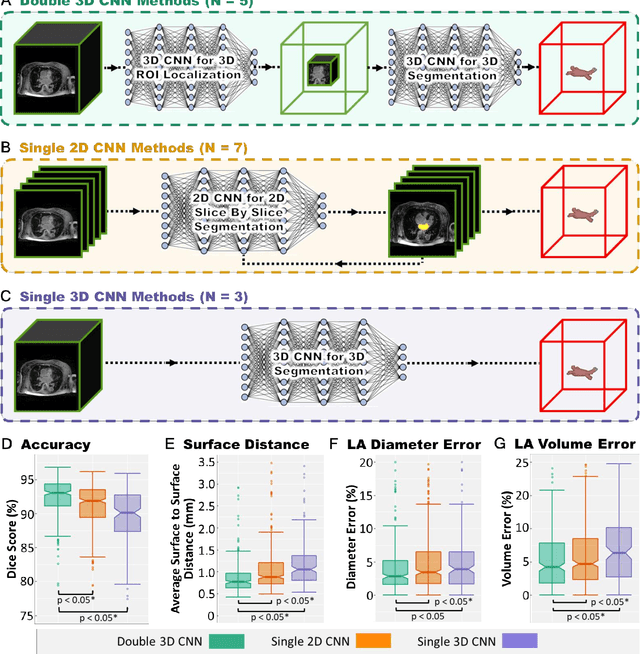
Abstract:Segmentation of cardiac images, particularly late gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (LGE-MRI) widely used for visualizing diseased cardiac structures, is a crucial first step for clinical diagnosis and treatment. However, direct segmentation of LGE-MRIs is challenging due to its attenuated contrast. Since most clinical studies have relied on manual and labor-intensive approaches, automatic methods are of high interest, particularly optimized machine learning approaches. To address this, we organized the "2018 Left Atrium Segmentation Challenge" using 154 3D LGE-MRIs, currently the world's largest cardiac LGE-MRI dataset, and associated labels of the left atrium segmented by three medical experts, ultimately attracting the participation of 27 international teams. In this paper, extensive analysis of the submitted algorithms using technical and biological metrics was performed by undergoing subgroup analysis and conducting hyper-parameter analysis, offering an overall picture of the major design choices of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and practical considerations for achieving state-of-the-art left atrium segmentation. Results show the top method achieved a dice score of 93.2% and a mean surface to a surface distance of 0.7 mm, significantly outperforming prior state-of-the-art. Particularly, our analysis demonstrated that double, sequentially used CNNs, in which a first CNN is used for automatic region-of-interest localization and a subsequent CNN is used for refined regional segmentation, achieved far superior results than traditional methods and pipelines containing single CNNs. This large-scale benchmarking study makes a significant step towards much-improved segmentation methods for cardiac LGE-MRIs, and will serve as an important benchmark for evaluating and comparing the future works in the field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge