Nayeon Kim
GraphT5: Unified Molecular Graph-Language Modeling via Multi-Modal Cross-Token Attention
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:Molecular language modeling tasks such as molecule captioning have been recognized for their potential to further understand molecular properties that can aid drug discovery or material synthesis based on chemical reactions. Unlike the common use of molecule graphs in predicting molecular properties, most methods in molecular language modeling rely heavily on SMILES sequences. This preference is because the task involves generating a sequence of multiple tokens using transformer-based models. Therefore, a main challenge is determining how to integrate graph data, which contains structural and spatial information about molecules, with text data. In addition, simply using both 1D SMILES text and 2D graph as inputs without addressing how they align and represent the molecule structure in different modalities makes it challenging to fully utilize structural knowledge about molecules. To this end, we propose GraphT5, a multi-modal framework that integrates 1D SMILES text and 2D graph representations of molecules for molecular language modeling. Specifically, we introduce a novel cross-token attention module in GraphT5 to bridge the gap arising from the fundamental differences between the two modalities of molecule representations. Cross-token attention exploits implicit information between SMILES and graphs of molecules, resulting from their interactions at a fine-grained token level that benefits molecular language modeling. Extensive experiments including molecule captioning, IUPAC name prediction tasks, and case studies show that our GraphT5 outperforms the latest baseline approaches, which validates the effectiveness of our GraphT5 in sufficiently utilizing 1D SMILES text and 2D graph representations.
Kanana: Compute-efficient Bilingual Language Models
Feb 26, 2025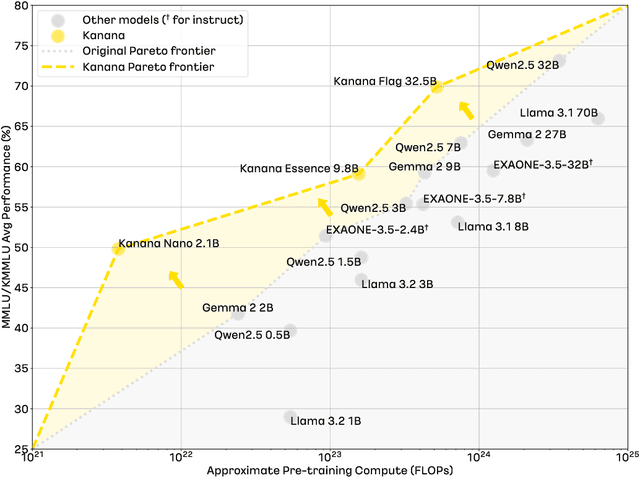



Abstract:We introduce Kanana, a series of bilingual language models that demonstrate exceeding performance in Korean and competitive performance in English. The computational cost of Kanana is significantly lower than that of state-of-the-art models of similar size. The report details the techniques employed during pre-training to achieve compute-efficient yet competitive models, including high quality data filtering, staged pre-training, depth up-scaling, and pruning and distillation. Furthermore, the report outlines the methodologies utilized during the post-training of the Kanana models, encompassing supervised fine-tuning and preference optimization, aimed at enhancing their capability for seamless interaction with users. Lastly, the report elaborates on plausible approaches used for language model adaptation to specific scenarios, such as embedding, retrieval augmented generation, and function calling. The Kanana model series spans from 2.1B to 32.5B parameters with 2.1B models (base, instruct, embedding) publicly released to promote research on Korean language models.
Unveiling the Hidden: Online Vectorized HD Map Construction with Clip-Level Token Interaction and Propagation
Nov 17, 2024Abstract:Predicting and constructing road geometric information (e.g., lane lines, road markers) is a crucial task for safe autonomous driving, while such static map elements can be repeatedly occluded by various dynamic objects on the road. Recent studies have shown significantly improved vectorized high-definition (HD) map construction performance, but there has been insufficient investigation of temporal information across adjacent input frames (i.e., clips), which may lead to inconsistent and suboptimal prediction results. To tackle this, we introduce a novel paradigm of clip-level vectorized HD map construction, MapUnveiler, which explicitly unveils the occluded map elements within a clip input by relating dense image representations with efficient clip tokens. Additionally, MapUnveiler associates inter-clip information through clip token propagation, effectively utilizing long-term temporal map information. MapUnveiler runs efficiently with the proposed clip-level pipeline by avoiding redundant computation with temporal stride while building a global map relationship. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that MapUnveiler achieves state-of-the-art performance on both the nuScenes and Argoverse2 benchmark datasets. We also showcase that MapUnveiler significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in a challenging setting, achieving +10.7% mAP improvement in heavily occluded driving road scenes. The project page can be found at https://mapunveiler.github.io.
Exploring the Impact of Corpus Diversity on Financial Pretrained Language Models
Oct 20, 2023Abstract:Over the past few years, various domain-specific pretrained language models (PLMs) have been proposed and have outperformed general-domain PLMs in specialized areas such as biomedical, scientific, and clinical domains. In addition, financial PLMs have been studied because of the high economic impact of financial data analysis. However, we found that financial PLMs were not pretrained on sufficiently diverse financial data. This lack of diverse training data leads to a subpar generalization performance, resulting in general-purpose PLMs, including BERT, often outperforming financial PLMs on many downstream tasks. To address this issue, we collected a broad range of financial corpus and trained the Financial Language Model (FiLM) on these diverse datasets. Our experimental results confirm that FiLM outperforms not only existing financial PLMs but also general domain PLMs. Furthermore, we provide empirical evidence that this improvement can be achieved even for unseen corpus groups.
Bespoke Nanoparticle Synthesis and Chemical Knowledge Discovery Via Autonomous Experimentations
Sep 01, 2023Abstract:The optimization of nanomaterial synthesis using numerous synthetic variables is considered to be extremely laborious task because the conventional combinatorial explorations are prohibitively expensive. In this work, we report an autonomous experimentation platform developed for the bespoke design of nanoparticles (NPs) with targeted optical properties. This platform operates in a closed-loop manner between a batch synthesis module of NPs and a UV- Vis spectroscopy module, based on the feedback of the AI optimization modeling. With silver (Ag) NPs as a representative example, we demonstrate that the Bayesian optimizer implemented with the early stopping criterion can efficiently produce Ag NPs precisely possessing the desired absorption spectra within only 200 iterations (when optimizing among five synthetic reagents). In addition to the outstanding material developmental efficiency, the analysis of synthetic variables further reveals a novel chemistry involving the effects of citrate in Ag NP synthesis. The amount of citrate is a key to controlling the competitions between spherical and plate-shaped NPs and, as a result, affects the shapes of the absorption spectra as well. Our study highlights both capabilities of the platform to enhance search efficiencies and to provide a novel chemical knowledge by analyzing datasets accumulated from the autonomous experimentations.
Detecting Human Rights Violations on Social Media during Russia-Ukraine War
Jun 06, 2023Abstract:The present-day Russia-Ukraine military conflict has exposed the pivotal role of social media in enabling the transparent and unbridled sharing of information directly from the frontlines. In conflict zones where freedom of expression is constrained and information warfare is pervasive, social media has emerged as an indispensable lifeline. Anonymous social media platforms, as publicly available sources for disseminating war-related information, have the potential to serve as effective instruments for monitoring and documenting Human Rights Violations (HRV). Our research focuses on the analysis of data from Telegram, the leading social media platform for reading independent news in post-Soviet regions. We gathered a dataset of posts sampled from 95 public Telegram channels that cover politics and war news, which we have utilized to identify potential occurrences of HRV. Employing a mBERT-based text classifier, we have conducted an analysis to detect any mentions of HRV in the Telegram data. Our final approach yielded an $F_2$ score of 0.71 for HRV detection, representing an improvement of 0.38 over the multilingual BERT base model. We release two datasets that contains Telegram posts: (1) large corpus with over 2.3 millions posts and (2) annotated at the sentence-level dataset to indicate HRVs. The Telegram posts are in the context of the Russia-Ukraine war. We posit that our findings hold significant implications for NGOs, governments, and researchers by providing a means to detect and document possible human rights violations.
Clinical Note Owns its Hierarchy: Multi-Level Hypergraph Neural Networks for Patient-Level Representation Learning
May 16, 2023



Abstract:Leveraging knowledge from electronic health records (EHRs) to predict a patient's condition is essential to the effective delivery of appropriate care. Clinical notes of patient EHRs contain valuable information from healthcare professionals, but have been underused due to their difficult contents and complex hierarchies. Recently, hypergraph-based methods have been proposed for document classifications. Directly adopting existing hypergraph methods on clinical notes cannot sufficiently utilize the hierarchy information of the patient, which can degrade clinical semantic information by (1) frequent neutral words and (2) hierarchies with imbalanced distribution. Thus, we propose a taxonomy-aware multi-level hypergraph neural network (TM-HGNN), where multi-level hypergraphs assemble useful neutral words with rare keywords via note and taxonomy level hyperedges to retain the clinical semantic information. The constructed patient hypergraphs are fed into hierarchical message passing layers for learning more balanced multi-level knowledge at the note and taxonomy levels. We validate the effectiveness of TM-HGNN by conducting extensive experiments with MIMIC-III dataset on benchmark in-hospital-mortality prediction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge