Doohae Jung
Kanana: Compute-efficient Bilingual Language Models
Feb 26, 2025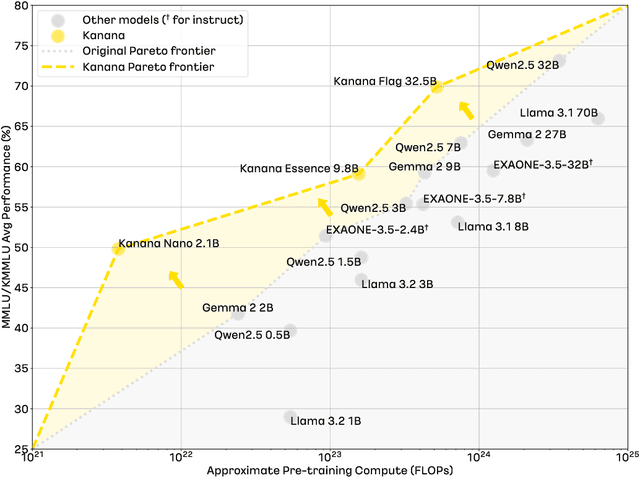



Abstract:We introduce Kanana, a series of bilingual language models that demonstrate exceeding performance in Korean and competitive performance in English. The computational cost of Kanana is significantly lower than that of state-of-the-art models of similar size. The report details the techniques employed during pre-training to achieve compute-efficient yet competitive models, including high quality data filtering, staged pre-training, depth up-scaling, and pruning and distillation. Furthermore, the report outlines the methodologies utilized during the post-training of the Kanana models, encompassing supervised fine-tuning and preference optimization, aimed at enhancing their capability for seamless interaction with users. Lastly, the report elaborates on plausible approaches used for language model adaptation to specific scenarios, such as embedding, retrieval augmented generation, and function calling. The Kanana model series spans from 2.1B to 32.5B parameters with 2.1B models (base, instruct, embedding) publicly released to promote research on Korean language models.
Exploiting the Potential of Seq2Seq Models as Robust Few-Shot Learners
Jul 27, 2023Abstract:In-context learning, which offers substantial advantages over fine-tuning, is predominantly observed in decoder-only models, while encoder-decoder (i.e., seq2seq) models excel in methods that rely on weight updates. Recently, a few studies have demonstrated the feasibility of few-shot learning with seq2seq models; however, this has been limited to tasks that align well with the seq2seq architecture, such as summarization and translation. Inspired by these initial studies, we provide a first-ever extensive experiment comparing the in-context few-shot learning capabilities of decoder-only and encoder-decoder models on a broad range of tasks. Furthermore, we propose two methods to more effectively elicit in-context learning ability in seq2seq models: objective-aligned prompting and a fusion-based approach. Remarkably, our approach outperforms a decoder-only model that is six times larger and exhibits significant performance improvements compared to conventional seq2seq models across a variety of settings. We posit that, with the right configuration and prompt design, seq2seq models can be highly effective few-shot learners for a wide spectrum of applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge