Muhammad Hassan
Computer Science and Technology, Jilin University, Changchun
Ammonia-Net: A Multi-task Joint Learning Model for Multi-class Segmentation and Classification in Tooth-marked Tongue Diagnosis
Oct 05, 2023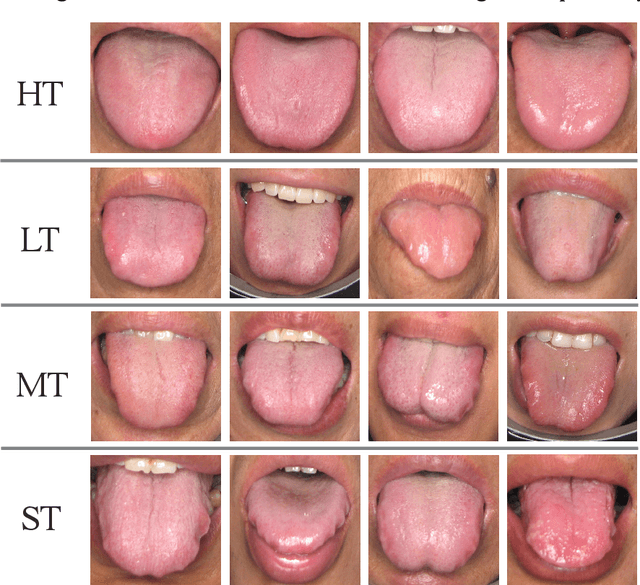
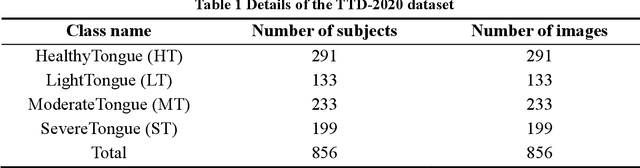
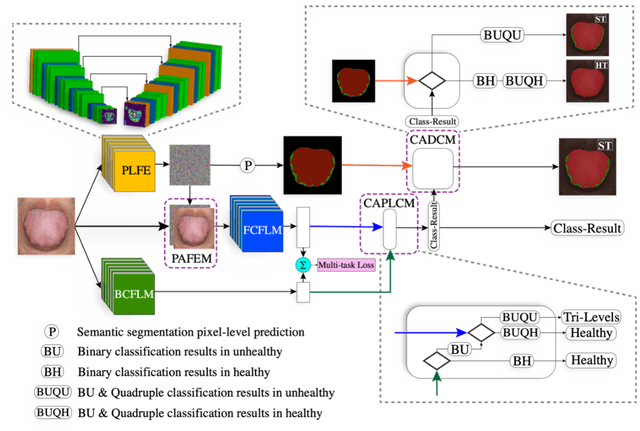
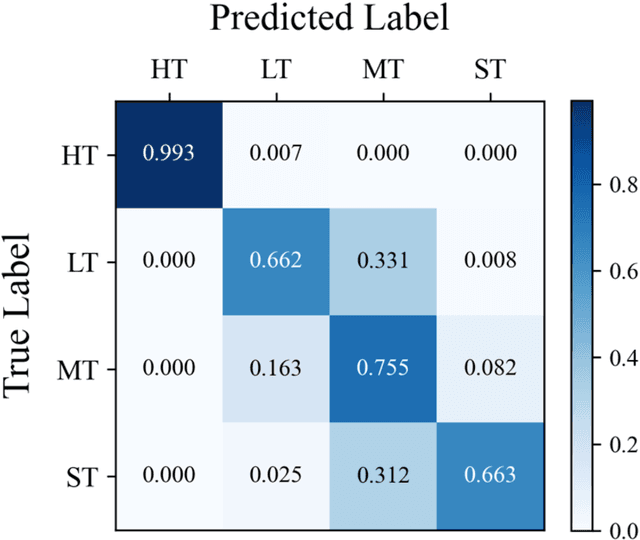
Abstract:In Traditional Chinese Medicine, the tooth marks on the tongue, stemming from prolonged dental pressure, serve as a crucial indicator for assessing qi (yang) deficiency, which is intrinsically linked to visceral health. Manual diagnosis of tooth-marked tongue solely relies on experience. Nonetheless, the diversity in shape, color, and type of tooth marks poses a challenge to diagnostic accuracy and consistency. To address these problems, herein we propose a multi-task joint learning model named Ammonia-Net. This model employs a convolutional neural network-based architecture, specifically designed for multi-class segmentation and classification of tongue images. Ammonia-Net performs semantic segmentation of tongue images to identify tongue and tooth marks. With the assistance of segmentation output, it classifies the images into the desired number of classes: healthy tongue, light tongue, moderate tongue, and severe tongue. As far as we know, this is the first attempt to apply the semantic segmentation results of tooth marks for tooth-marked tongue classification. To train Ammonia-Net, we collect 856 tongue images from 856 subjects. After a number of extensive experiments, the experimental results show that the proposed model achieves 99.06% accuracy in the two-class classification task of tooth-marked tongue identification and 80.02%. As for the segmentation task, mIoU for tongue and tooth marks amounts to 71.65%.
Futuristic Variations and Analysis in Fundus Images Corresponding to Biological Traits
Feb 08, 2023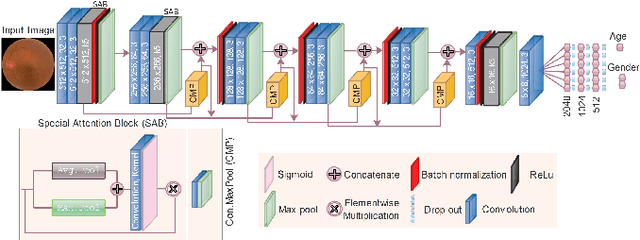
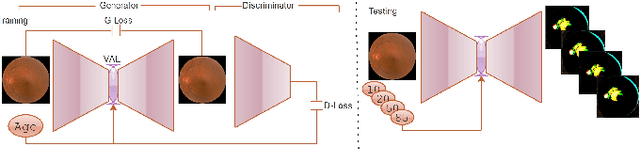
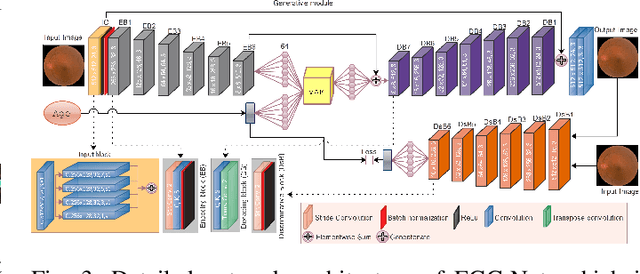
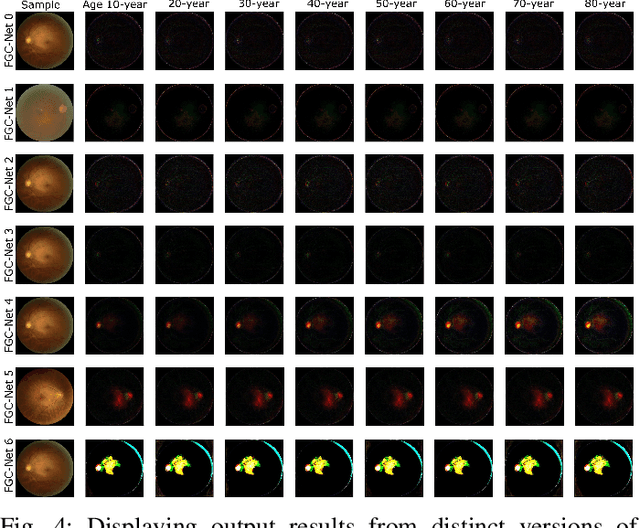
Abstract:Fundus image captures rear of an eye, and which has been studied for the diseases identification, classification, segmentation, generation, and biological traits association using handcrafted, conventional, and deep learning methods. In biological traits estimation, most of the studies have been carried out for the age prediction and gender classification with convincing results. However, the current study utilizes the cutting-edge deep learning (DL) algorithms to estimate biological traits in terms of age and gender together with associating traits to retinal visuals. For the traits association, our study embeds aging as the label information into the proposed DL model to learn knowledge about the effected regions with aging. Our proposed DL models, named FAG-Net and FGC-Net, correspondingly estimate biological traits (age and gender) and generates fundus images. FAG-Net can generate multiple variants of an input fundus image given a list of ages as conditions. Our study analyzes fundus images and their corresponding association with biological traits, and predicts of possible spreading of ocular disease on fundus images given age as condition to the generative model. Our proposed models outperform the randomly selected state of-the-art DL models.
Neuro-Symbolic Learning: Principles and Applications in Ophthalmology
Jul 31, 2022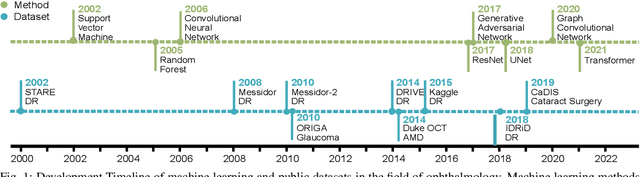
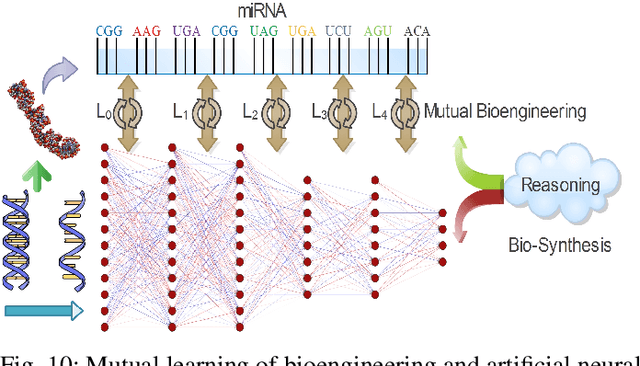
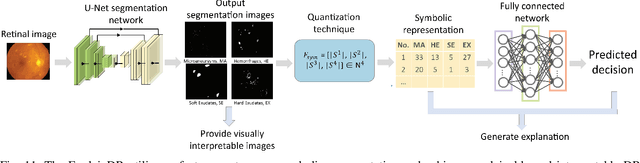
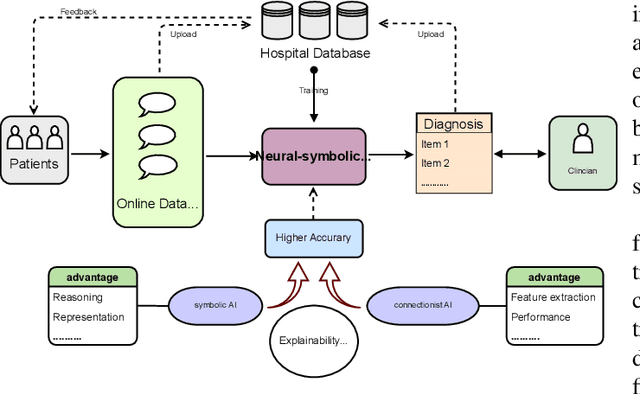
Abstract:Neural networks have been rapidly expanding in recent years, with novel strategies and applications. However, challenges such as interpretability, explainability, robustness, safety, trust, and sensibility remain unsolved in neural network technologies, despite the fact that they will unavoidably be addressed for critical applications. Attempts have been made to overcome the challenges in neural network computing by representing and embedding domain knowledge in terms of symbolic representations. Thus, the neuro-symbolic learning (NeSyL) notion emerged, which incorporates aspects of symbolic representation and bringing common sense into neural networks (NeSyL). In domains where interpretability, reasoning, and explainability are crucial, such as video and image captioning, question-answering and reasoning, health informatics, and genomics, NeSyL has shown promising outcomes. This review presents a comprehensive survey on the state-of-the-art NeSyL approaches, their principles, advances in machine and deep learning algorithms, applications such as opthalmology, and most importantly, future perspectives of this emerging field.
Deep Learning Analysis and Age Prediction from Shoeprints
Nov 07, 2020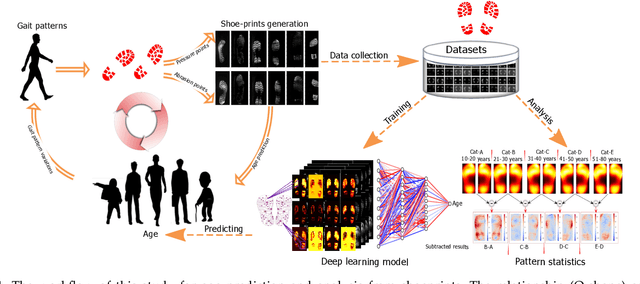
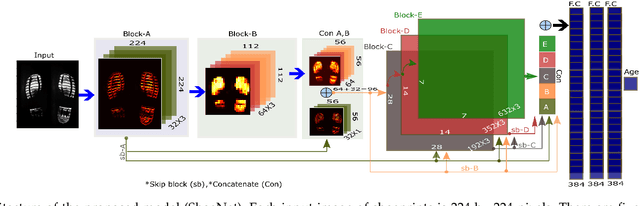
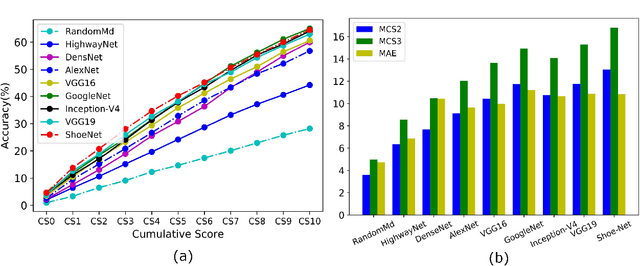
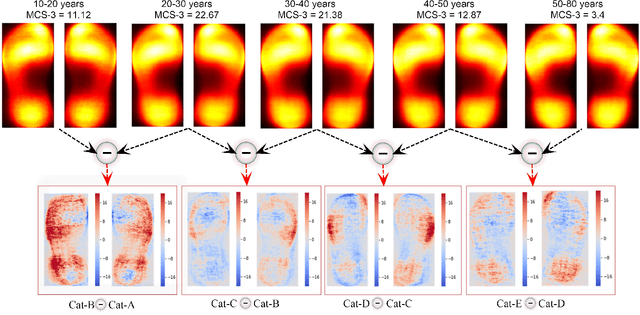
Abstract:Human walking and gaits involve several complex body parts and are influenced by personality, mood, social and cultural traits, and aging. These factors are reflected in shoeprints, which in turn can be used to predict age, a problem not systematically addressed using any computational approach. We collected 100,000 shoeprints of subjects ranging from 7 to 80 years old and used the data to develop a deep learning end-to-end model ShoeNet to analyze age-related patterns and predict age. The model integrates various convolutional neural network models together using a skip mechanism to extract age-related features, especially in pressure and abrasion regions from pair-wise shoeprints. The results show that 40.23% of the subjects had prediction errors within 5-years of age and the prediction accuracy for gender classification reached 86.07%. Interestingly, the age-related features mostly reside in the asymmetric differences between left and right shoeprints. The analysis also reveals interesting age-related and gender-related patterns in the pressure distributions on shoeprints; in particular, the pressure forces spread from the middle of the toe toward outside regions over age with gender-specific variations on heel regions. Such statistics provide insight into new methods for forensic investigations, medical studies of gait-pattern disorders, biometrics, and sport studies.
Design and Implementation of a DTMF Based Pick and Place Robotic Arm
Apr 10, 2020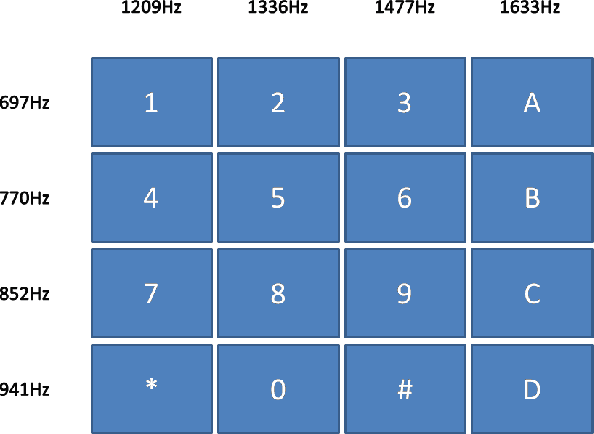
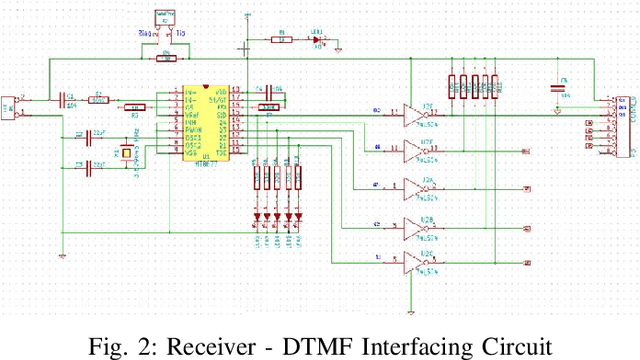
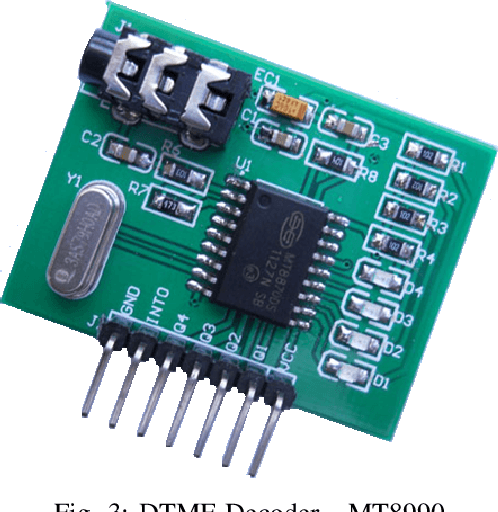
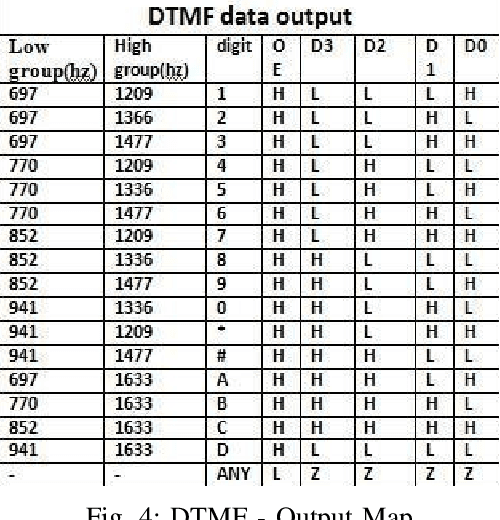
Abstract:In recent times, developments in field of communication and robotics has progressed with leaps and bounds. In addition, the blend of both disciplines has contributed heavily in making human life easier and better. So in this work while making use of both the aforementioned technologies, a procedure for design and implementation of a mobile operated mechanical arm is proposed, that is, the proposed arm will be operated via a cellular device that connects with the receiver mounted on the robotic arm. Moreover, over the duration of a call, if any key is pressed from the cellular device than an indicator indistinct to the key pressed is noticed at the receiver side. This tone represents superimposition of two distinct frequencies and referred to as DTMF (dual tone multi-frequency). Further, the mechanical arm is handled via the DTMF tone. Also, the acquired tone at the receiver is taken into a micro-controller (ATMEGA16) using the DTMF decipher module i.e. MT8870. Further, the decipher module unwinds the DTMF signal into its corresponding two bit representation and then the matched number is transmitted to the micro-controller. The micro-controller is programmed to take an action based on the decoded value. Further, the micro-controller forwards control signals to the motor driver unit to move the arm in forward/backward or multi-directional course. Lastly, the mechanical arm is capable of picking and placing objects while being controlled wirelessly over GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications).
* Journal Article
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge