Mitja Nikolaus
ILCB, LPL, LIS, TALEP
Towards Developmentally Plausible Rewards: Communicative Success as a Learning Signal for Interactive Language Models
May 09, 2025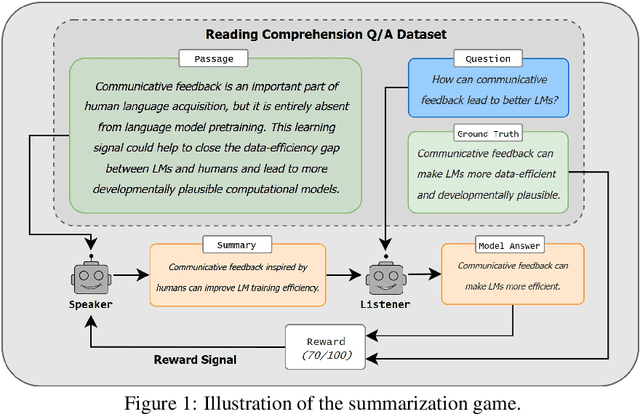
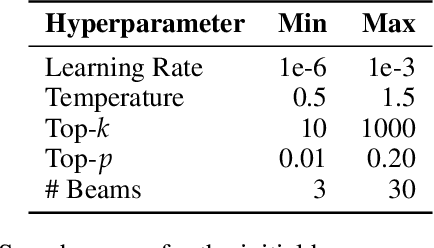
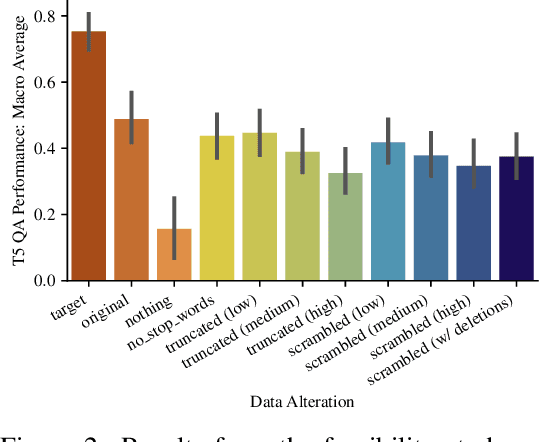
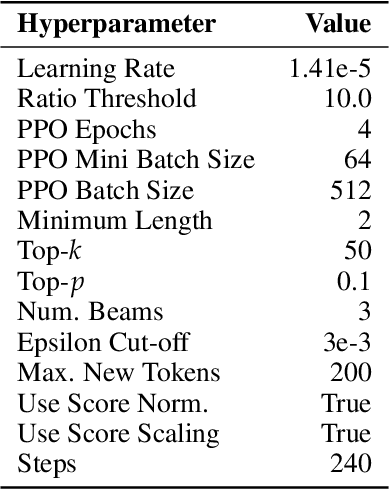
Abstract:We propose a method for training language models in an interactive setting inspired by child language acquisition. In our setting, a speaker attempts to communicate some information to a listener in a single-turn dialogue and receives a reward if communicative success is achieved. Unlike earlier related work using image--caption data for interactive reference games, we operationalize communicative success in a more abstract language-only question--answering setting. First, we present a feasibility study demonstrating that our reward provides an indirect signal about grammaticality. Second, we conduct experiments using reinforcement learning to fine-tune language models. We observe that cognitively plausible constraints on the communication channel lead to interpretable changes in speaker behavior. However, we do not yet see improvements on linguistic evaluations from our training regime. We outline potential modifications to the task design and training configuration that could better position future work to use our methodology to observe the benefits of interaction on language learning in computational cognitive models.
Automatic Annotation of Grammaticality in Child-Caregiver Conversations
Mar 21, 2024

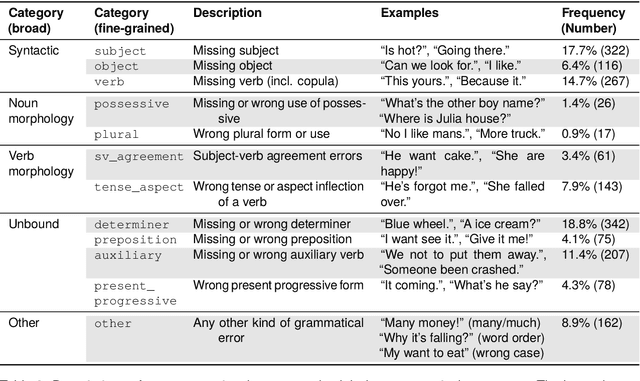

Abstract:The acquisition of grammar has been a central question to adjudicate between theories of language acquisition. In order to conduct faster, more reproducible, and larger-scale corpus studies on grammaticality in child-caregiver conversations, tools for automatic annotation can offer an effective alternative to tedious manual annotation. We propose a coding scheme for context-dependent grammaticality in child-caregiver conversations and annotate more than 4,000 utterances from a large corpus of transcribed conversations. Based on these annotations, we train and evaluate a range of NLP models. Our results show that fine-tuned Transformer-based models perform best, achieving human inter-annotation agreement levels.As a first application and sanity check of this tool, we use the trained models to annotate a corpus almost two orders of magnitude larger than the manually annotated data and verify that children's grammaticality shows a steady increase with age.This work contributes to the growing literature on applying state-of-the-art NLP methods to help study child language acquisition at scale.
Modality-Agnostic fMRI Decoding of Vision and Language
Mar 18, 2024



Abstract:Previous studies have shown that it is possible to map brain activation data of subjects viewing images onto the feature representation space of not only vision models (modality-specific decoding) but also language models (cross-modal decoding). In this work, we introduce and use a new large-scale fMRI dataset (~8,500 trials per subject) of people watching both images and text descriptions of such images. This novel dataset enables the development of modality-agnostic decoders: a single decoder that can predict which stimulus a subject is seeing, irrespective of the modality (image or text) in which the stimulus is presented. We train and evaluate such decoders to map brain signals onto stimulus representations from a large range of publicly available vision, language and multimodal (vision+language) models. Our findings reveal that (1) modality-agnostic decoders perform as well as (and sometimes even better than) modality-specific decoders (2) modality-agnostic decoders mapping brain data onto representations from unimodal models perform as well as decoders relying on multimodal representations (3) while language and low-level visual (occipital) brain regions are best at decoding text and image stimuli, respectively, high-level visual (temporal) regions perform well on both stimulus types.
Learning English with Peppa Pig
Feb 25, 2022



Abstract:Attempts to computationally simulate the acquisition of spoken language via grounding in perception have a long tradition but have gained momentum in the past few years. Current neural approaches exploit associations between the spoken and visual modality and learn to represent speech and visual data in a joint vector space. A major unresolved issue from the point of ecological validity is the training data, typically consisting of images or videos paired with spoken descriptions of what is depicted. Such a setup guarantees an unrealistically strong correlation between speech and the visual world. In the real world the coupling between the linguistic and the visual is loose, and often contains confounds in the form of correlations with non-semantic aspects of the speech signal. The current study is a first step towards simulating a naturalistic grounding scenario by using a dataset based on the children's cartoon Peppa Pig. We train a simple bi-modal architecture on the portion of the data consisting of naturalistic dialog between characters, and evaluate on segments containing descriptive narrations. Despite the weak and confounded signal in this training data our model succeeds at learning aspects of the visual semantics of spoken language.
Compositional Generalization in Image Captioning
Sep 16, 2019



Abstract:Image captioning models are usually evaluated on their ability to describe a held-out set of images, not on their ability to generalize to unseen concepts. We study the problem of compositional generalization, which measures how well a model composes unseen combinations of concepts when describing images. State-of-the-art image captioning models show poor generalization performance on this task. We propose a multi-task model to address the poor performance, that combines caption generation and image--sentence ranking, and uses a decoding mechanism that re-ranks the captions according their similarity to the image. This model is substantially better at generalizing to unseen combinations of concepts compared to state-of-the-art captioning models.
On the Realization of Compositionality in Neural Networks
Jun 06, 2019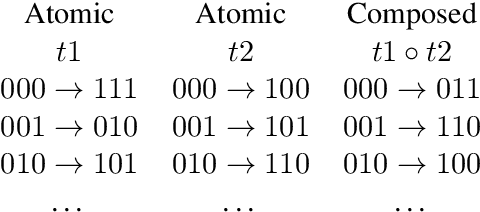
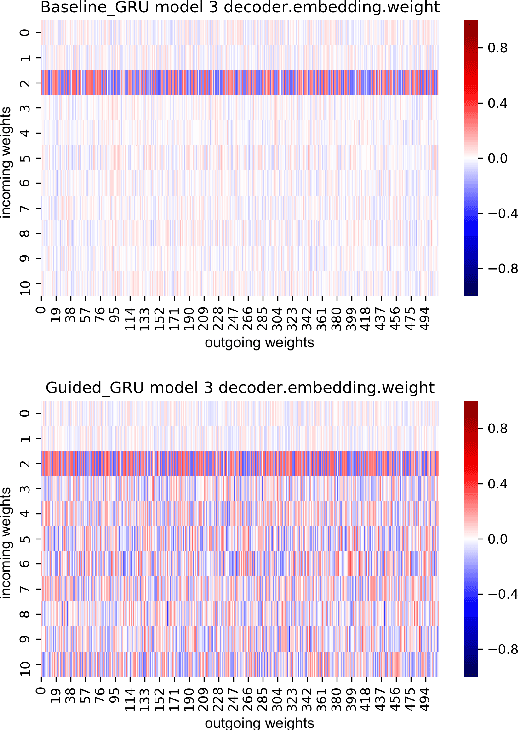
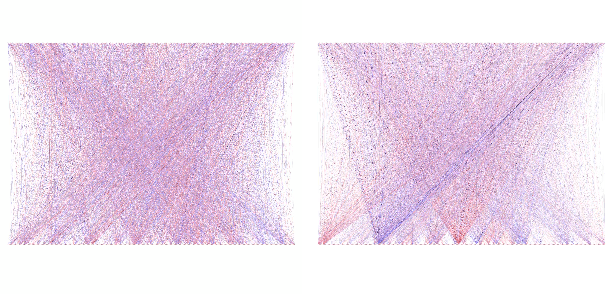
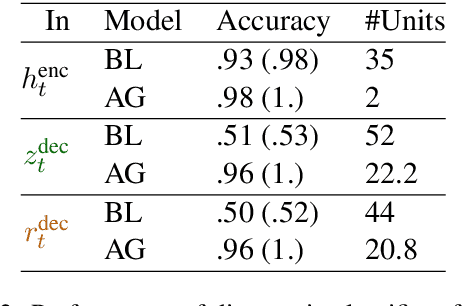
Abstract:We present a detailed comparison of two types of sequence to sequence models trained to conduct a compositional task. The models are architecturally identical at inference time, but differ in the way that they are trained: our baseline model is trained with a task-success signal only, while the other model receives additional supervision on its attention mechanism (Attentive Guidance), which has shown to be an effective method for encouraging more compositional solutions (Hupkes et al.,2019). We first confirm that the models with attentive guidance indeed infer more compositional solutions than the baseline, by training them on the lookup table task presented by Li\v{s}ka et al. (2019). We then do an in-depth analysis of the structural differences between the two model types, focusing in particular on the organisation of the parameter space and the hidden layer activations and find noticeable differences in both these aspects. Guided networks focus more on the components of the input rather than the sequence as a whole and develop small functional groups of neurons with specific purposes that use their gates more selectively. Results from parameter heat maps, component swapping and graph analysis also indicate that guided networks exhibit a more modular structure with a small number of specialized, strongly connected neurons.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge