Mingliang Wang
MorphSAM: Learning the Morphological Prompts from Atlases for Spine Image Segmentation
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Spine image segmentation is crucial for clinical diagnosis and treatment of spine diseases. The complex structure of the spine and the high morphological similarity between individual vertebrae and adjacent intervertebral discs make accurate spine segmentation a challenging task. Although the Segment Anything Model (SAM) has been developed, it still struggles to effectively capture and utilize morphological information, limiting its ability to enhance spine image segmentation performance. To address these challenges, in this paper, we propose a MorphSAM that explicitly learns morphological information from atlases, thereby strengthening the spine image segmentation performance of SAM. Specifically, the MorphSAM includes two fully automatic prompt learning networks, 1) an anatomical prompt learning network that directly learns morphological information from anatomical atlases, and 2) a semantic prompt learning network that derives morphological information from text descriptions converted from the atlases. Then, the two learned morphological prompts are fed into the SAM model to boost the segmentation performance. We validate our MorphSAM on two spine image segmentation tasks, including a spine anatomical structure segmentation task with CT images and a lumbosacral plexus segmentation task with MR images. Experimental results demonstrate that our MorphSAM achieves superior segmentation performance when compared to the state-of-the-art methods.
Dual Graph Multitask Framework for Imbalanced Delivery Time Estimation
Feb 17, 2023Abstract:Delivery Time Estimation (DTE) is a crucial component of the e-commerce supply chain that predicts delivery time based on merchant information, sending address, receiving address, and payment time. Accurate DTE can boost platform revenue and reduce customer complaints and refunds. However, the imbalanced nature of industrial data impedes previous models from reaching satisfactory prediction performance. Although imbalanced regression methods can be applied to the DTE task, we experimentally find that they improve the prediction performance of low-shot data samples at the sacrifice of overall performance. To address the issue, we propose a novel Dual Graph Multitask framework for imbalanced Delivery Time Estimation (DGM-DTE). Our framework first classifies package delivery time as head and tail data. Then, a dual graph-based model is utilized to learn representations of the two categories of data. In particular, DGM-DTE re-weights the embedding of tail data by estimating its kernel density. We fuse two graph-based representations to capture both high- and low-shot data representations. Experiments on real-world Taobao logistics datasets demonstrate the superior performance of DGM-DTE compared to baselines.
A Survey on Deep Learning for Neuroimaging-based Brain Disorder Analysis
May 10, 2020
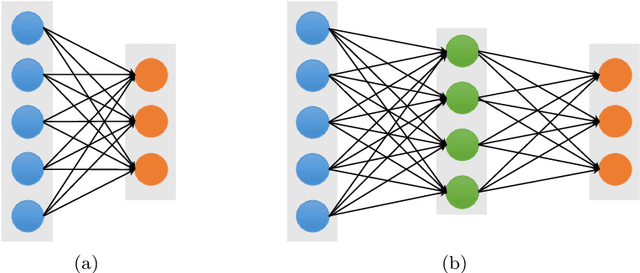
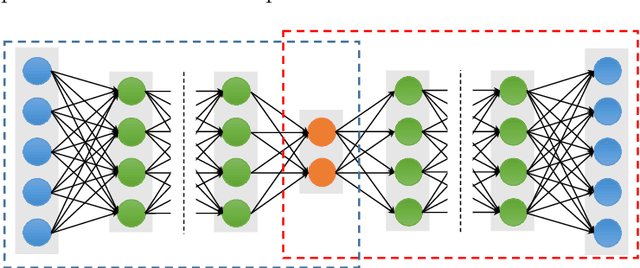
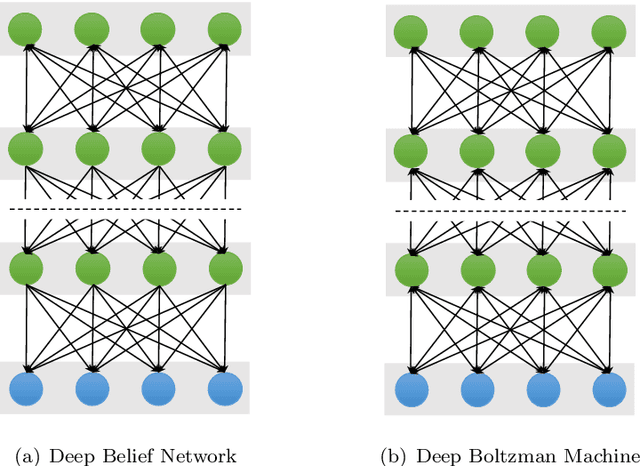
Abstract:Deep learning has been recently used for the analysis of neuroimages, such as structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), functional MRI, and positron emission tomography (PET), and has achieved significant performance improvements over traditional machine learning in computer-aided diagnosis of brain disorders. This paper reviews the applications of deep learning methods for neuroimaging-based brain disorder analysis. We first provide a comprehensive overview of deep learning techniques and popular network architectures, by introducing various types of deep neural networks and recent developments. We then review deep learning methods for computer-aided analysis of four typical brain disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Autism spectrum disorder, and Schizophrenia, where the first two diseases are neurodegenerative disorders and the last two are neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders, respectively. More importantly, we discuss the limitations of existing studies and present possible future directions.
Deep & Cross Network for Ad Click Predictions
Aug 17, 2017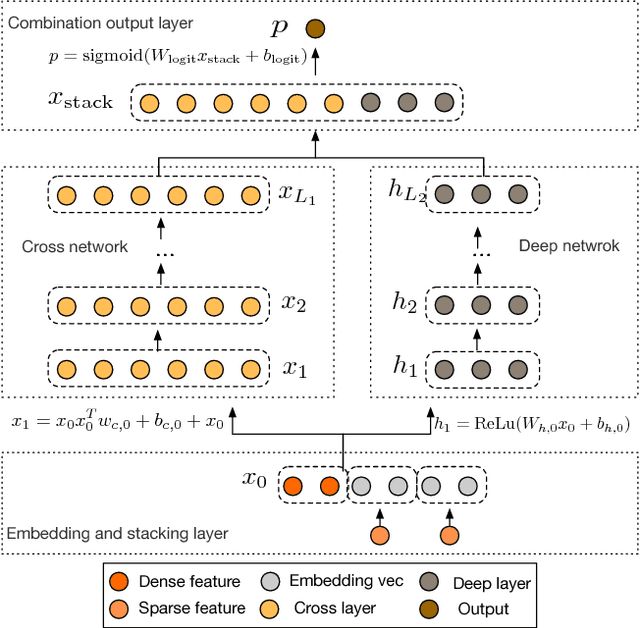
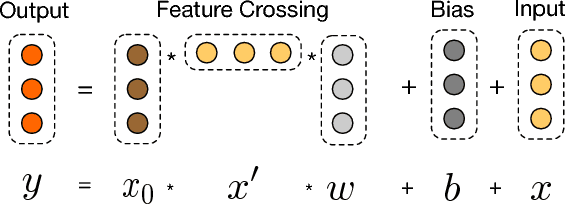
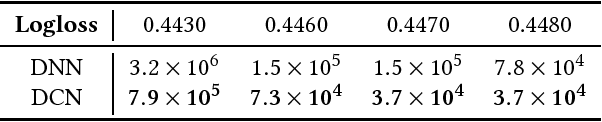

Abstract:Feature engineering has been the key to the success of many prediction models. However, the process is non-trivial and often requires manual feature engineering or exhaustive searching. DNNs are able to automatically learn feature interactions; however, they generate all the interactions implicitly, and are not necessarily efficient in learning all types of cross features. In this paper, we propose the Deep & Cross Network (DCN) which keeps the benefits of a DNN model, and beyond that, it introduces a novel cross network that is more efficient in learning certain bounded-degree feature interactions. In particular, DCN explicitly applies feature crossing at each layer, requires no manual feature engineering, and adds negligible extra complexity to the DNN model. Our experimental results have demonstrated its superiority over the state-of-art algorithms on the CTR prediction dataset and dense classification dataset, in terms of both model accuracy and memory usage.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge