Mehwish Alam
IP Paris
It's All About the Confidence: An Unsupervised Approach for Multilingual Historical Entity Linking using Large Language Models
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Despite the recent advancements in NLP with the advent of Large Language Models (LLMs), Entity Linking (EL) for historical texts remains challenging due to linguistic variation, noisy inputs, and evolving semantic conventions. Existing solutions either require substantial training data or rely on domain-specific rules that limit scalability. In this paper, we present MHEL-LLaMo (Multilingual Historical Entity Linking with Large Language MOdels), an unsupervised ensemble approach combining a Small Language Model (SLM) and an LLM. MHEL-LLaMo leverages a multilingual bi-encoder (BELA) for candidate retrieval and an instruction-tuned LLM for NIL prediction and candidate selection via prompt chaining. Our system uses SLM's confidence scores to discriminate between easy and hard samples, applying an LLM only for hard cases. This strategy reduces computational costs while preventing hallucinations on straightforward cases. We evaluate MHEL-LLaMo on four established benchmarks in six European languages (English, Finnish, French, German, Italian and Swedish) from the 19th and 20th centuries. Results demonstrate that MHEL-LLaMo outperforms state-of-the-art models without requiring fine-tuning, offering a scalable solution for low-resource historical EL. The implementation of MHEL-LLaMo is available on Github.
Thinking Before Constraining: A Unified Decoding Framework for Large Language Models
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Natural generation allows Language Models (LMs) to produce free-form responses with rich reasoning, but the lack of guaranteed structure makes outputs difficult to parse or verify. Structured generation, or constrained decoding, addresses this drawback by producing content in standardized formats such as JSON, ensuring consistency and guaranteed-parsable outputs, but it can inadvertently restrict the model's reasoning capabilities. In this work, we propose a simple approach that combines the advantages of both natural and structured generation. By allowing LLMs to reason freely until specific trigger tokens are generated, and then switching to structured generation, our method preserves the expressive power of natural language reasoning while ensuring the reliability of structured outputs. We further evaluate our approach on several datasets, covering both classification and reasoning tasks, to demonstrate its effectiveness, achieving a substantial gain of up to 27% in accuracy compared to natural generation, while requiring only a small overhead of 10-20 extra tokens.
DELICATE: Diachronic Entity LInking using Classes And Temporal Evidence
Nov 13, 2025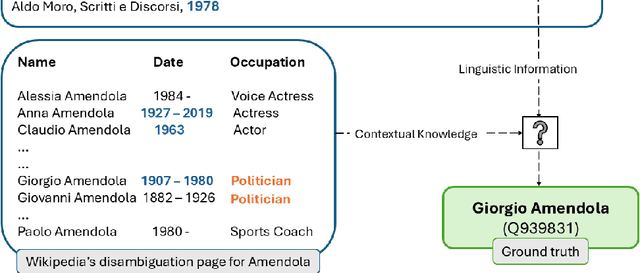
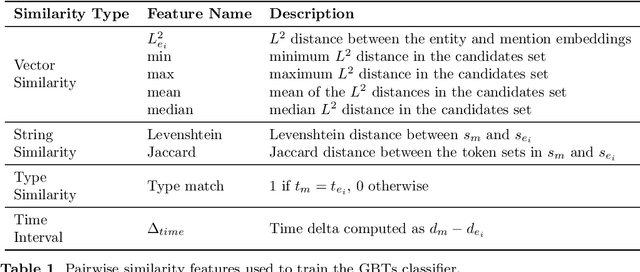
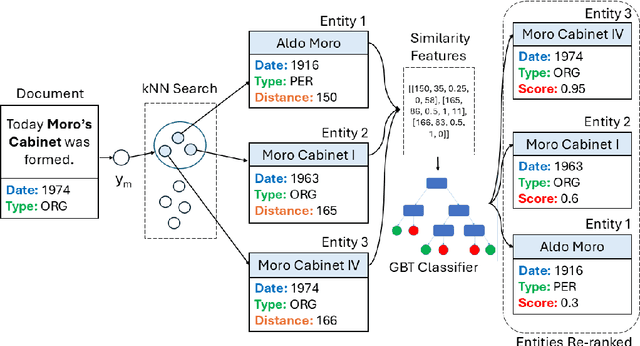
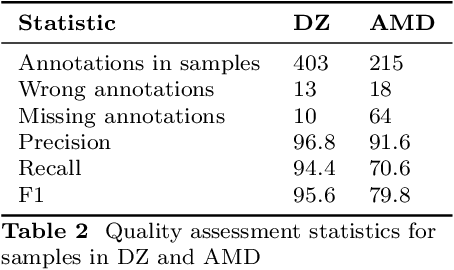
Abstract:In spite of the remarkable advancements in the field of Natural Language Processing, the task of Entity Linking (EL) remains challenging in the field of humanities due to complex document typologies, lack of domain-specific datasets and models, and long-tail entities, i.e., entities under-represented in Knowledge Bases (KBs). The goal of this paper is to address these issues with two main contributions. The first contribution is DELICATE, a novel neuro-symbolic method for EL on historical Italian which combines a BERT-based encoder with contextual information from Wikidata to select appropriate KB entities using temporal plausibility and entity type consistency. The second contribution is ENEIDE, a multi-domain EL corpus in historical Italian semi-automatically extracted from two annotated editions spanning from the 19th to the 20th century and including literary and political texts. Results show how DELICATE outperforms other EL models in historical Italian even if compared with larger architectures with billions of parameters. Moreover, further analyses reveal how DELICATE confidence scores and features sensitivity provide results which are more explainable and interpretable than purely neural methods.
Two-dimensional Taxonomy for N-ary Knowledge Representation Learning Methods
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Real-world knowledge can take various forms, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Among these, knowledge graphs are a form of structured human knowledge that integrate heterogeneous data sources into structured representations but typically reduce complex n-ary relations to simple triples, thereby losing higher-order relational details. In contrast, hypergraphs naturally represent n-ary relations with hyperedges, which directly connect multiple entities together. Yet hypergraph representation learning often overlooks entity roles in hyperedges, limiting the fine-grained semantic modelling. To address these issues, knowledge hypergraphs and hyper-relational knowledge graphs combine the advantages of knowledge graphs and hypergraphs to better capture the complex structures and role-specific semantics of real-world knowledge. This survey provides a comprehensive review of methods handling n-ary relational data, covering both knowledge hypergraphs and hyper-relational knowledge graphs literatures. We propose a two-dimensional taxonomy: the first dimension categorises models based on their methodology, i.e., translation-based models, tensor factorisation-based models, deep neural network-based models, logic rules-based models, and hyperedge expansion-based models. The second dimension classifies models according to their awareness of entity roles and positions in n-ary relations, dividing them into aware-less, position-aware, and role-aware approaches. Finally, we discuss existing datasets, negative sampling strategies, and outline open challenges to inspire future research.
Markov Process-Based Graph Convolutional Networks for Entity Classification in Knowledge Graphs
Dec 23, 2024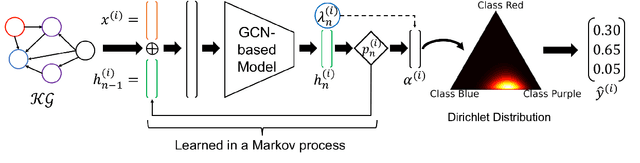


Abstract:Despite the vast amount of information encoded in Knowledge Graphs (KGs), information about the class affiliation of entities remains often incomplete. Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) have been shown to be effective predictors of complete information about the class affiliation of entities in KGs. However, these models do not learn the class affiliation of entities in KGs incorporating the complexity of the task, which negatively affects the models prediction capabilities. To address this problem, we introduce a Markov process-based architecture into well-known GCN architectures. This end-to-end network learns the prediction of class affiliation of entities in KGs within a Markov process. The number of computational steps is learned during training using a geometric distribution. At the same time, the loss function combines insights from the field of evidential learning. The experiments show a performance improvement over existing models in several studied architectures and datasets. Based on the chosen hyperparameters for the geometric distribution, the expected number of computation steps can be adjusted to improve efficiency and accuracy during training.
Neurosymbolic Methods for Dynamic Knowledge Graphs
Sep 06, 2024Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KGs) have recently been used for many tools and applications, making them rich resources in structured format. However, in the real world, KGs grow due to the additions of new knowledge in the form of entities and relations, making these KGs dynamic. This chapter formally defines several types of dynamic KGs and summarizes how these KGs can be represented. Additionally, many neurosymbolic methods have been proposed for learning representations over static KGs for several tasks such as KG completion and entity alignment. This chapter further focuses on neurosymbolic methods for dynamic KGs with or without temporal information. More specifically, it provides an insight into neurosymbolic methods for dynamic (temporal or non-temporal) KG completion and entity alignment tasks. It further discusses the challenges of current approaches and provides some future directions.
Refining Wikidata Taxonomy using Large Language Models
Sep 06, 2024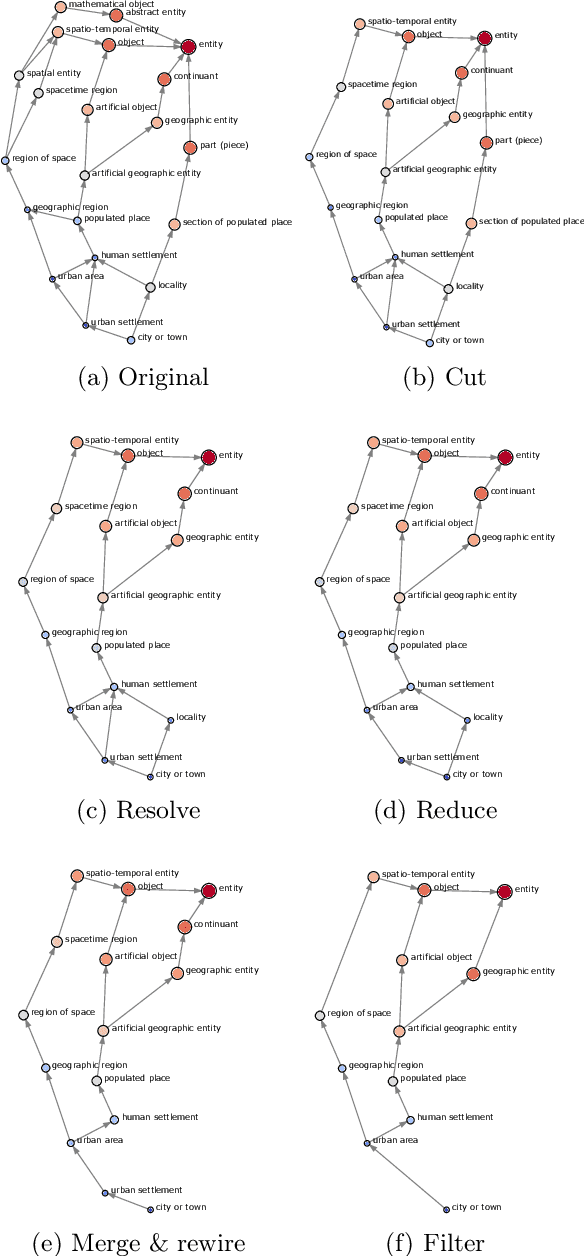
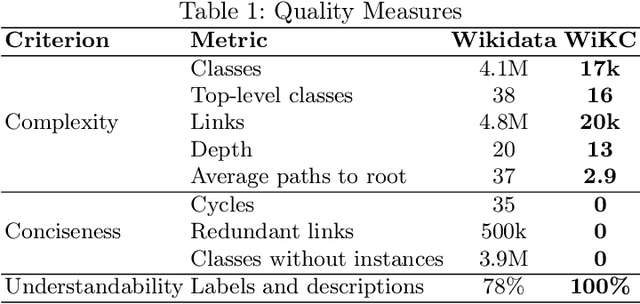

Abstract:Due to its collaborative nature, Wikidata is known to have a complex taxonomy, with recurrent issues like the ambiguity between instances and classes, the inaccuracy of some taxonomic paths, the presence of cycles, and the high level of redundancy across classes. Manual efforts to clean up this taxonomy are time-consuming and prone to errors or subjective decisions. We present WiKC, a new version of Wikidata taxonomy cleaned automatically using a combination of Large Language Models (LLMs) and graph mining techniques. Operations on the taxonomy, such as cutting links or merging classes, are performed with the help of zero-shot prompting on an open-source LLM. The quality of the refined taxonomy is evaluated from both intrinsic and extrinsic perspectives, on a task of entity typing for the latter, showing the practical interest of WiKC.
Neurosymbolic Methods for Rule Mining
Aug 11, 2024

Abstract:In this chapter, we address the problem of rule mining, beginning with essential background information, including measures of rule quality. We then explore various rule mining methodologies, categorized into three groups: inductive logic programming, path sampling and generalization, and linear programming. Following this, we delve into neurosymbolic methods, covering topics such as the integration of deep learning with rules, the use of embeddings for rule learning, and the application of large language models in rule learning.
NeMig -- A Bilingual News Collection and Knowledge Graph about Migration
Sep 01, 2023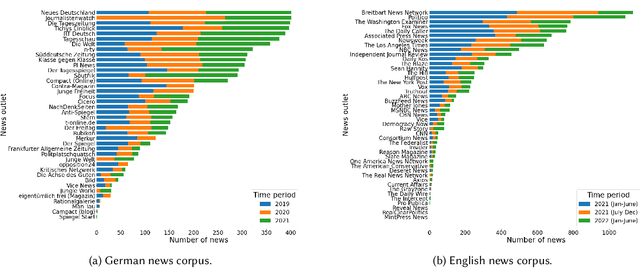
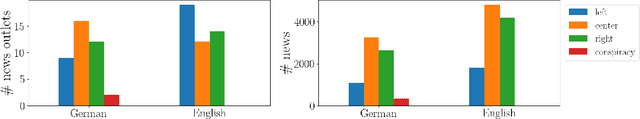
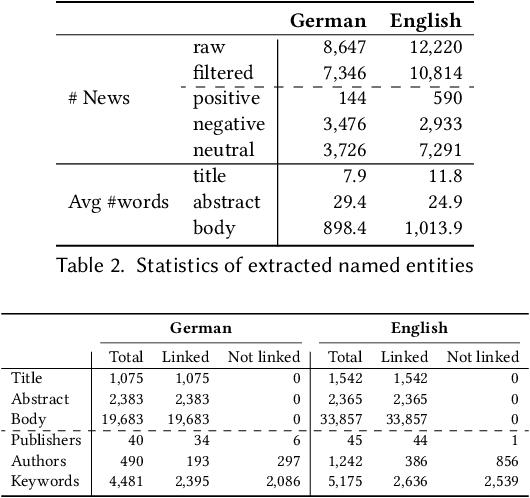
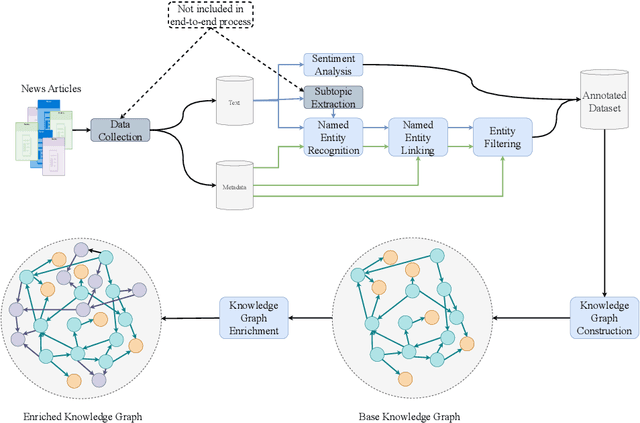
Abstract:News recommendation plays a critical role in shaping the public's worldviews through the way in which it filters and disseminates information about different topics. Given the crucial impact that media plays in opinion formation, especially for sensitive topics, understanding the effects of personalized recommendation beyond accuracy has become essential in today's digital society. In this work, we present NeMig, a bilingual news collection on the topic of migration, and corresponding rich user data. In comparison to existing news recommendation datasets, which comprise a large variety of monolingual news, NeMig covers articles on a single controversial topic, published in both Germany and the US. We annotate the sentiment polarization of the articles and the political leanings of the media outlets, in addition to extracting subtopics and named entities disambiguated through Wikidata. These features can be used to analyze the effects of algorithmic news curation beyond accuracy-based performance, such as recommender biases and the creation of filter bubbles. We construct domain-specific knowledge graphs from the news text and metadata, thus encoding knowledge-level connections between articles. Importantly, while existing datasets include only click behavior, we collect user socio-demographic and political information in addition to explicit click feedback. We demonstrate the utility of NeMig through experiments on the tasks of news recommenders benchmarking, analysis of biases in recommenders, and news trends analysis. NeMig aims to provide a useful resource for the news recommendation community and to foster interdisciplinary research into the multidimensional effects of algorithmic news curation.
Integrating the Wikidata Taxonomy into YAGO
Aug 23, 2023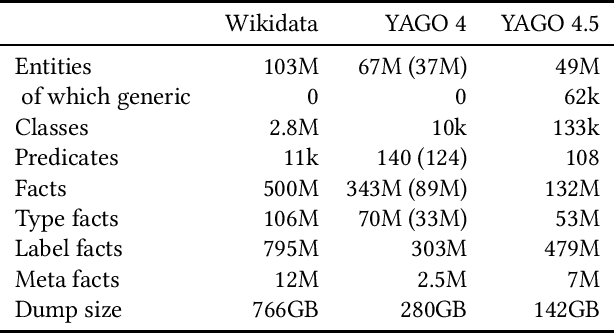
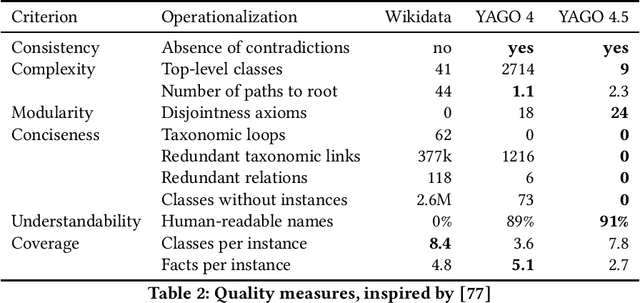
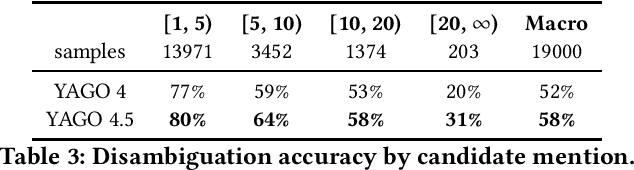
Abstract:Wikidata is one of the largest public general-purpose Knowledge Bases (KBs). Yet, due to its collaborative nature, its schema and taxonomy have become convoluted. For the YAGO 4 KB, we combined Wikidata with the ontology from Schema.org, which reduced and cleaned up the taxonomy and constraints and made it possible to run automated reasoners on the data. However, it also cut away large parts of the Wikidata taxonomy. In this paper, we present our effort to merge the entire Wikidata taxonomy into the YAGO KB as much as possible. We pay particular attention to logical constraints and a careful distinction of classes and instances. Our work creates YAGO 4.5, which adds a rich layer of informative classes to YAGO, while at the same time keeping the KB logically consistent.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge