Maxime Descoteaux
SCIL
Clinical-ComBAT: a diffusion-weighted MRI harmonization method for clinical applications
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) derived scalar maps are effective for assessing neurodegenerative diseases and microstructural properties of white matter in large number of brain conditions. However, DW-MRI inherently limits the combination of data from multiple acquisition sites without harmonization to mitigate scanner-specific biases. While the widely used ComBAT method reduces site effects in research, its reliance on linear covariate relationships, homogeneous populations, fixed site numbers, and well populated sites constrains its clinical use. To overcome these limitations, we propose Clinical-ComBAT, a method designed for real-world clinical scenarios. Clinical-ComBAT harmonizes each site independently, enabling flexibility as new data and clinics are introduced. It incorporates a non-linear polynomial data model, site-specific harmonization referenced to a normative site, and variance priors adaptable to small cohorts. It further includes hyperparameter tuning and a goodness-of-fit metric for harmonization assessment. We demonstrate its effectiveness on simulated and real data, showing improved alignment of diffusion metrics and enhanced applicability for normative modeling.
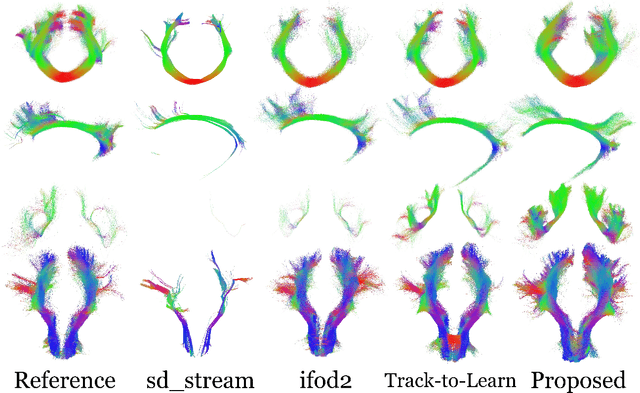
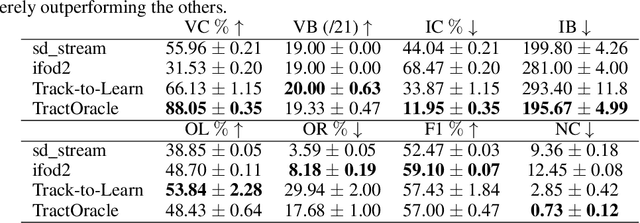
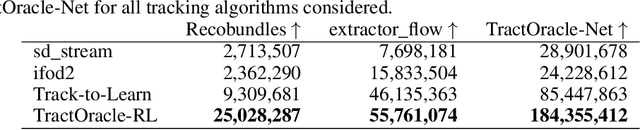
Exploring the robustness of TractOracle methods in RL-based tractography
Jul 15, 2025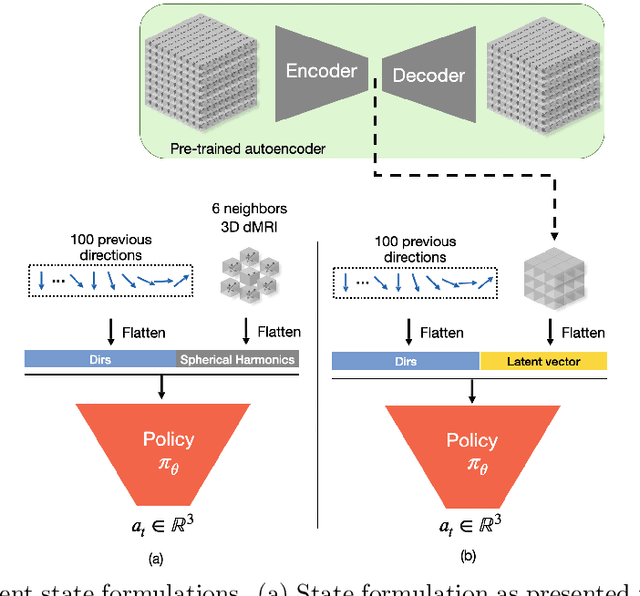
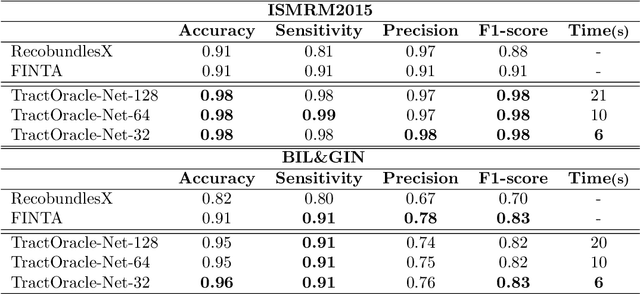
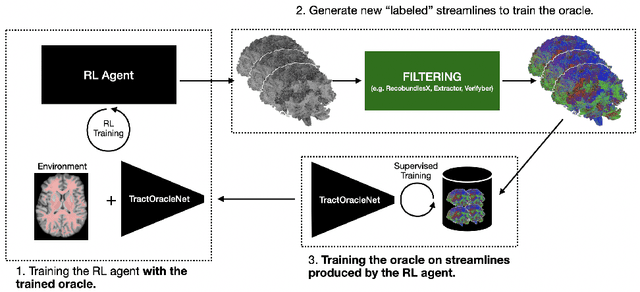
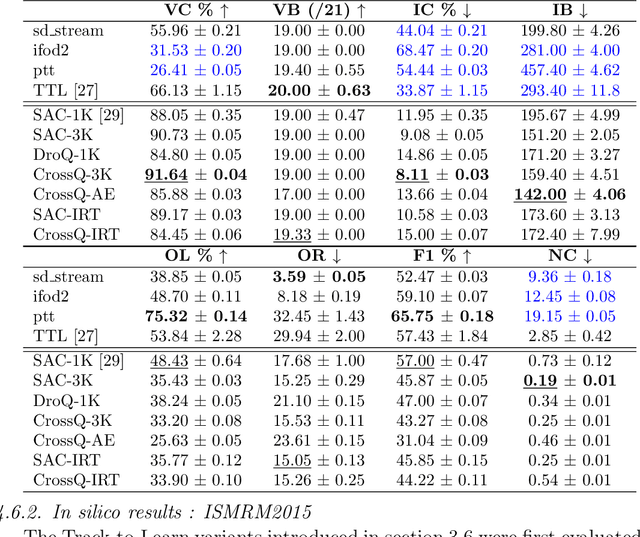
Abstract:Tractography algorithms leverage diffusion MRI to reconstruct the fibrous architecture of the brain's white matter. Among machine learning approaches, reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as a promising framework for tractography, outperforming traditional methods in several key aspects. TractOracle-RL, a recent RL-based approach, reduces false positives by incorporating anatomical priors into the training process via a reward-based mechanism. In this paper, we investigate four extensions of the original TractOracle-RL framework by integrating recent advances in RL, and we evaluate their performance across five diverse diffusion MRI datasets. Results demonstrate that combining an oracle with the RL framework consistently leads to robust and reliable tractography, regardless of the specific method or dataset used. We also introduce a novel RL training scheme called Iterative Reward Training (IRT), inspired by the Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) paradigm. Instead of relying on human input, IRT leverages bundle filtering methods to iteratively refine the oracle's guidance throughout training. Experimental results show that RL methods trained with oracle feedback significantly outperform widely used tractography techniques in terms of accuracy and anatomical validity.
ComBAT Harmonization for diffusion MRI: Challenges and Best Practices
May 19, 2025Abstract:Over the years, ComBAT has become the standard method for harmonizing MRI-derived measurements, with its ability to compensate for site-related additive and multiplicative biases while preserving biological variability. However, ComBAT relies on a set of assumptions that, when violated, can result in flawed harmonization. In this paper, we thoroughly review ComBAT's mathematical foundation, outlining these assumptions, and exploring their implications for the demographic composition necessary for optimal results. Through a series of experiments involving a slightly modified version of ComBAT called Pairwise-ComBAT tailored for normative modeling applications, we assess the impact of various population characteristics, including population size, age distribution, the absence of certain covariates, and the magnitude of additive and multiplicative factors. Based on these experiments, we present five essential recommendations that should be carefully considered to enhance consistency and supporting reproducibility, two essential factors for open science, collaborative research, and real-life clinical deployment.
TractOracle: towards an anatomically-informed reward function for RL-based tractography
Mar 26, 2024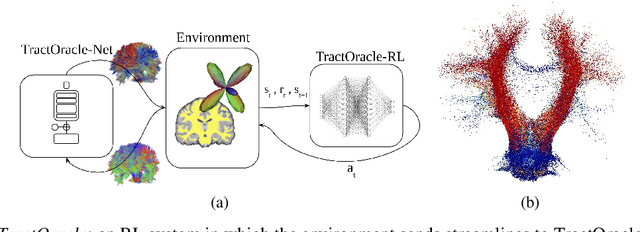
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL)-based tractography is a competitive alternative to machine learning and classical tractography algorithms due to its high anatomical accuracy obtained without the need for any annotated data. However, the reward functions so far used to train RL agents do not encapsulate anatomical knowledge which causes agents to generate spurious false positives tracts. In this paper, we propose a new RL tractography system, TractOracle, which relies on a reward network trained for streamline classification. This network is used both as a reward function during training as well as a mean for stopping the tracking process early and thus reduce the number of false positive streamlines. This makes our system a unique method that evaluates and reconstructs WM streamlines at the same time. We report an improvement of true positive ratios by almost 20\% and a reduction of 3x of false positive ratios on one dataset and an increase between 2x and 7x in the number true positive streamlines on another dataset.
Merging multiple input descriptors and supervisors in a deep neural network for tractogram filtering
Jul 11, 2023Abstract:One of the main issues of the current tractography methods is their high false-positive rate. Tractogram filtering is an option to remove false-positive streamlines from tractography data in a post-processing step. In this paper, we train a deep neural network for filtering tractography data in which every streamline of a tractogram is classified as {\em plausible, implausible}, or {\em inconclusive}. For this, we use four different tractogram filtering strategies as supervisors: TractQuerier, RecobundlesX, TractSeg, and an anatomy-inspired filter. Their outputs are combined to obtain the classification labels for the streamlines. We assessed the importance of different types of information along the streamlines for performing this classification task, including the coordinates of the streamlines, diffusion data, landmarks, T1-weighted information, and a brain parcellation. We found that the streamline coordinates are the most relevant followed by the diffusion data in this particular classification task.
What Matters in Reinforcement Learning for Tractography
May 17, 2023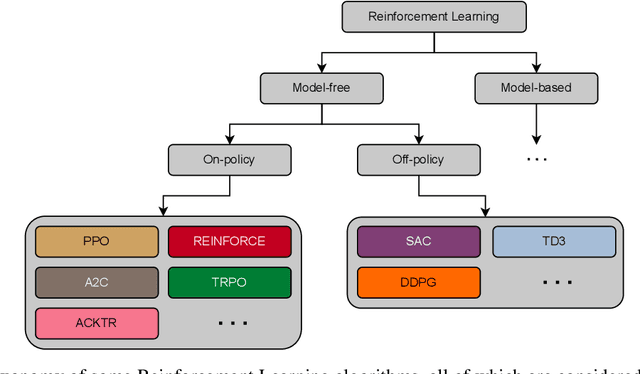
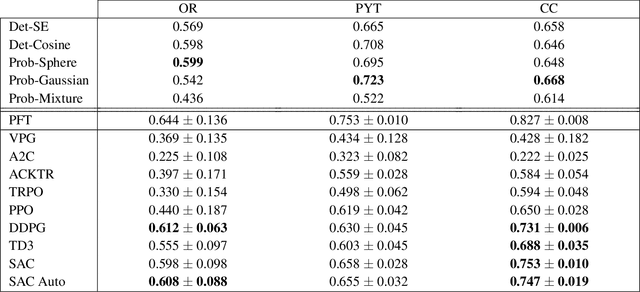
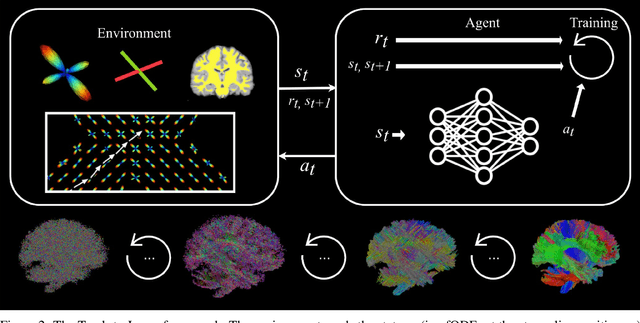
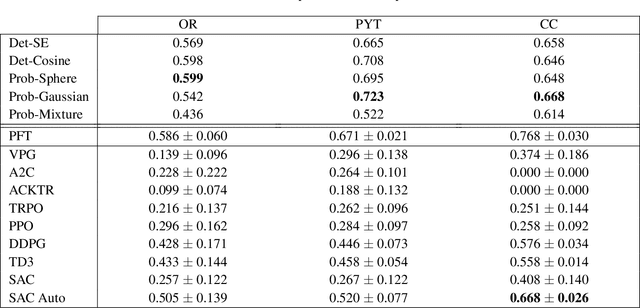
Abstract:Recently, deep reinforcement learning (RL) has been proposed to learn the tractography procedure and train agents to reconstruct the structure of the white matter without manually curated reference streamlines. While the performances reported were competitive, the proposed framework is complex, and little is still known about the role and impact of its multiple parts. In this work, we thoroughly explore the different components of the proposed framework, such as the choice of the RL algorithm, seeding strategy, the input signal and reward function, and shed light on their impact. Approximately 7,400 models were trained for this work, totalling nearly 41,000 hours of GPU time. Our goal is to guide researchers eager to explore the possibilities of deep RL for tractography by exposing what works and what does not work with the category of approach. As such, we ultimately propose a series of recommendations concerning the choice of RL algorithm, the input to the agents, the reward function and more to help future work using reinforcement learning for tractography. We also release the open source codebase, trained models, and datasets for users and researchers wanting to explore reinforcement learning for tractography.
FIESTA: Autoencoders for accurate fiber segmentation in tractography
Dec 12, 2022Abstract:White matter bundle segmentation is a cornerstone of modern tractography to study the brain's structural connectivity in domains such as neurological disorders, neurosurgery, and aging. In this study, we present FIESTA (FIbEr Segmentation in Tractography using Autoencoders), a reliable and robust, fully automated, and easily semi-automatically calibrated pipeline based on deep autoencoders that can dissect and fully populate WM bundles. Our framework allows the transition from one anatomical bundle definition to another with marginal calibrating time. This pipeline is built upon FINTA, CINTA, and GESTA methods that demonstrated how autoencoders can be used successfully for streamline filtering, bundling, and streamline generation in tractography. Our proposed method improves bundling coverage by recovering hard-to-track bundles with generative sampling through the latent space seeding of the subject bundle and the atlas bundle. A latent space of streamlines is learned using autoencoder-based modeling combined with contrastive learning. Using an atlas of bundles in standard space (MNI), our proposed method segments new tractograms using the autoencoder latent distance between each tractogram streamline and its closest neighbor bundle in the atlas of bundles. Intra-subject bundle reliability is improved by recovering hard-to-track streamlines, using the autoencoder to generate new streamlines that increase each bundle's spatial coverage while remaining anatomically meaningful. Results show that our method is more reliable than state-of-the-art automated virtual dissection methods such as RecoBundles, RecoBundlesX, TractSeg, White Matter Analysis and XTRACT. Overall, these results show that our framework improves the practicality and usability of current state-of-the-art bundling framework
Generative sampling in tractography using autoencoders (GESTA)
Apr 22, 2022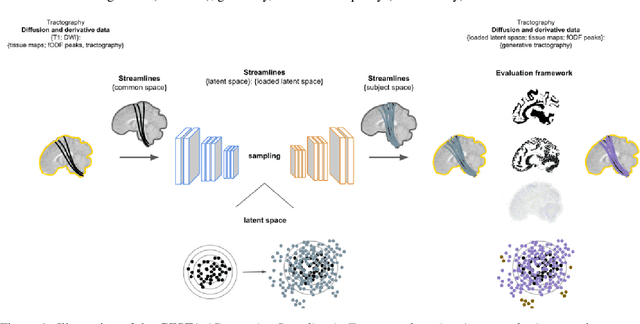

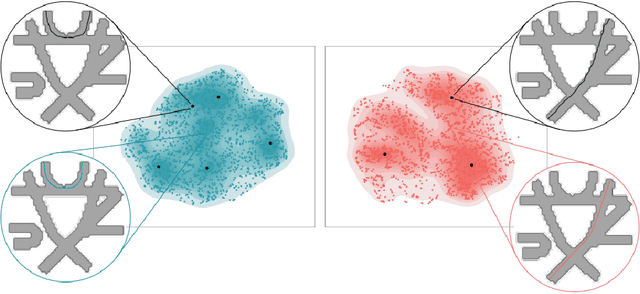
Abstract:Current tractography methods use the local orientation information to propagate streamlines from seed locations. Many such seeds provide streamlines that stop prematurely or fail to map the true pathways because some white matter bundles are "harder-to-track" than others. This results in tractography reconstructions with poor white and gray matter spatial coverage. In this work, we propose a generative, autoencoder-based method, named GESTA (Generative Sampling in Tractography using Autoencoders), that produces streamlines with better spatial coverage. Compared to other deep learning methods, our autoencoder-based framework is not constrained by any prior or a fixed set of bundles. GESTA produces new and complete streamlines for any white matter bundle. GESTA is shown to be effective on both synthetic and human brain in vivo data. Our streamline evaluation framework ensures that the streamlines produced by GESTA are anatomically plausible and fit well to the local diffusion signal. The streamline evaluation criteria assess anatomy (white matter coverage), local orientation alignment (direction), geometry features of streamlines, and optionally, gray matter connectivity. The GESTA framework offers considerable gains in bundle coverage using a reduced set of seeding streamlines with a 1.5x improvement for the "Fiber Cup", and 6x for the ISMRM 2015 Tractography Challenge datasets. Similarly, it provides a 4x white matter volume increase on the BIL&GIN callosal homotopic dataset. It also successfully generates new streamlines in poorly populated bundles, such as the fornix and other hard-to-track bundles, on in vivo data. GESTA is thus the first deep tractography generative method that can improve white matter reconstruction of hard-to-track bundles.
Manifold-aware Synthesis of High-resolution Diffusion from Structural Imaging
Aug 11, 2021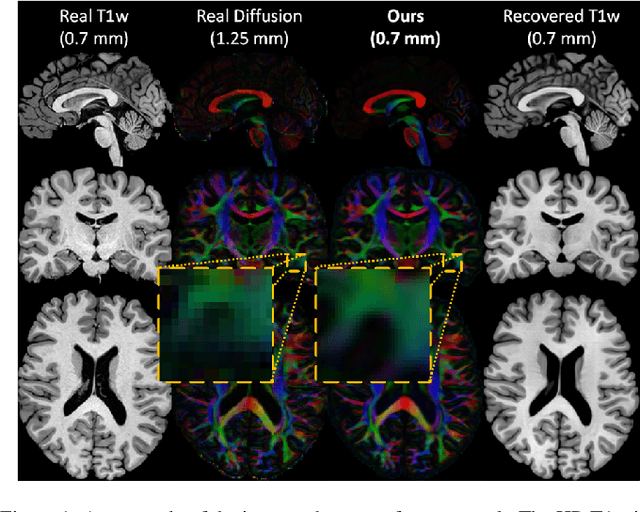
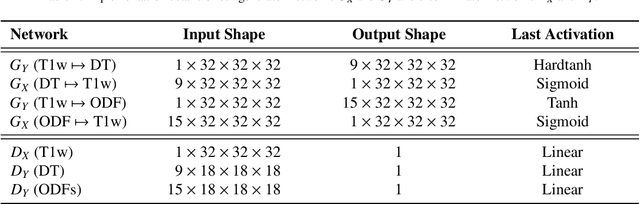
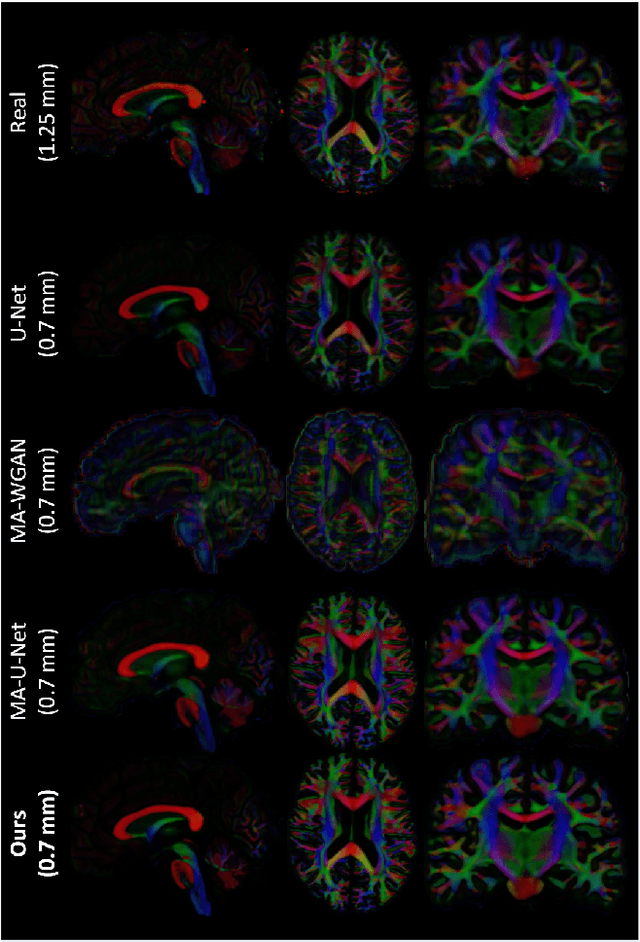
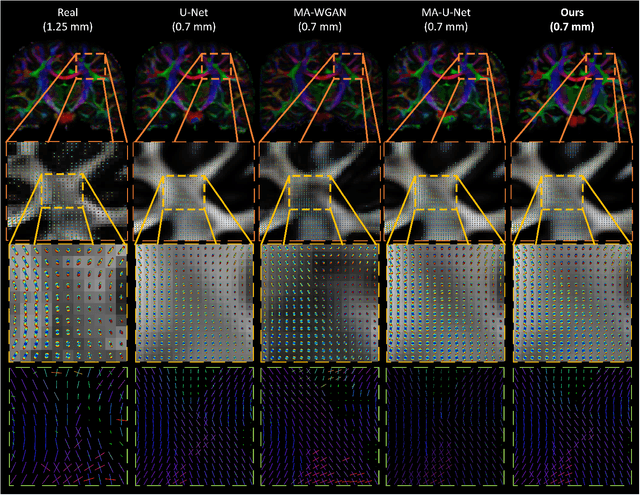
Abstract:The physical and clinical constraints surrounding diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) often limit the spatial resolution of the produced images to voxels up to 8 times larger than those of T1w images. Thus, the detailed information contained in T1w imagescould help in the synthesis of diffusion images in higher resolution. However, the non-Euclidean nature of diffusion imaging hinders current deep generative models from synthesizing physically plausible images. In this work, we propose the first Riemannian network architecture for the direct generation of diffusion tensors (DT) and diffusion orientation distribution functions (dODFs) from high-resolution T1w images. Our integration of the Log-Euclidean Metric into a learning objective guarantees, unlike standard Euclidean networks, the mathematically-valid synthesis of diffusion. Furthermore, our approach improves the fractional anisotropy mean squared error (FA MSE) between the synthesized diffusion and the ground-truth by more than 23% and the cosine similarity between principal directions by almost 5% when compared to our baselines. We validate our generated diffusion by comparing the resulting tractograms to our expected real data. We observe similar fiber bundles with streamlines having less than 3% difference in length, less than 1% difference in volume, and a visually close shape. While our method is able to generate high-resolution diffusion images from structural inputs in less than 15 seconds, we acknowledge and discuss the limits of diffusion inference solely relying on T1w images. Our results nonetheless suggest a relationship between the high-level geometry of the brain and the overall white matter architecture.
Tractography filtering using autoencoders
Oct 07, 2020
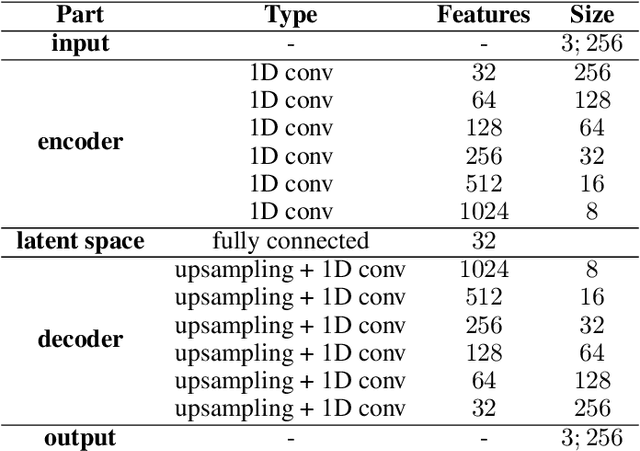
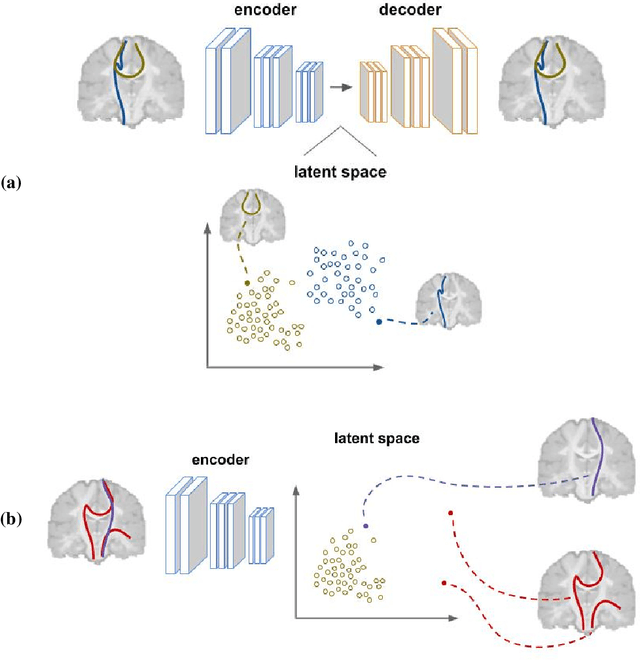

Abstract:Current brain white matter fiber tracking techniques show a number of problems, including: generating large proportions of streamlines that do not accurately describe the underlying anatomy; extracting streamlines that are not supported by the underlying diffusion signal; and under-representing some fiber populations, among others. In this paper, we describe a novel unsupervised learning method to filter streamlines from diffusion MRI tractography, and hence, to obtain more reliable tractograms. We show that a convolutional neural network autoencoder provides a straightforward and elegant way to learn a robust representation of brain streamlines, which can be used to filter undesired samples with a nearest neighbor algorithm. Our method, dubbed FINTA (Filtering in Tractography using Autoencoders) comes with several key advantages: training does not need labeled data, as it uses raw tractograms, it is fast and easily reproducible, it does not rely on the input diffusion MRI data, and thus, does not suffer from domain adaptation issues. We demonstrate the ability of FINTA to discriminate between "plausible" and "implausible" streamlines as well as to recover individual streamline group instances from a raw tractogram, from both synthetic and real human brain diffusion MRI tractography data, including partial tractograms. Results reveal that FINTA has a superior filtering performance compared to state-of-the-art methods. Together, this work brings forward a new deep learning framework in tractography based on autoencoders, and shows how it can be applied for filtering purposes. It sets the foundations for opening up new prospects towards more accurate and robust tractometry and connectivity diffusion MRI analyses, which may ultimately lead to improve the imaging of the white matter anatomy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge