Antoine Théberge
Exploring the robustness of TractOracle methods in RL-based tractography
Jul 15, 2025
Abstract:Tractography algorithms leverage diffusion MRI to reconstruct the fibrous architecture of the brain's white matter. Among machine learning approaches, reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as a promising framework for tractography, outperforming traditional methods in several key aspects. TractOracle-RL, a recent RL-based approach, reduces false positives by incorporating anatomical priors into the training process via a reward-based mechanism. In this paper, we investigate four extensions of the original TractOracle-RL framework by integrating recent advances in RL, and we evaluate their performance across five diverse diffusion MRI datasets. Results demonstrate that combining an oracle with the RL framework consistently leads to robust and reliable tractography, regardless of the specific method or dataset used. We also introduce a novel RL training scheme called Iterative Reward Training (IRT), inspired by the Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) paradigm. Instead of relying on human input, IRT leverages bundle filtering methods to iteratively refine the oracle's guidance throughout training. Experimental results show that RL methods trained with oracle feedback significantly outperform widely used tractography techniques in terms of accuracy and anatomical validity.
TractOracle: towards an anatomically-informed reward function for RL-based tractography
Mar 26, 2024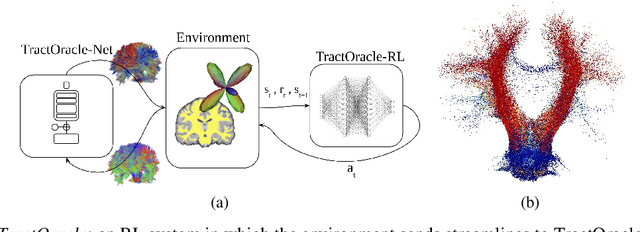
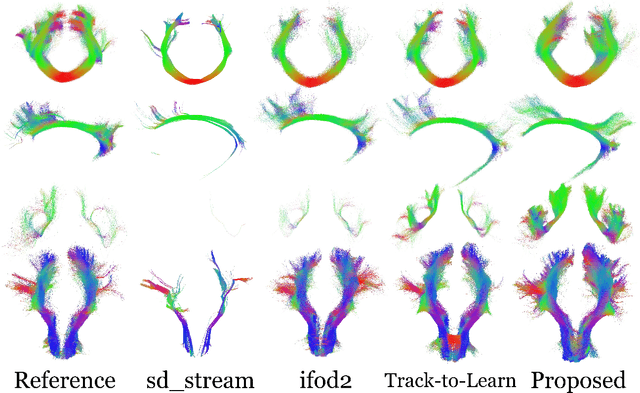
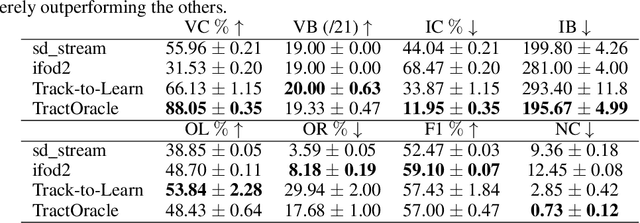
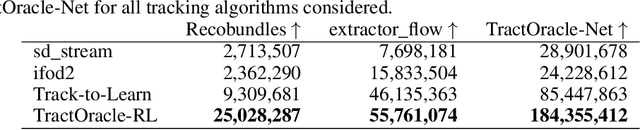
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL)-based tractography is a competitive alternative to machine learning and classical tractography algorithms due to its high anatomical accuracy obtained without the need for any annotated data. However, the reward functions so far used to train RL agents do not encapsulate anatomical knowledge which causes agents to generate spurious false positives tracts. In this paper, we propose a new RL tractography system, TractOracle, which relies on a reward network trained for streamline classification. This network is used both as a reward function during training as well as a mean for stopping the tracking process early and thus reduce the number of false positive streamlines. This makes our system a unique method that evaluates and reconstructs WM streamlines at the same time. We report an improvement of true positive ratios by almost 20\% and a reduction of 3x of false positive ratios on one dataset and an increase between 2x and 7x in the number true positive streamlines on another dataset.
What Matters in Reinforcement Learning for Tractography
May 17, 2023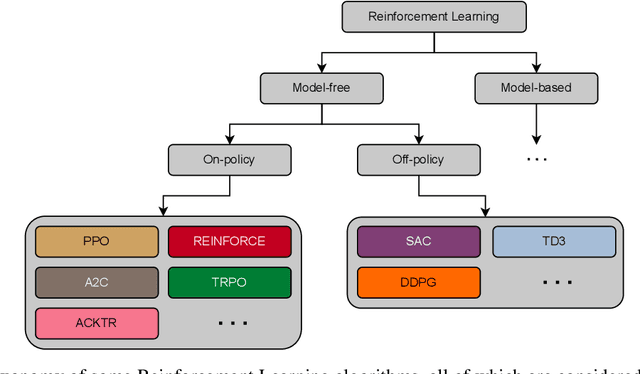
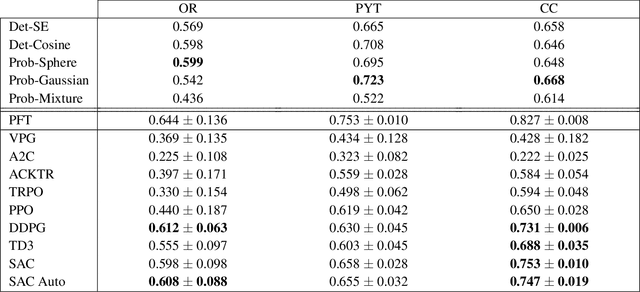
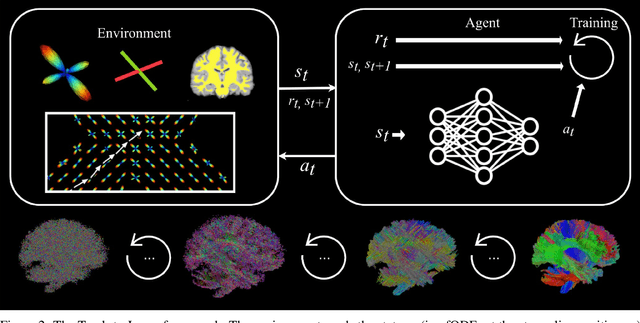
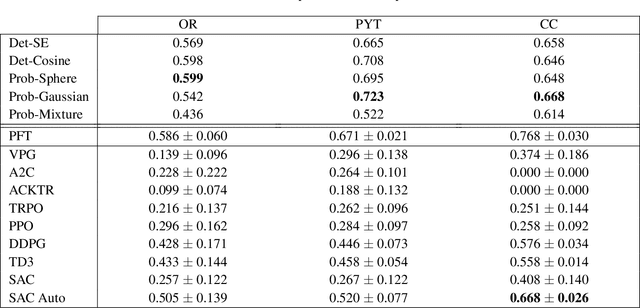
Abstract:Recently, deep reinforcement learning (RL) has been proposed to learn the tractography procedure and train agents to reconstruct the structure of the white matter without manually curated reference streamlines. While the performances reported were competitive, the proposed framework is complex, and little is still known about the role and impact of its multiple parts. In this work, we thoroughly explore the different components of the proposed framework, such as the choice of the RL algorithm, seeding strategy, the input signal and reward function, and shed light on their impact. Approximately 7,400 models were trained for this work, totalling nearly 41,000 hours of GPU time. Our goal is to guide researchers eager to explore the possibilities of deep RL for tractography by exposing what works and what does not work with the category of approach. As such, we ultimately propose a series of recommendations concerning the choice of RL algorithm, the input to the agents, the reward function and more to help future work using reinforcement learning for tractography. We also release the open source codebase, trained models, and datasets for users and researchers wanting to explore reinforcement learning for tractography.
Biomedical image analysis competitions: The state of current participation practice
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:The number of international benchmarking competitions is steadily increasing in various fields of machine learning (ML) research and practice. So far, however, little is known about the common practice as well as bottlenecks faced by the community in tackling the research questions posed. To shed light on the status quo of algorithm development in the specific field of biomedical imaging analysis, we designed an international survey that was issued to all participants of challenges conducted in conjunction with the IEEE ISBI 2021 and MICCAI 2021 conferences (80 competitions in total). The survey covered participants' expertise and working environments, their chosen strategies, as well as algorithm characteristics. A median of 72% challenge participants took part in the survey. According to our results, knowledge exchange was the primary incentive (70%) for participation, while the reception of prize money played only a minor role (16%). While a median of 80 working hours was spent on method development, a large portion of participants stated that they did not have enough time for method development (32%). 25% perceived the infrastructure to be a bottleneck. Overall, 94% of all solutions were deep learning-based. Of these, 84% were based on standard architectures. 43% of the respondents reported that the data samples (e.g., images) were too large to be processed at once. This was most commonly addressed by patch-based training (69%), downsampling (37%), and solving 3D analysis tasks as a series of 2D tasks. K-fold cross-validation on the training set was performed by only 37% of the participants and only 50% of the participants performed ensembling based on multiple identical models (61%) or heterogeneous models (39%). 48% of the respondents applied postprocessing steps.
Manifold-aware Synthesis of High-resolution Diffusion from Structural Imaging
Aug 11, 2021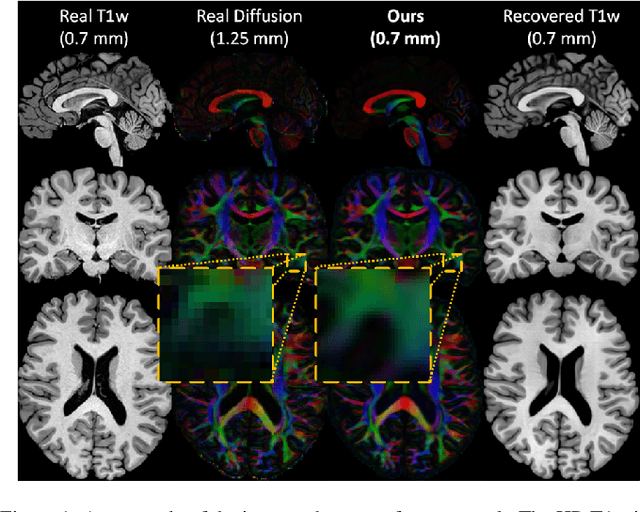
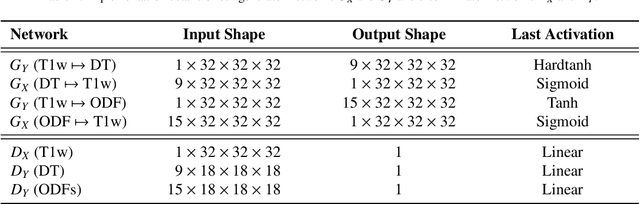
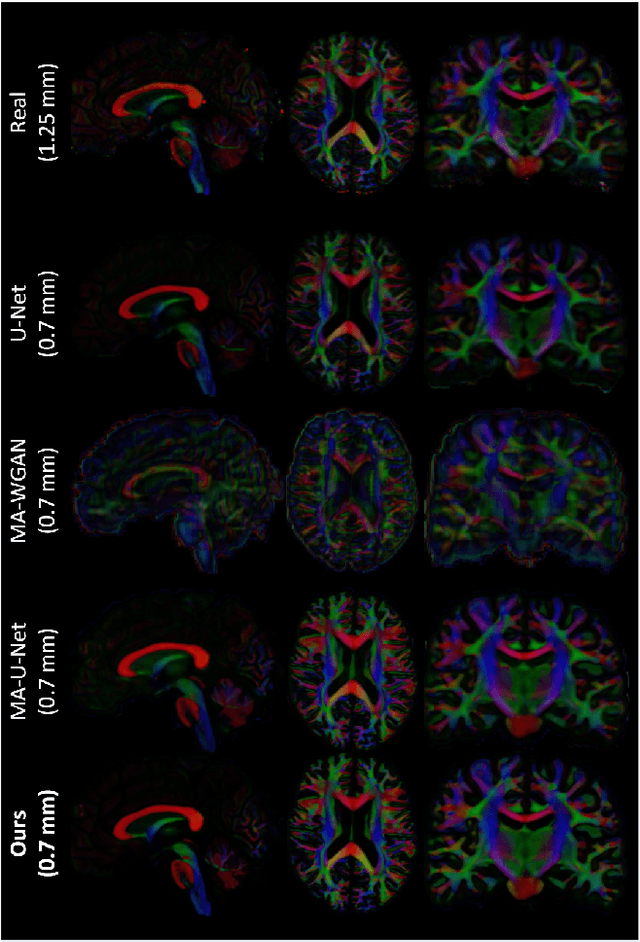
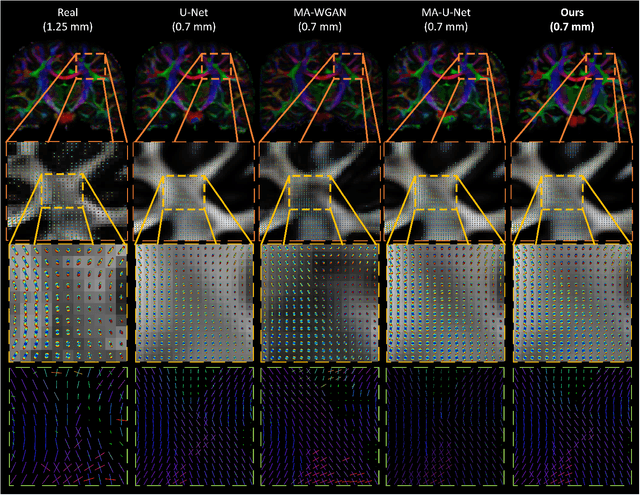
Abstract:The physical and clinical constraints surrounding diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) often limit the spatial resolution of the produced images to voxels up to 8 times larger than those of T1w images. Thus, the detailed information contained in T1w imagescould help in the synthesis of diffusion images in higher resolution. However, the non-Euclidean nature of diffusion imaging hinders current deep generative models from synthesizing physically plausible images. In this work, we propose the first Riemannian network architecture for the direct generation of diffusion tensors (DT) and diffusion orientation distribution functions (dODFs) from high-resolution T1w images. Our integration of the Log-Euclidean Metric into a learning objective guarantees, unlike standard Euclidean networks, the mathematically-valid synthesis of diffusion. Furthermore, our approach improves the fractional anisotropy mean squared error (FA MSE) between the synthesized diffusion and the ground-truth by more than 23% and the cosine similarity between principal directions by almost 5% when compared to our baselines. We validate our generated diffusion by comparing the resulting tractograms to our expected real data. We observe similar fiber bundles with streamlines having less than 3% difference in length, less than 1% difference in volume, and a visually close shape. While our method is able to generate high-resolution diffusion images from structural inputs in less than 15 seconds, we acknowledge and discuss the limits of diffusion inference solely relying on T1w images. Our results nonetheless suggest a relationship between the high-level geometry of the brain and the overall white matter architecture.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge