Christian Desrosiers
SPARK: Stochastic Propagation via Affinity-guided Random walK for training-free unsupervised segmentation
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:We argue that existing training-free segmentation methods rely on an implicit and limiting assumption, that segmentation is a spectral graph partitioning problem over diffusion-derived affinities. Such approaches, based on global graph partitioning and eigenvector-based formulations of affinity matrices, suffer from several fundamental drawbacks, they require pre-selecting the number of clusters, induce boundary oversmoothing due to spectral relaxation, and remain highly sensitive to noisy or multi-modal affinity distributions. Moreover, many prior works neglect the importance of local neighborhood structure, which plays a crucial role in stabilizing affinity propagation and preserving fine-grained contours. To address these limitations, we reformulate training-free segmentation as a stochastic flow equilibrium problem over diffusion-induced affinity graphs, where segmentation emerges from a stochastic propagation process that integrates global diffusion attention with local neighborhoods extracted from stable diffusion, yielding a sparse yet expressive affinity structure. Building on this formulation, we introduce a Markov propagation scheme that performs random-walk-based label diffusion with an adaptive pruning strategy that suppresses unreliable transitions while reinforcing confident affinity paths. Experiments across seven widely used semantic segmentation benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art zero-shot performance, producing sharper boundaries, more coherent regions, and significantly more stable masks compared to prior spectral-clustering-based approaches.
OCTOPUS: Enhancing the Spatial-Awareness of Vision SSMs with Multi-Dimensional Scans and Traversal Selection
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:State space models (SSMs) have recently emerged as an alternative to transformers due to their unique ability of modeling global relationships in text with linear complexity. However, their success in vision tasks has been limited due to their causal formulation, which is suitable for sequential text but detrimental in the spatial domain where causality breaks the inherent spatial relationships among pixels or patches. As a result, standard SSMs fail to capture local spatial coherence, often linking non-adjacent patches while ignoring neighboring ones that are visually correlated. To address these limitations, we introduce OCTOPUS , a novel architecture that preserves both global context and local spatial structure within images, while maintaining the linear complexity of SSMs. OCTOPUS performs discrete reoccurrence along eight principal orientations, going forward or backward in the horizontal, vertical, and diagonal directions, allowing effective information exchange across all spatially connected regions while maintaining independence among unrelated patches. This design enables multi-directional recurrence, capturing both global context and local spatial structure with SSM-level efficiency. In our classification and segmentation benchmarks, OCTOPUS demonstrates notable improvements in boundary preservation and region consistency, as evident from the segmentation results, while maintaining relatively better classification accuracy compared to existing V-SSM based models. These results suggest that OCTOPUS appears as a foundation method for multi-directional recurrence as a scalable and effective mechanism for building spatially aware and computationally efficient vision architectures.
Anatomically-aware conformal prediction for medical image segmentation with random walks
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:The reliable deployment of deep learning in medical imaging requires uncertainty quantification that provides rigorous error guarantees while remaining anatomically meaningful. Conformal prediction (CP) is a powerful distribution-free framework for constructing statistically valid prediction intervals. However, standard applications in segmentation often ignore anatomical context, resulting in fragmented, spatially incoherent, and over-segmented prediction sets that limit clinical utility. To bridge this gap, this paper proposes Random-Walk Conformal Prediction (RW-CP), a model-agnostic framework which can be added on top of any segmentation method. RW-CP enforces spatial coherence to generate anatomically valid sets. Our method constructs a k-nearest neighbour graph from pre-trained vision foundation model features and applies a random walk to diffuse uncertainty. The random walk diffusion regularizes the non-conformity scores, making the prediction sets less sensitive to the conformal calibration parameter $λ$, ensuring more stable and continuous anatomical boundaries. RW-CP maintains rigorous marginal coverage while significantly improving segmentation quality. Evaluations on multi-modal public datasets show improvements of up to $35.4\%$ compared to standard CP baselines, given an allowable error rate of $α=0.1$.
Histopath-C: Towards Realistic Domain Shifts for Histopathology Vision-Language Adaptation
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Medical Vision-language models (VLMs) have shown remarkable performances in various medical imaging domains such as histo\-pathology by leveraging pre-trained, contrastive models that exploit visual and textual information. However, histopathology images may exhibit severe domain shifts, such as staining, contamination, blurring, and noise, which may severely degrade the VLM's downstream performance. In this work, we introduce Histopath-C, a new benchmark with realistic synthetic corruptions designed to mimic real-world distribution shifts observed in digital histopathology. Our framework dynamically applies corruptions to any available dataset and evaluates Test-Time Adaptation (TTA) mechanisms on the fly. We then propose LATTE, a transductive, low-rank adaptation strategy that exploits multiple text templates, mitigating the sensitivity of histopathology VLMs to diverse text inputs. Our approach outperforms state-of-the-art TTA methods originally designed for natural images across a breadth of histopathology datasets, demonstrating the effectiveness of our proposed design for robust adaptation in histopathology images. Code and data are available at https://github.com/Mehrdad-Noori/Histopath-C.
Revisiting the Learning Objectives of Vision-Language Reward Models
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:Learning generalizable reward functions is a core challenge in embodied intelligence. Recent work leverages contrastive vision language models (VLMs) to obtain dense, domain-agnostic rewards without human supervision. These methods adapt VLMs into reward models through increasingly complex learning objectives, yet meaningful comparison remains difficult due to differences in training data, architectures, and evaluation settings. In this work, we isolate the impact of the learning objective by evaluating recent VLM-based reward models under a unified framework with identical backbones, finetuning data, and evaluation environments. Using Meta-World tasks, we assess modeling accuracy by measuring consistency with ground truth reward and correlation with expert progress. Remarkably, we show that a simple triplet loss outperforms state-of-the-art methods, suggesting that much of the improvements in recent approaches could be attributed to differences in data and architectures.
NERVE: Neighbourhood & Entropy-guided Random-walk for training free open-Vocabulary sEgmentation
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Despite recent advances in Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation (OVSS), existing training-free methods face several limitations: use of computationally expensive affinity refinement strategies, ineffective fusion of transformer attention maps due to equal weighting or reliance on fixed-size Gaussian kernels to reinforce local spatial smoothness, enforcing isotropic neighborhoods. We propose a strong baseline for training-free OVSS termed as NERVE (Neighbourhood \& Entropy-guided Random-walk for open-Vocabulary sEgmentation), which uniquely integrates global and fine-grained local information, exploiting the neighbourhood structure from the self-attention layer of a stable diffusion model. We also introduce a stochastic random walk for refining the affinity rather than relying on fixed-size Gaussian kernels for local context. This spatial diffusion process encourages propagation across connected and semantically related areas, enabling it to effectively delineate objects with arbitrary shapes. Whereas most existing approaches treat self-attention maps from different transformer heads or layers equally, our method uses entropy-based uncertainty to select the most relevant maps. Notably, our method does not require any conventional post-processing techniques like Conditional Random Fields (CRF) or Pixel-Adaptive Mask Refinement (PAMR). Experiments are performed on 7 popular semantic segmentation benchmarks, yielding an overall state-of-the-art zero-shot segmentation performance, providing an effective approach to open-vocabulary semantic segmentation.
Reinforcement Learning for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation in Spatio-Temporal Echocardiography Segmentation
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:Domain adaptation methods aim to bridge the gap between datasets by enabling knowledge transfer across domains, reducing the need for additional expert annotations. However, many approaches struggle with reliability in the target domain, an issue particularly critical in medical image segmentation, where accuracy and anatomical validity are essential. This challenge is further exacerbated in spatio-temporal data, where the lack of temporal consistency can significantly degrade segmentation quality, and particularly in echocardiography, where the presence of artifacts and noise can further hinder segmentation performance. To address these issues, we present RL4Seg3D, an unsupervised domain adaptation framework for 2D + time echocardiography segmentation. RL4Seg3D integrates novel reward functions and a fusion scheme to enhance key landmark precision in its segmentations while processing full-sized input videos. By leveraging reinforcement learning for image segmentation, our approach improves accuracy, anatomical validity, and temporal consistency while also providing, as a beneficial side effect, a robust uncertainty estimator, which can be used at test time to further enhance segmentation performance. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework on over 30,000 echocardiographic videos, showing that it outperforms standard domain adaptation techniques without the need for any labels on the target domain. Code is available at https://github.com/arnaudjudge/RL4Seg3D.
THUNDER: Tile-level Histopathology image UNDERstanding benchmark
Jul 10, 2025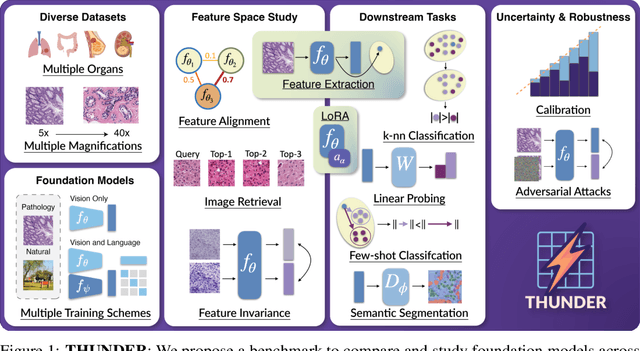
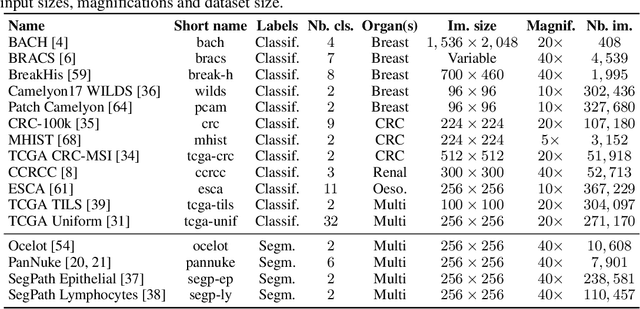

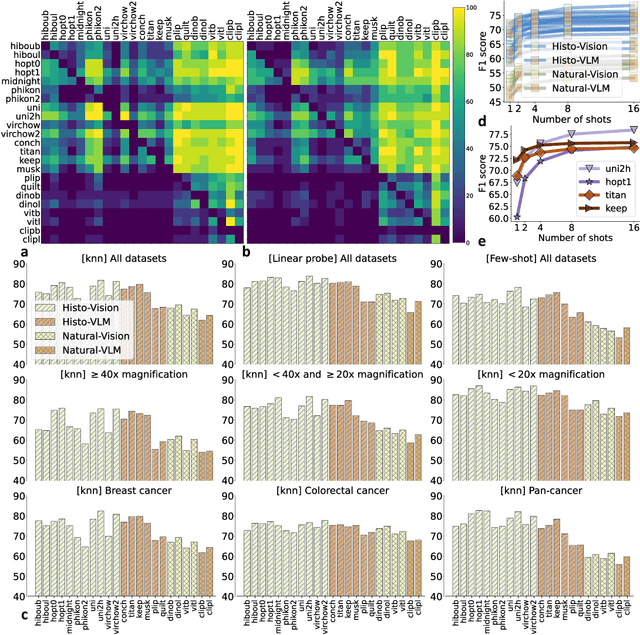
Abstract:Progress in a research field can be hard to assess, in particular when many concurrent methods are proposed in a short period of time. This is the case in digital pathology, where many foundation models have been released recently to serve as feature extractors for tile-level images, being used in a variety of downstream tasks, both for tile- and slide-level problems. Benchmarking available methods then becomes paramount to get a clearer view of the research landscape. In particular, in critical domains such as healthcare, a benchmark should not only focus on evaluating downstream performance, but also provide insights about the main differences between methods, and importantly, further consider uncertainty and robustness to ensure a reliable usage of proposed models. For these reasons, we introduce THUNDER, a tile-level benchmark for digital pathology foundation models, allowing for efficient comparison of many models on diverse datasets with a series of downstream tasks, studying their feature spaces and assessing the robustness and uncertainty of predictions informed by their embeddings. THUNDER is a fast, easy-to-use, dynamic benchmark that can already support a large variety of state-of-the-art foundation, as well as local user-defined models for direct tile-based comparison. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive comparison of 23 foundation models on 16 different datasets covering diverse tasks, feature analysis, and robustness. The code for THUNDER is publicly available at https://github.com/MICS-Lab/thunder.
Prompt learning with bounding box constraints for medical image segmentation
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Pixel-wise annotations are notoriously labourious and costly to obtain in the medical domain. To mitigate this burden, weakly supervised approaches based on bounding box annotations-much easier to acquire-offer a practical alternative. Vision foundation models have recently shown noteworthy segmentation performance when provided with prompts such as points or bounding boxes. Prompt learning exploits these models by adapting them to downstream tasks and automating segmentation, thereby reducing user intervention. However, existing prompt learning approaches depend on fully annotated segmentation masks. This paper proposes a novel framework that combines the representational power of foundation models with the annotation efficiency of weakly supervised segmentation. More specifically, our approach automates prompt generation for foundation models using only bounding box annotations. Our proposed optimization scheme integrates multiple constraints derived from box annotations with pseudo-labels generated by the prompted foundation model. Extensive experiments across multimodal datasets reveal that our weakly supervised method achieves an average Dice score of 84.90% in a limited data setting, outperforming existing fully-supervised and weakly-supervised approaches. The code is available at https://github.com/Minimel/box-prompt-learning-VFM.git
Test-Time Adaptation of Vision-Language Models for Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
May 28, 2025Abstract:Recently, test-time adaptation has attracted wide interest in the context of vision-language models for image classification. However, to the best of our knowledge, the problem is completely overlooked in dense prediction tasks such as Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation (OVSS). In response, we propose a novel TTA method tailored to adapting VLMs for segmentation during test time. Unlike TTA methods for image classification, our Multi-Level and Multi-Prompt (MLMP) entropy minimization integrates features from intermediate vision-encoder layers and is performed with different text-prompt templates at both the global CLS token and local pixel-wise levels. Our approach could be used as plug-and-play for any segmentation network, does not require additional training data or labels, and remains effective even with a single test sample. Furthermore, we introduce a comprehensive OVSS TTA benchmark suite, which integrates a rigorous evaluation protocol, seven segmentation datasets, and 15 common corruptions, with a total of 82 distinct test scenarios, establishing a standardized and comprehensive testbed for future TTA research in open-vocabulary segmentation. Our experiments on this suite demonstrate that our segmentation-tailored method consistently delivers significant gains over direct adoption of TTA classification baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge