Rajarshi Bhattacharya
DART$^3$: Leveraging Distance for Test Time Adaptation in Person Re-Identification
May 23, 2025Abstract:Person re-identification (ReID) models are known to suffer from camera bias, where learned representations cluster according to camera viewpoints rather than identity, leading to significant performance degradation under (inter-camera) domain shifts in real-world surveillance systems when new cameras are added to camera networks. State-of-the-art test-time adaptation (TTA) methods, largely designed for classification tasks, rely on classification entropy-based objectives that fail to generalize well to ReID, thus making them unsuitable for tackling camera bias. In this paper, we introduce DART$^3$, a TTA framework specifically designed to mitigate camera-induced domain shifts in person ReID. DART$^3$ (Distance-Aware Retrieval Tuning at Test Time) leverages a distance-based objective that aligns better with image retrieval tasks like ReID by exploiting the correlation between nearest-neighbor distance and prediction error. Unlike prior ReID-specific domain adaptation methods, DART$^3$ requires no source data, architectural modifications, or retraining, and can be deployed in both fully black-box and hybrid settings. Empirical evaluations on multiple ReID benchmarks indicate that DART$^3$ and DART$^3$ LITE, a lightweight alternative to the approach, consistently outperforms state-of-the-art TTA baselines, making for a viable option to online learning to mitigate the adverse effects of camera bias.
Beyond Patches: Mining Interpretable Part-Prototypes for Explainable AI
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Deep learning has provided considerable advancements for multimedia systems, yet the interpretability of deep models remains a challenge. State-of-the-art post-hoc explainability methods, such as GradCAM, provide visual interpretation based on heatmaps but lack conceptual clarity. Prototype-based approaches, like ProtoPNet and PIPNet, offer a more structured explanation but rely on fixed patches, limiting their robustness and semantic consistency. To address these limitations, a part-prototypical concept mining network (PCMNet) is proposed that dynamically learns interpretable prototypes from meaningful regions. PCMNet clusters prototypes into concept groups, creating semantically grounded explanations without requiring additional annotations. Through a joint process of unsupervised part discovery and concept activation vector extraction, PCMNet effectively captures discriminative concepts and makes interpretable classification decisions. Our extensive experiments comparing PCMNet against state-of-the-art methods on multiple datasets show that it can provide a high level of interpretability, stability, and robustness under clean and occluded scenarios.
Prompting classes: Exploring the Power of Prompt Class Learning in Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Jul 08, 2023Abstract:Recently, CLIP-based approaches have exhibited remarkable performance on generalization and few-shot learning tasks, fueled by the power of contrastive language-vision pre-training. In particular, prompt tuning has emerged as an effective strategy to adapt the pre-trained language-vision models to downstream tasks by employing task-related textual tokens. Motivated by this progress, in this work we question whether other fundamental problems, such as weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS), can benefit from prompt tuning. Our findings reveal two interesting observations that shed light on the impact of prompt tuning on WSSS. First, modifying only the class token of the text prompt results in a greater impact on the Class Activation Map (CAM), compared to arguably more complex strategies that optimize the context. And second, the class token associated with the image ground truth does not necessarily correspond to the category that yields the best CAM. Motivated by these observations, we introduce a novel approach based on a PrOmpt cLass lEarning (POLE) strategy. Through extensive experiments we demonstrate that our simple, yet efficient approach achieves SOTA performance in a well-known WSSS benchmark. These results highlight not only the benefits of language-vision models in WSSS but also the potential of prompt learning for this problem. The code is available at https://github.com/rB080/WSS_POLE.
An Embarrassingly Simple Consistency Regularization Method for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Feb 03, 2022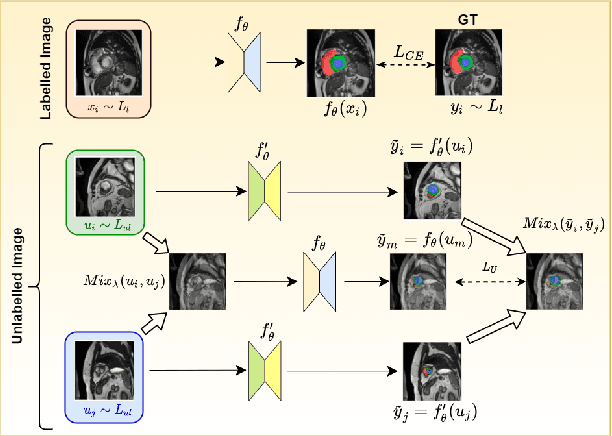
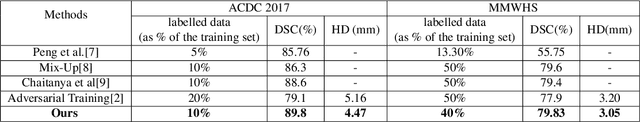
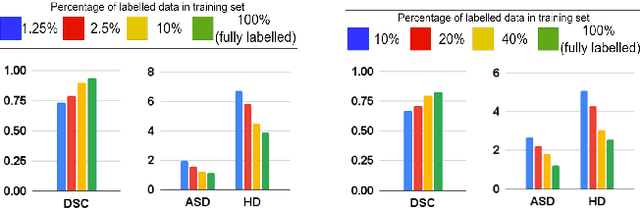
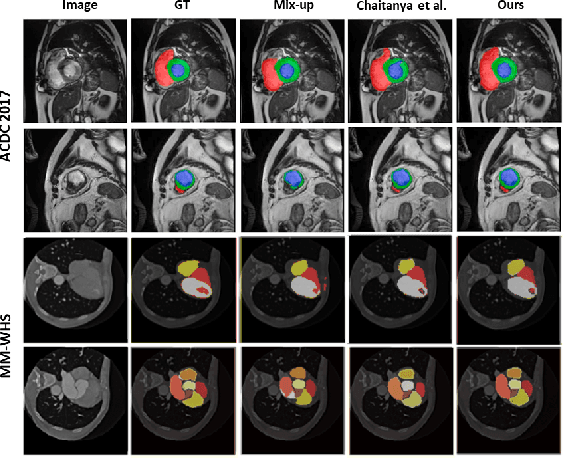
Abstract:The scarcity of pixel-level annotation is a prevalent problem in medical image segmentation tasks. In this paper, we introduce a novel regularization strategy involving interpolation-based mixing for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. The proposed method is a new consistency regularization strategy that encourages segmentation of interpolation of two unlabelled data to be consistent with the interpolation of segmentation maps of those data. This method represents a specific type of data-adaptive regularization paradigm which aids to minimize the overfitting of labelled data under high confidence values. The proposed method is advantageous over adversarial and generative models as it requires no additional computation. Upon evaluation on two publicly available MRI datasets: ACDC and MMWHS, experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method in comparison to existing semi-supervised models. Code is available at: https://github.com/hritam-98/ICT-MedSeg
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge