Agniv Chatterjee
PICO: Reconstructing 3D People In Contact with Objects
Apr 24, 2025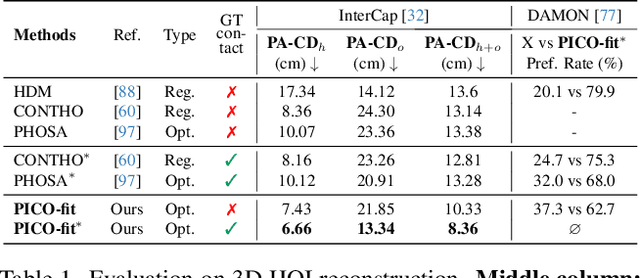

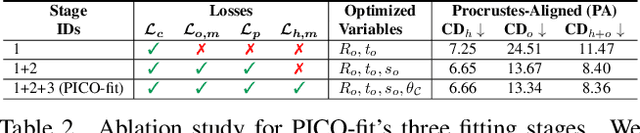
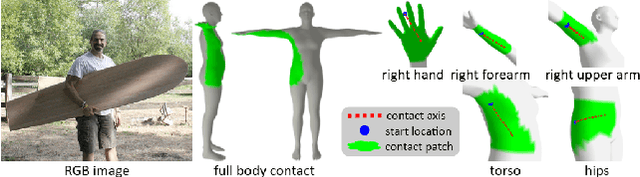
Abstract:Recovering 3D Human-Object Interaction (HOI) from single color images is challenging due to depth ambiguities, occlusions, and the huge variation in object shape and appearance. Thus, past work requires controlled settings such as known object shapes and contacts, and tackles only limited object classes. Instead, we need methods that generalize to natural images and novel object classes. We tackle this in two main ways: (1) We collect PICO-db, a new dataset of natural images uniquely paired with dense 3D contact on both body and object meshes. To this end, we use images from the recent DAMON dataset that are paired with contacts, but these contacts are only annotated on a canonical 3D body. In contrast, we seek contact labels on both the body and the object. To infer these given an image, we retrieve an appropriate 3D object mesh from a database by leveraging vision foundation models. Then, we project DAMON's body contact patches onto the object via a novel method needing only 2 clicks per patch. This minimal human input establishes rich contact correspondences between bodies and objects. (2) We exploit our new dataset of contact correspondences in a novel render-and-compare fitting method, called PICO-fit, to recover 3D body and object meshes in interaction. PICO-fit infers contact for the SMPL-X body, retrieves a likely 3D object mesh and contact from PICO-db for that object, and uses the contact to iteratively fit the 3D body and object meshes to image evidence via optimization. Uniquely, PICO-fit works well for many object categories that no existing method can tackle. This is crucial to enable HOI understanding to scale in the wild. Our data and code are available at https://pico.is.tue.mpg.de.
DECO: Dense Estimation of 3D Human-Scene Contact In The Wild
Sep 26, 2023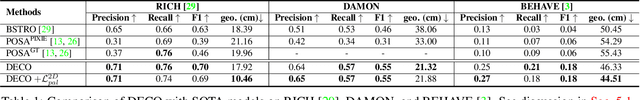
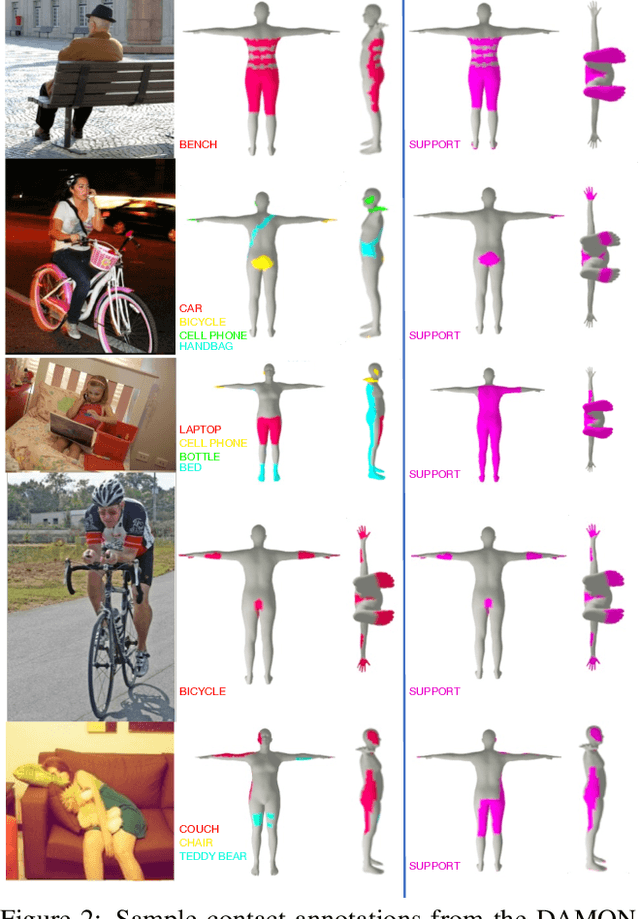
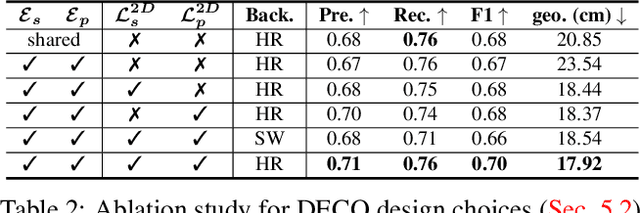
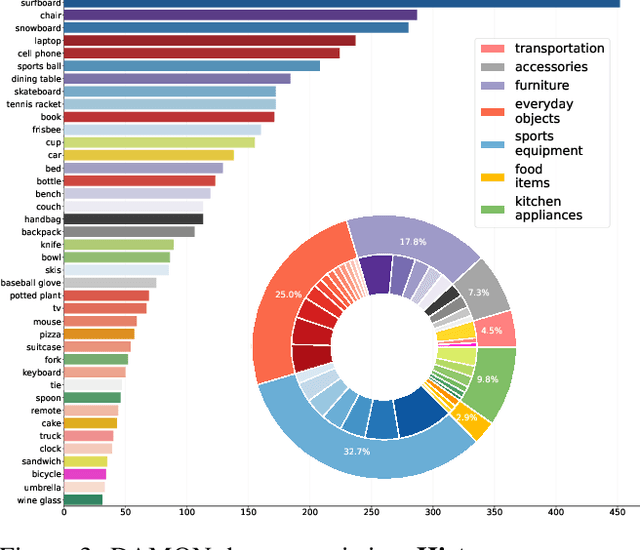
Abstract:Understanding how humans use physical contact to interact with the world is key to enabling human-centric artificial intelligence. While inferring 3D contact is crucial for modeling realistic and physically-plausible human-object interactions, existing methods either focus on 2D, consider body joints rather than the surface, use coarse 3D body regions, or do not generalize to in-the-wild images. In contrast, we focus on inferring dense, 3D contact between the full body surface and objects in arbitrary images. To achieve this, we first collect DAMON, a new dataset containing dense vertex-level contact annotations paired with RGB images containing complex human-object and human-scene contact. Second, we train DECO, a novel 3D contact detector that uses both body-part-driven and scene-context-driven attention to estimate vertex-level contact on the SMPL body. DECO builds on the insight that human observers recognize contact by reasoning about the contacting body parts, their proximity to scene objects, and the surrounding scene context. We perform extensive evaluations of our detector on DAMON as well as on the RICH and BEHAVE datasets. We significantly outperform existing SOTA methods across all benchmarks. We also show qualitatively that DECO generalizes well to diverse and challenging real-world human interactions in natural images. The code, data, and models are available at https://deco.is.tue.mpg.de.
An Embarrassingly Simple Consistency Regularization Method for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Feb 03, 2022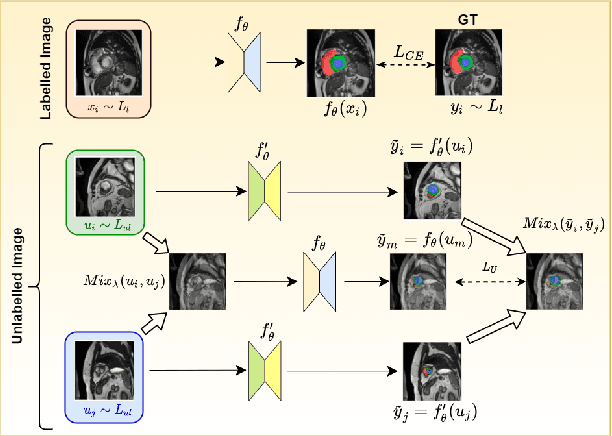
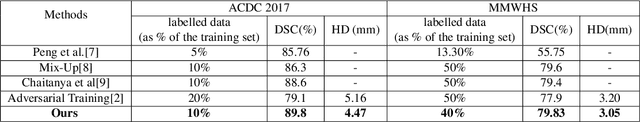
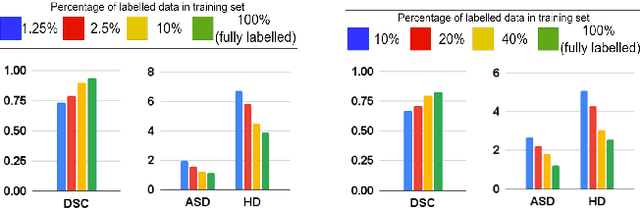
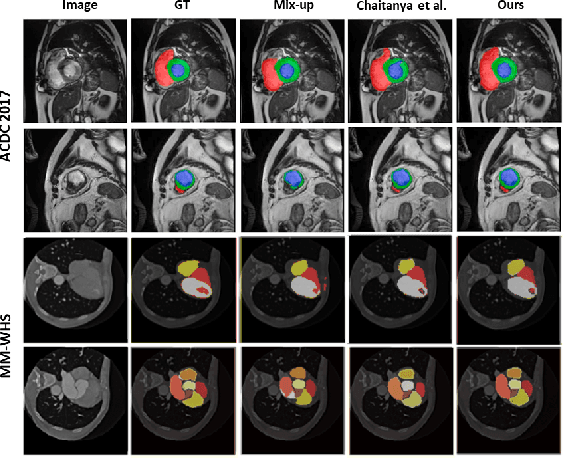
Abstract:The scarcity of pixel-level annotation is a prevalent problem in medical image segmentation tasks. In this paper, we introduce a novel regularization strategy involving interpolation-based mixing for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. The proposed method is a new consistency regularization strategy that encourages segmentation of interpolation of two unlabelled data to be consistent with the interpolation of segmentation maps of those data. This method represents a specific type of data-adaptive regularization paradigm which aids to minimize the overfitting of labelled data under high confidence values. The proposed method is advantageous over adversarial and generative models as it requires no additional computation. Upon evaluation on two publicly available MRI datasets: ACDC and MMWHS, experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method in comparison to existing semi-supervised models. Code is available at: https://github.com/hritam-98/ICT-MedSeg
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge