Mattia Antonino Di Gangi
On Target Segmentation for Direct Speech Translation
Sep 10, 2020



Abstract:Recent studies on direct speech translation show continuous improvements by means of data augmentation techniques and bigger deep learning models. While these methods are helping to close the gap between this new approach and the more traditional cascaded one, there are many incongruities among different studies that make it difficult to assess the state of the art. Surprisingly, one point of discussion is the segmentation of the target text. Character-level segmentation has been initially proposed to obtain an open vocabulary, but it results on long sequences and long training time. Then, subword-level segmentation became the state of the art in neural machine translation as it produces shorter sequences that reduce the training time, while being superior to word-level models. As such, recent works on speech translation started using target subwords despite the initial use of characters and some recent claims of better results at the character level. In this work, we perform an extensive comparison of the two methods on three benchmarks covering 8 language directions and multilingual training. Subword-level segmentation compares favorably in all settings, outperforming its character-level counterpart in a range of 1 to 3 BLEU points.
Contextualized Translation of Automatically Segmented Speech
Aug 05, 2020



Abstract:Direct speech-to-text translation (ST) models are usually trained on corpora segmented at sentence level, but at inference time they are commonly fed with audio split by a voice activity detector (VAD). Since VAD segmentation is not syntax-informed, the resulting segments do not necessarily correspond to well-formed sentences uttered by the speaker but, most likely, to fragments of one or more sentences. This segmentation mismatch degrades considerably the quality of ST models' output. So far, researchers have focused on improving audio segmentation towards producing sentence-like splits. In this paper, instead, we address the issue in the model, making it more robust to a different, potentially sub-optimal segmentation. To this aim, we train our models on randomly segmented data and compare two approaches: fine-tuning and adding the previous segment as context. We show that our context-aware solution is more robust to VAD-segmented input, outperforming a strong base model and the fine-tuning on different VAD segmentations of an English-German test set by up to 4.25 BLEU points.
Gender in Danger? Evaluating Speech Translation Technology on the MuST-SHE Corpus
Jun 10, 2020



Abstract:Translating from languages without productive grammatical gender like English into gender-marked languages is a well-known difficulty for machines. This difficulty is also due to the fact that the training data on which models are built typically reflect the asymmetries of natural languages, gender bias included. Exclusively fed with textual data, machine translation is intrinsically constrained by the fact that the input sentence does not always contain clues about the gender identity of the referred human entities. But what happens with speech translation, where the input is an audio signal? Can audio provide additional information to reduce gender bias? We present the first thorough investigation of gender bias in speech translation, contributing with: i) the release of a benchmark useful for future studies, and ii) the comparison of different technologies (cascade and end-to-end) on two language directions (English-Italian/French).
End-to-End Speech-Translation with Knowledge Distillation: FBK@IWSLT2020
Jun 04, 2020


Abstract:This paper describes FBK's participation in the IWSLT 2020 offline speech translation (ST) task. The task evaluates systems' ability to translate English TED talks audio into German texts. The test talks are provided in two versions: one contains the data already segmented with automatic tools and the other is the raw data without any segmentation. Participants can decide whether to work on custom segmentation or not. We used the provided segmentation. Our system is an end-to-end model based on an adaptation of the Transformer for speech data. Its training process is the main focus of this paper and it is based on: i) transfer learning (ASR pretraining and knowledge distillation), ii) data augmentation (SpecAugment, time stretch and synthetic data), iii) combining synthetic and real data marked as different domains, and iv) multi-task learning using the CTC loss. Finally, after the training with word-level knowledge distillation is complete, our ST models are fine-tuned using label smoothed cross entropy. Our best model scored 29 BLEU on the MuST-C En-De test set, which is an excellent result compared to recent papers, and 23.7 BLEU on the same data segmented with VAD, showing the need for researching solutions addressing this specific data condition.
Instance-Based Model Adaptation For Direct Speech Translation
Oct 23, 2019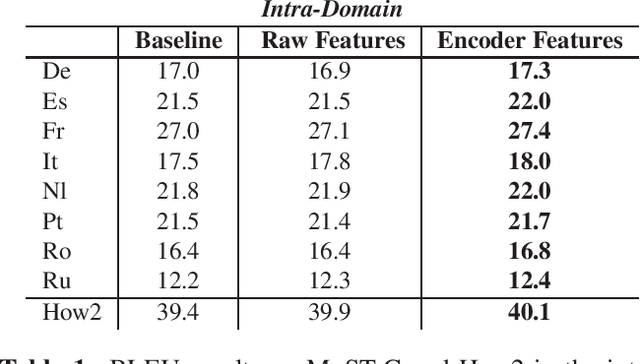
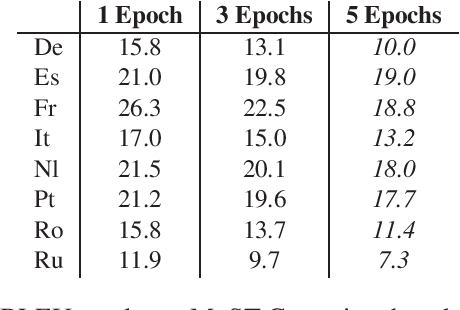
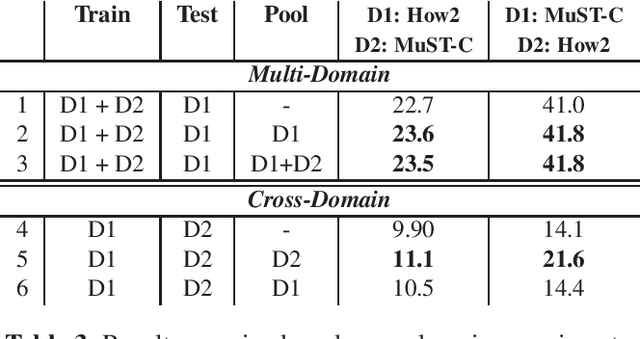
Abstract:Despite recent technology advancements, the effectiveness of neural approaches to end-to-end speech-to-text translation is still limited by the paucity of publicly available training corpora. We tackle this limitation with a method to improve data exploitation and boost the system's performance at inference time. Our approach allows us to customize "on the fly" an existing model to each incoming translation request. At its core, it exploits an instance selection procedure to retrieve, from a given pool of data, a small set of samples similar to the input query in terms of latent properties of its audio signal. The retrieved samples are then used for an instance-specific fine-tuning of the model. We evaluate our approach in three different scenarios. In all data conditions (different languages, in/out-of-domain adaptation), our instance-based adaptation yields coherent performance gains over static models.
Robust Neural Machine Translation for Clean and Noisy Speech Transcripts
Oct 22, 2019



Abstract:Neural machine translation models have shown to achieve high quality when trained and fed with well structured and punctuated input texts. Unfortunately, the latter condition is not met in spoken language translation, where the input is generated by an automatic speech recognition (ASR) system. In this paper, we study how to adapt a strong NMT system to make it robust to typical ASR errors. As in our application scenarios transcripts might be post-edited by human experts, we propose adaptation strategies to train a single system that can translate either clean or noisy input with no supervision on the input type. Our experimental results on a public speech translation data set show that adapting a model on a significant amount of parallel data including ASR transcripts is beneficial with test data of the same type, but produces a small degradation when translating clean text. Adapting on both clean and noisy variants of the same data leads to the best results on both input types.
One-To-Many Multilingual End-to-end Speech Translation
Oct 08, 2019



Abstract:Nowadays, training end-to-end neural models for spoken language translation (SLT) still has to confront with extreme data scarcity conditions. The existing SLT parallel corpora are indeed orders of magnitude smaller than those available for the closely related tasks of automatic speech recognition (ASR) and machine translation (MT), which usually comprise tens of millions of instances. To cope with data paucity, in this paper we explore the effectiveness of transfer learning in end-to-end SLT by presenting a multilingual approach to the task. Multilingual solutions are widely studied in MT and usually rely on ``\textit{target forcing}'', in which multilingual parallel data are combined to train a single model by prepending to the input sequences a language token that specifies the target language. However, when tested in speech translation, our experiments show that MT-like \textit{target forcing}, used as is, is not effective in discriminating among the target languages. Thus, we propose a variant that uses target-language embeddings to shift the input representations in different portions of the space according to the language, so to better support the production of output in the desired target language. Our experiments on end-to-end SLT from English into six languages show important improvements when translating into similar languages, especially when these are supported by scarce data. Further improvements are obtained when using English ASR data as an additional language (up to $+2.5$ BLEU points).
Assessing the Tolerance of Neural Machine Translation Systems Against Speech Recognition Errors
Apr 24, 2019



Abstract:Machine translation systems are conventionally trained on textual resources that do not model phenomena that occur in spoken language. While the evaluation of neural machine translation systems on textual inputs is actively researched in the literature , little has been discovered about the complexities of translating spoken language data with neural models. We introduce and motivate interesting problems one faces when considering the translation of automatic speech recognition (ASR) outputs on neural machine translation (NMT) systems. We test the robustness of sentence encoding approaches for NMT encoder-decoder modeling, focusing on word-based over byte-pair encoding. We compare the translation of utterances containing ASR errors in state-of-the-art NMT encoder-decoder systems against a strong phrase-based machine translation baseline in order to better understand which phenomena present in ASR outputs are better represented under the NMT framework than approaches that represent translation as a linear model.
Effectiveness of Data-Driven Induction of Semantic Spaces and Traditional Classifiers for Sarcasm Detection
Apr 15, 2019



Abstract:Irony and sarcasm are two complex linguistic phenomena that are widely used in everyday language and especially over the social media, but they represent two serious issues for automated text understanding. Many labelled corpora have been extracted from several sources to accomplish this task, and it seems that sarcasm is conveyed in different ways for different domains. Nonetheless, very little work has been done for comparing different methods among the available corpora. Furthermore, usually, each author collects and uses its own dataset to evaluate his own method. In this paper, we show that sarcasm detection can be tackled by applying classical machine learning algorithms to input texts sub-symbolically represented in a Latent Semantic space. The main consequence is that our studies establish both reference datasets and baselines for the sarcasm detection problem that could serve to the scientific community to test newly proposed methods.
* 37 pages, 7 figures, version 3
Fine-tuning on Clean Data for End-to-End Speech Translation: FBK @ IWSLT 2018
Oct 16, 2018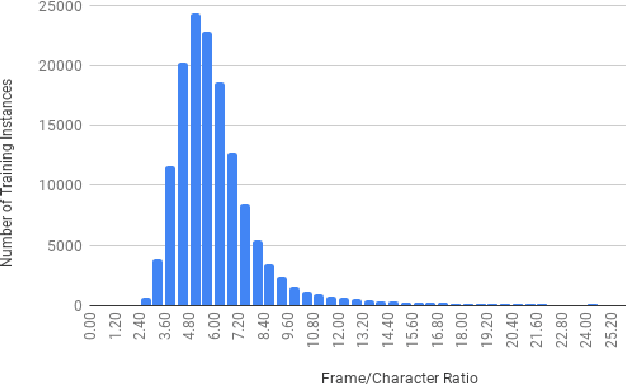
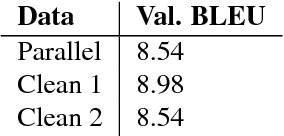
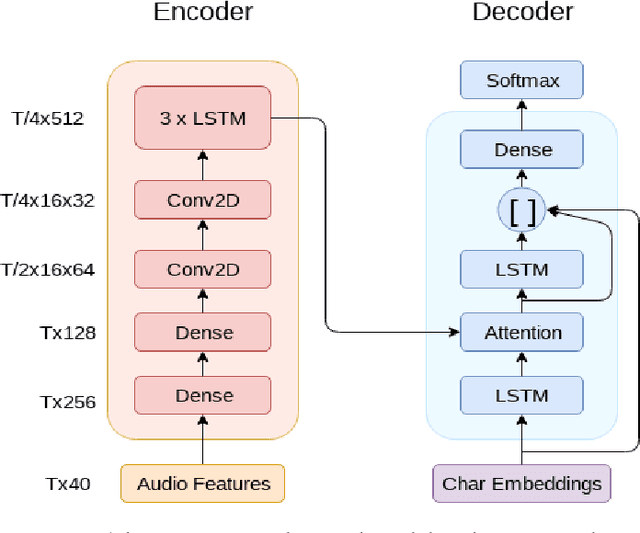
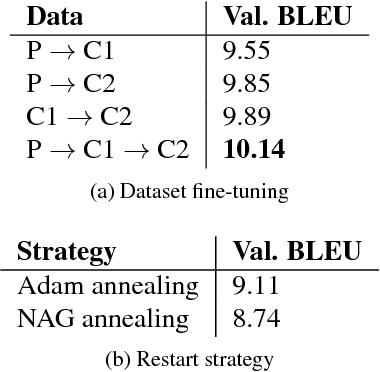
Abstract:This paper describes FBK's submission to the end-to-end English-German speech translation task at IWSLT 2018. Our system relies on a state-of-the-art model based on LSTMs and CNNs, where the CNNs are used to reduce the temporal dimension of the audio input, which is in general much higher than machine translation input. Our model was trained only on the audio-to-text parallel data released for the task, and fine-tuned on cleaned subsets of the original training corpus. The addition of weight normalization and label smoothing improved the baseline system by 1.0 BLEU point on our validation set. The final submission also featured checkpoint averaging within a training run and ensemble decoding of models trained during multiple runs. On test data, our best single model obtained a BLEU score of 9.7, while the ensemble obtained a BLEU score of 10.24.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge