Matti Lassas
Stroke classification using Virtual Hybrid Edge Detection from in silico electrical impedance tomography data
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a non-invasive imaging method for recovering the internal conductivity of a physical body from electric boundary measurements. EIT combined with machine learning has shown promise for the classification of strokes. However, most previous works have used raw EIT voltage data as network inputs. We build upon a recent development which suggested the use of special noise-robust Virtual Hybrid Edge Detection (VHED) functions as network inputs, although that work used only highly simplified and mathematically ideal models. In this work we strengthen the case for the use of EIT, and VHED functions especially, for stroke classification. We design models with high detail and mathematical realism to test the use of VHED functions as inputs. Virtual patients are created using a physically detailed 2D head model which includes features known to create challenges in real-world imaging scenarios. Conductivity values are drawn from statistically realistic distributions, and phantoms are afflicted with either hemorrhagic or ischemic strokes of various shapes and sizes. Simulated noisy EIT electrode data, generated using the realistic Complete Electrode Model (CEM) as opposed to the mathematically ideal continuum model, is processed to obtain VHED functions. We compare the use of VHED functions as inputs against the alternative paradigm of using raw EIT voltages. Our results show that (i) stroke classification can be performed with high accuracy using 2D EIT data from physically detailed and mathematically realistic models, and (ii) in the presence of noise, VHED functions outperform raw data as network inputs.
Semialgebraic Neural Networks: From roots to representations
Jan 02, 2025Abstract:Many numerical algorithms in scientific computing -- particularly in areas like numerical linear algebra, PDE simulation, and inverse problems -- produce outputs that can be represented by semialgebraic functions; that is, the graph of the computed function can be described by finitely many polynomial equalities and inequalities. In this work, we introduce Semialgebraic Neural Networks (SANNs), a neural network architecture capable of representing any bounded semialgebraic function, and computing such functions up to the accuracy of a numerical ODE solver chosen by the programmer. Conceptually, we encode the graph of the learned function as the kernel of a piecewise polynomial selected from a class of functions whose roots can be evaluated using a particular homotopy continuation method. We show by construction that the SANN architecture is able to execute this continuation method, thus evaluating the learned semialgebraic function. Furthermore, the architecture can exactly represent even discontinuous semialgebraic functions by executing a continuation method on each connected component of the target function. Lastly, we provide example applications of these networks and show they can be trained with traditional deep-learning techniques.
Learning sparsity-promoting regularizers for linear inverse problems
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces a novel approach to learning sparsity-promoting regularizers for solving linear inverse problems. We develop a bilevel optimization framework to select an optimal synthesis operator, denoted as $B$, which regularizes the inverse problem while promoting sparsity in the solution. The method leverages statistical properties of the underlying data and incorporates prior knowledge through the choice of $B$. We establish the well-posedness of the optimization problem, provide theoretical guarantees for the learning process, and present sample complexity bounds. The approach is demonstrated through examples, including compact perturbations of a known operator and the problem of learning the mother wavelet, showcasing its flexibility in incorporating prior knowledge into the regularization framework. This work extends previous efforts in Tikhonov regularization by addressing non-differentiable norms and proposing a data-driven approach for sparse regularization in infinite dimensions.
Can neural operators always be continuously discretized?
Dec 04, 2024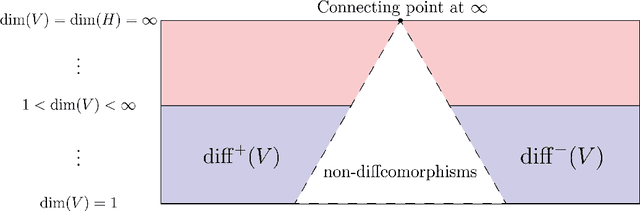
Abstract:We consider the problem of discretization of neural operators between Hilbert spaces in a general framework including skip connections. We focus on bijective neural operators through the lens of diffeomorphisms in infinite dimensions. Framed using category theory, we give a no-go theorem that shows that diffeomorphisms between Hilbert spaces or Hilbert manifolds may not admit any continuous approximations by diffeomorphisms on finite-dimensional spaces, even if the approximations are nonlinear. The natural way out is the introduction of strongly monotone diffeomorphisms and layerwise strongly monotone neural operators which have continuous approximations by strongly monotone diffeomorphisms on finite-dimensional spaces. For these, one can guarantee discretization invariance, while ensuring that finite-dimensional approximations converge not only as sequences of functions, but that their representations converge in a suitable sense as well. Finally, we show that bilipschitz neural operators may always be written in the form of an alternating composition of strongly monotone neural operators, plus a simple isometry. Thus we realize a rigorous platform for discretization of a generalization of a neural operator. We also show that neural operators of this type may be approximated through the composition of finite-rank residual neural operators, where each block is strongly monotone, and may be inverted locally via iteration. We conclude by providing a quantitative approximation result for the discretization of general bilipschitz neural operators.
Reducing the cost of posterior sampling in linear inverse problems via task-dependent score learning
May 24, 2024

Abstract:Score-based diffusion models (SDMs) offer a flexible approach to sample from the posterior distribution in a variety of Bayesian inverse problems. In the literature, the prior score is utilized to sample from the posterior by different methods that require multiple evaluations of the forward mapping in order to generate a single posterior sample. These methods are often designed with the objective of enabling the direct use of the unconditional prior score and, therefore, task-independent training. In this paper, we focus on linear inverse problems, when evaluation of the forward mapping is computationally expensive and frequent posterior sampling is required for new measurement data, such as in medical imaging. We demonstrate that the evaluation of the forward mapping can be entirely bypassed during posterior sample generation. Instead, without introducing any error, the computational effort can be shifted to an offline task of training the score of a specific diffusion-like random process. In particular, the training is task-dependent requiring information about the forward mapping but not about the measurement data. It is shown that the conditional score corresponding to the posterior can be obtained from the auxiliary score by suitable affine transformations. We prove that this observation generalizes to the framework of infinite-dimensional diffusion models introduced recently and provide numerical analysis of the method. Moreover, we validate our findings with numerical experiments.
Mixture of Experts Soften the Curse of Dimensionality in Operator Learning
Apr 13, 2024
Abstract:In this paper, we construct a mixture of neural operators (MoNOs) between function spaces whose complexity is distributed over a network of expert neural operators (NOs), with each NO satisfying parameter scaling restrictions. Our main result is a \textit{distributed} universal approximation theorem guaranteeing that any Lipschitz non-linear operator between $L^2([0,1]^d)$ spaces can be approximated uniformly over the Sobolev unit ball therein, to any given $\varepsilon>0$ accuracy, by an MoNO while satisfying the constraint that: each expert NO has a depth, width, and rank of $\mathcal{O}(\varepsilon^{-1})$. Naturally, our result implies that the required number of experts must be large, however, each NO is guaranteed to be small enough to be loadable into the active memory of most computers for reasonable accuracies $\varepsilon$. During our analysis, we also obtain new quantitative expression rates for classical NOs approximating uniformly continuous non-linear operators uniformly on compact subsets of $L^2([0,1]^d)$.
TILT: topological interface recovery in limited-angle tomography
Oct 25, 2023



Abstract:A novel reconstruction method is introduced for the severely ill-posed inverse problem of limited-angle tomography. It is well known that, depending on the available measurement, angles specify a subset of the wavefront set of the unknown target, while some oriented singularities remain invisible in the data. Topological Interface recovery for Limited-angle Tomography, or TILT, is based on lifting the visible part of the wavefront set under a universal covering map. In the space provided, it is possible to connect the appropriate pieces of the lifted wavefront set correctly using dual-tree complex wavelets, a dedicated metric, and persistent homology. The result is not only a suggested invisible boundary but also a computational representation for all interfaces in the target.
Globally injective and bijective neural operators
Jun 06, 2023Abstract:Recently there has been great interest in operator learning, where networks learn operators between function spaces from an essentially infinite-dimensional perspective. In this work we present results for when the operators learned by these networks are injective and surjective. As a warmup, we combine prior work in both the finite-dimensional ReLU and operator learning setting by giving sharp conditions under which ReLU layers with linear neural operators are injective. We then consider the case the case when the activation function is pointwise bijective and obtain sufficient conditions for the layer to be injective. We remark that this question, while trivial in the finite-rank case, is subtler in the infinite-rank case and is proved using tools from Fredholm theory. Next, we prove that our supplied injective neural operators are universal approximators and that their implementation, with finite-rank neural networks, are still injective. This ensures that injectivity is not `lost' in the transcription from analytical operators to their finite-rank implementation with networks. Finally, we conclude with an increase in abstraction and consider general conditions when subnetworks, which may be many layers deep, are injective and surjective and provide an exact inversion from a `linearization.' This section uses general arguments from Fredholm theory and Leray-Schauder degree theory for non-linear integral equations to analyze the mapping properties of neural operators in function spaces. These results apply to subnetworks formed from the layers considered in this work, under natural conditions. We believe that our work has applications in Bayesian UQ where injectivity enables likelihood estimation and in inverse problems where surjectivity and injectivity corresponds to existence and uniqueness, respectively.
A Transfer Principle: Universal Approximators Between Metric Spaces From Euclidean Universal Approximators
Apr 24, 2023Abstract:We build universal approximators of continuous maps between arbitrary Polish metric spaces $\mathcal{X}$ and $\mathcal{Y}$ using universal approximators between Euclidean spaces as building blocks. Earlier results assume that the output space $\mathcal{Y}$ is a topological vector space. We overcome this limitation by "randomization": our approximators output discrete probability measures over $\mathcal{Y}$. When $\mathcal{X}$ and $\mathcal{Y}$ are Polish without additional structure, we prove very general qualitative guarantees; when they have suitable combinatorial structure, we prove quantitative guarantees for H\"older-like maps, including maps between finite graphs, solution operators to rough differential equations between certain Carnot groups, and continuous non-linear operators between Banach spaces arising in inverse problems. In particular, we show that the required number of Dirac measures is determined by the combinatorial structure of $\mathcal{X}$ and $\mathcal{Y}$. For barycentric $\mathcal{Y}$, including Banach spaces, $\mathbb{R}$-trees, Hadamard manifolds, or Wasserstein spaces on Polish metric spaces, our approximators reduce to $\mathcal{Y}$-valued functions. When the Euclidean approximators are neural networks, our constructions generalize transformer networks, providing a new probabilistic viewpoint of geometric deep learning.
Deep Invertible Approximation of Topologically Rich Maps between Manifolds
Oct 02, 2022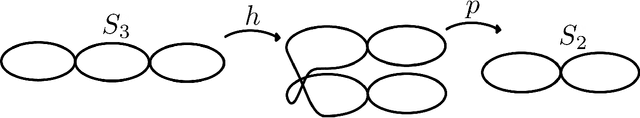
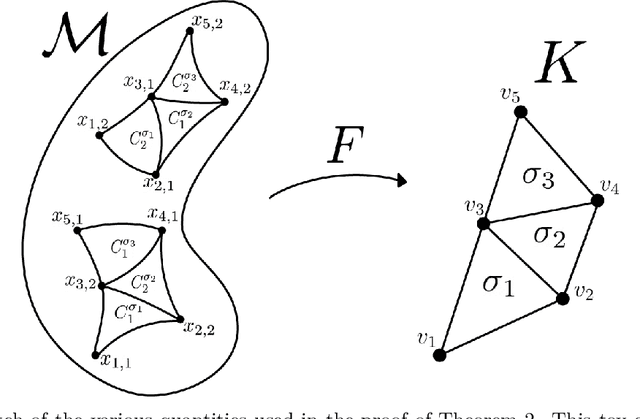
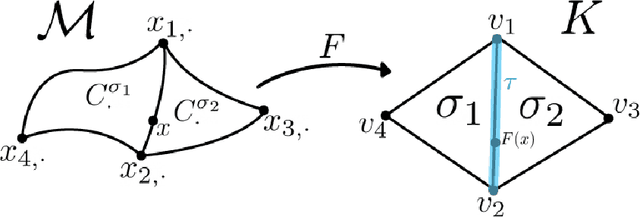
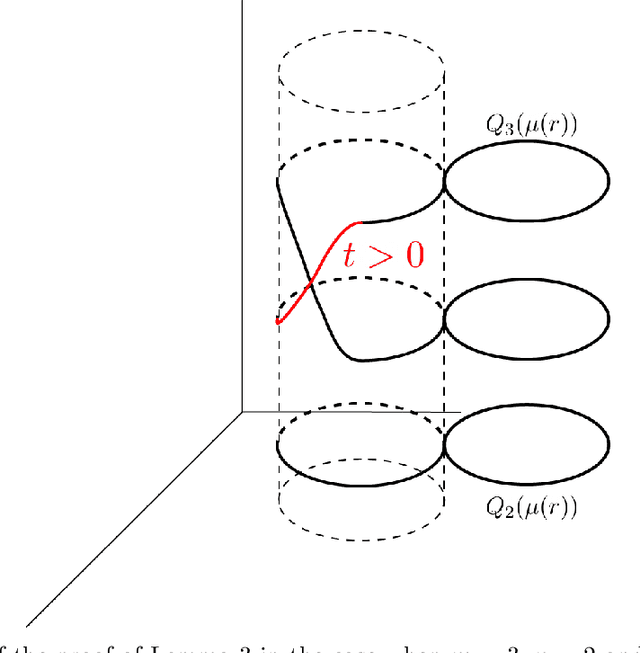
Abstract:How can we design neural networks that allow for stable universal approximation of maps between topologically interesting manifolds? The answer is with a coordinate projection. Neural networks based on topological data analysis (TDA) use tools such as persistent homology to learn topological signatures of data and stabilize training but may not be universal approximators or have stable inverses. Other architectures universally approximate data distributions on submanifolds but only when the latter are given by a single chart, making them unable to learn maps that change topology. By exploiting the topological parallels between locally bilipschitz maps, covering spaces, and local homeomorphisms, and by using universal approximation arguments from machine learning, we find that a novel network of the form $\mathcal{T} \circ p \circ \mathcal{E}$, where $\mathcal{E}$ is an injective network, $p$ a fixed coordinate projection, and $\mathcal{T}$ a bijective network, is a universal approximator of local diffeomorphisms between compact smooth submanifolds embedded in $\mathbb{R}^n$. We emphasize the case when the target map changes topology. Further, we find that by constraining the projection $p$, multivalued inversions of our networks can be computed without sacrificing universality. As an application, we show that learning a group invariant function with unknown group action naturally reduces to the question of learning local diffeomorphisms for finite groups. Our theory permits us to recover orbits of the group action. We also outline possible extensions of our architecture to address molecular imaging of molecules with symmetries. Finally, our analysis informs the choice of topologically expressive starting spaces in generative problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge