Matthew Maciejewski
Improving Neural Diarization through Speaker Attribute Attractors and Local Dependency Modeling
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:In recent years, end-to-end approaches have made notable progress in addressing the challenge of speaker diarization, which involves segmenting and identifying speakers in multi-talker recordings. One such approach, Encoder-Decoder Attractors (EDA), has been proposed to handle variable speaker counts as well as better guide the network during training. In this study, we extend the attractor paradigm by moving beyond direct speaker modeling and instead focus on representing more detailed `speaker attributes' through a multi-stage process of intermediate representations. Additionally, we enhance the architecture by replacing transformers with conformers, a convolution-augmented transformer, to model local dependencies. Experiments demonstrate improved diarization performance on the CALLHOME dataset.
The CHiME-8 DASR Challenge for Generalizable and Array Agnostic Distant Automatic Speech Recognition and Diarization
Jul 23, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents the CHiME-8 DASR challenge which carries on from the previous edition CHiME-7 DASR (C7DASR) and the past CHiME-6 challenge. It focuses on joint multi-channel distant speech recognition (DASR) and diarization with one or more, possibly heterogeneous, devices. The main goal is to spur research towards meeting transcription approaches that can generalize across arbitrary number of speakers, diverse settings (formal vs. informal conversations), meeting duration, wide-variety of acoustic scenarios and different recording configurations. Novelties with respect to C7DASR include: i) the addition of NOTSOFAR-1, an additional office/corporate meeting scenario, ii) a manually corrected Mixer 6 development set, iii) a new track in which we allow the use of large-language models (LLM) iv) a jury award mechanism to encourage participants to explore also more practical and innovative solutions. To lower the entry barrier for participants, we provide a standalone toolkit for downloading and preparing such datasets as well as performing text normalization and scoring their submissions. Furthermore, this year we also provide two baseline systems, one directly inherited from C7DASR and based on ESPnet and another one developed on NeMo and based on NeMo team submission in last year C7DASR. Baseline system results suggest that the addition of the NOTSOFAR-1 scenario significantly increases the task's difficulty due to its high number of speakers and very short duration.
On Speaker Attribution with SURT
Jan 28, 2024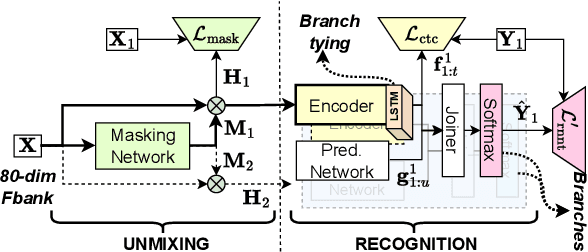
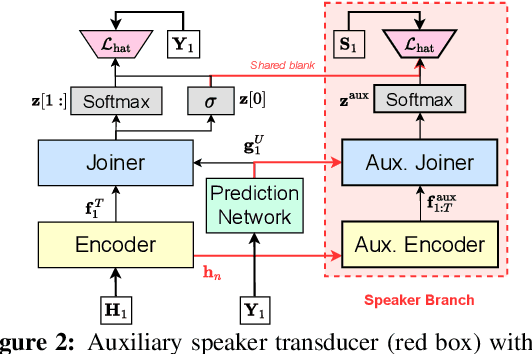

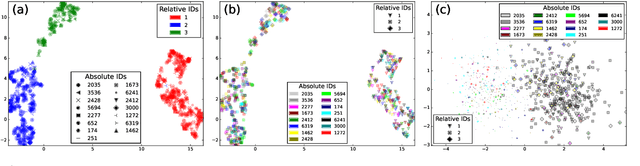
Abstract:The Streaming Unmixing and Recognition Transducer (SURT) has recently become a popular framework for continuous, streaming, multi-talker speech recognition (ASR). With advances in architecture, objectives, and mixture simulation methods, it was demonstrated that SURT can be an efficient streaming method for speaker-agnostic transcription of real meetings. In this work, we push this framework further by proposing methods to perform speaker-attributed transcription with SURT, for both short mixtures and long recordings. We achieve this by adding an auxiliary speaker branch to SURT, and synchronizing its label prediction with ASR token prediction through HAT-style blank factorization. In order to ensure consistency in relative speaker labels across different utterance groups in a recording, we propose "speaker prefixing" -- appending each chunk with high-confidence frames of speakers identified in previous chunks, to establish the relative order. We perform extensive ablation experiments on synthetic LibriSpeech mixtures to validate our design choices, and demonstrate the efficacy of our final model on the AMI corpus.
The CHiME-7 DASR Challenge: Distant Meeting Transcription with Multiple Devices in Diverse Scenarios
Jul 14, 2023



Abstract:The CHiME challenges have played a significant role in the development and evaluation of robust automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. We introduce the CHiME-7 distant ASR (DASR) task, within the 7th CHiME challenge. This task comprises joint ASR and diarization in far-field settings with multiple, and possibly heterogeneous, recording devices. Different from previous challenges, we evaluate systems on 3 diverse scenarios: CHiME-6, DiPCo, and Mixer 6. The goal is for participants to devise a single system that can generalize across different array geometries and use cases with no a-priori information. Another departure from earlier CHiME iterations is that participants are allowed to use open-source pre-trained models and datasets. In this paper, we describe the challenge design, motivation, and fundamental research questions in detail. We also present the baseline system, which is fully array-topology agnostic and features multi-channel diarization, channel selection, guided source separation and a robust ASR model that leverages self-supervised speech representations (SSLR).
Building Corpora for Single-Channel Speech Separation Across Multiple Domains
Nov 06, 2018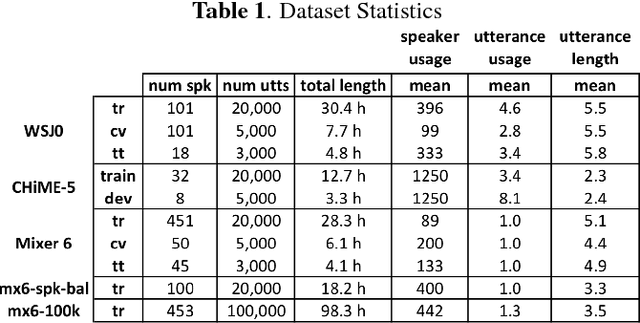
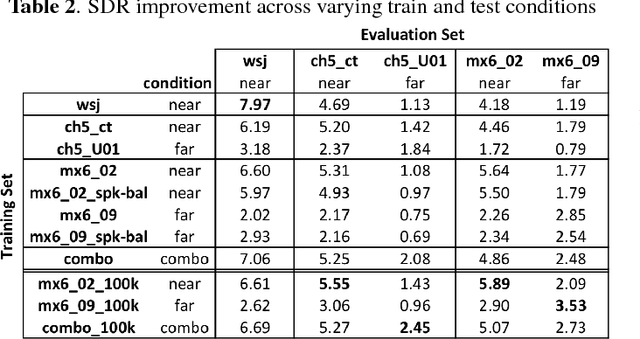
Abstract:To date, the bulk of research on single-channel speech separation has been conducted using clean, near-field, read speech, which is not representative of many modern applications. In this work, we develop a procedure for constructing high-quality synthetic overlap datasets, necessary for most deep learning-based separation frameworks. We produced datasets that are more representative of realistic applications using the CHiME-5 and Mixer 6 corpora and evaluate standard methods on this data to demonstrate the shortcomings of current source-separation performance. We also demonstrate the value of a wide variety of data in training robust models that generalize well to multiple conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge