Steve Huang
The CHiME-8 DASR Challenge for Generalizable and Array Agnostic Distant Automatic Speech Recognition and Diarization
Jul 23, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents the CHiME-8 DASR challenge which carries on from the previous edition CHiME-7 DASR (C7DASR) and the past CHiME-6 challenge. It focuses on joint multi-channel distant speech recognition (DASR) and diarization with one or more, possibly heterogeneous, devices. The main goal is to spur research towards meeting transcription approaches that can generalize across arbitrary number of speakers, diverse settings (formal vs. informal conversations), meeting duration, wide-variety of acoustic scenarios and different recording configurations. Novelties with respect to C7DASR include: i) the addition of NOTSOFAR-1, an additional office/corporate meeting scenario, ii) a manually corrected Mixer 6 development set, iii) a new track in which we allow the use of large-language models (LLM) iv) a jury award mechanism to encourage participants to explore also more practical and innovative solutions. To lower the entry barrier for participants, we provide a standalone toolkit for downloading and preparing such datasets as well as performing text normalization and scoring their submissions. Furthermore, this year we also provide two baseline systems, one directly inherited from C7DASR and based on ESPnet and another one developed on NeMo and based on NeMo team submission in last year C7DASR. Baseline system results suggest that the addition of the NOTSOFAR-1 scenario significantly increases the task's difficulty due to its high number of speakers and very short duration.
Instruction Data Generation and Unsupervised Adaptation for Speech Language Models
Jun 18, 2024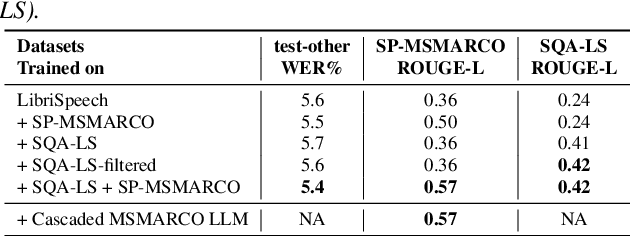
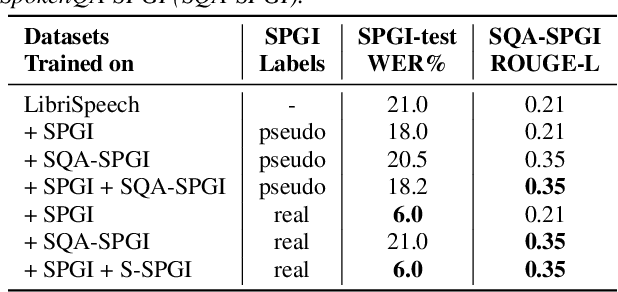

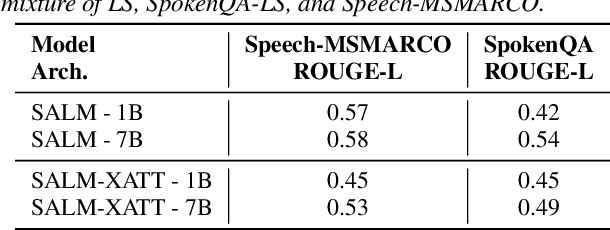
Abstract:In this paper, we propose three methods for generating synthetic samples to train and evaluate multimodal large language models capable of processing both text and speech inputs. Addressing the scarcity of samples containing both modalities, synthetic data generation emerges as a crucial strategy to enhance the performance of such systems and facilitate the modeling of cross-modal relationships between the speech and text domains. Our process employs large language models to generate textual components and text-to-speech systems to generate speech components. The proposed methods offer a practical and effective means to expand the training dataset for these models. Experimental results show progress in achieving an integrated understanding of text and speech. We also highlight the potential of using unlabeled speech data to generate synthetic samples comparable in quality to those with available transcriptions, enabling the expansion of these models to more languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge