Maria J. Ledesma-Carbayo
Mask-HybridGNet: Graph-based segmentation with emergent anatomical correspondence from pixel-level supervision
Feb 24, 2026Abstract:Graph-based medical image segmentation represents anatomical structures using boundary graphs, providing fixed-topology landmarks and inherent population-level correspondences. However, their clinical adoption has been hindered by a major requirement: training datasets with manually annotated landmarks that maintain point-to-point correspondences across patients rarely exist in practice. We introduce Mask-HybridGNet, a framework that trains graph-based models directly using standard pixel-wise masks, eliminating the need for manual landmark annotations. Our approach aligns variable-length ground truth boundaries with fixed-length landmark predictions by combining Chamfer distance supervision and edge-based regularization to ensure local smoothness and regular landmark distribution, further refined via differentiable rasterization. A significant emergent property of this framework is that predicted landmark positions become consistently associated with specific anatomical locations across patients without explicit correspondence supervision. This implicit atlas learning enables temporal tracking, cross-slice reconstruction, and morphological population analyses. Beyond direct segmentation, Mask-HybridGNet can extract correspondences from existing segmentation masks, allowing it to generate stable anatomical atlases from any high-quality pixel-based model. Experiments across chest radiography, cardiac ultrasound, cardiac MRI, and fetal imaging demonstrate that our model achieves competitive results against state-of-the-art pixel-based methods, while ensuring anatomical plausibility by enforcing boundary connectivity through a fixed graph adjacency matrix. This framework leverages the vast availability of standard segmentation masks to build structured models that maintain topological integrity and provide implicit correspondences.
FeTTL: Federated Template and Task Learning for Multi-Institutional Medical Imaging
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Federated learning enables collaborative model training across geographically distributed medical centers while preserving data privacy. However, domain shifts and heterogeneity in data often lead to a degradation in model performance. Medical imaging applications are particularly affected by variations in acquisition protocols, scanner types, and patient populations. To address these issues, we introduce Federated Template and Task Learning (FeTTL), a novel framework designed to harmonize multi-institutional medical imaging data in federated environments. FeTTL learns a global template together with a task model to align data distributions among clients. We evaluated FeTTL on two challenging and diverse multi-institutional medical imaging tasks: retinal fundus optical disc segmentation and histopathological metastasis classification. Experimental results show that FeTTL significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art federated learning baselines (p-values <0.002) for optical disc segmentation and classification of metastases from multi-institutional data. Our experiments further highlight the importance of jointly learning the template and the task. These findings suggest that FeTTL offers a principled and extensible solution for mitigating distribution shifts in federated learning, supporting robust model deployment in real-world, multi-institutional environments.
Model Ensemble for Brain Tumor Segmentation in Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Sep 12, 2024



Abstract:Segmenting brain tumors in multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging enables performing quantitative analysis in support of clinical trials and personalized patient care. This analysis provides the potential to impact clinical decision-making processes, including diagnosis and prognosis. In 2023, the well-established Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) challenge presented a substantial expansion with eight tasks and 4,500 brain tumor cases. In this paper, we present a deep learning-based ensemble strategy that is evaluated for newly included tumor cases in three tasks: pediatric brain tumors (PED), intracranial meningioma (MEN), and brain metastases (MET). In particular, we ensemble outputs from state-of-the-art nnU-Net and Swin UNETR models on a region-wise basis. Furthermore, we implemented a targeted post-processing strategy based on a cross-validated threshold search to improve the segmentation results for tumor sub-regions. The evaluation of our proposed method on unseen test cases for the three tasks resulted in lesion-wise Dice scores for PED: 0.653, 0.809, 0.826; MEN: 0.876, 0.867, 0.849; and MET: 0.555, 0.6, 0.58; for the enhancing tumor, tumor core, and whole tumor, respectively. Our method was ranked first for PED, third for MEN, and fourth for MET, respectively.
DiCoM -- Diverse Concept Modeling towards Enhancing Generalizability in Chest X-Ray Studies
Feb 22, 2024Abstract:Chest X-Ray (CXR) is a widely used clinical imaging modality and has a pivotal role in the diagnosis and prognosis of various lung and heart related conditions. Conventional automated clinical diagnostic tool design strategies relying on radiology reads and supervised learning, entail the cumbersome requirement of high quality annotated training data. To address this challenge, self-supervised pre-training has proven to outperform supervised pre-training in numerous downstream vision tasks, representing a significant breakthrough in the field. However, medical imaging pre-training significantly differs from pre-training with natural images (e.g., ImageNet) due to unique attributes of clinical images. In this context, we introduce Diverse Concept Modeling (DiCoM), a novel self-supervised training paradigm that leverages a student teacher framework for learning diverse concepts and hence effective representation of the CXR data. Hence, expanding beyond merely modeling a single primary label within an image, instead, effectively harnessing the information from all the concepts inherent in the CXR. The pre-trained model is subsequently fine-tuned to address diverse domain-specific tasks. Our proposed paradigm consistently demonstrates robust performance across multiple downstream tasks on multiple datasets, highlighting the success and generalizability of the pre-training strategy. To establish the efficacy of our methods we analyze both the power of learned representations and the speed of convergence (SoC) of our models. For diverse data and tasks, DiCoM is able to achieve in most cases better results compared to other state-of-the-art pre-training strategies. This when combined with the higher SoC and generalization capabilities positions DiCoM to be established as a foundation model for CXRs, a widely used imaging modality.
Deep learning-based lung segmentation and automatic regional template in chest X-ray images for pediatric tuberculosis
Jan 31, 2023Abstract:Tuberculosis (TB) is still considered a leading cause of death and a substantial threat to global child health. Both TB infection and disease are curable using antibiotics. However, most children who die of TB are never diagnosed or treated. In clinical practice, experienced physicians assess TB by examining chest X-rays (CXR). Pediatric CXR has specific challenges compared to adult CXR, which makes TB diagnosis in children more difficult. Computer-aided diagnosis systems supported by Artificial Intelligence have shown performance comparable to experienced radiologist TB readings, which could ease mass TB screening and reduce clinical burden. We propose a multi-view deep learning-based solution which, by following a proposed template, aims to automatically regionalize and extract lung and mediastinal regions of interest from pediatric CXR images where key TB findings may be present. Experimental results have shown accurate region extraction, which can be used for further analysis to confirm TB finding presence and severity assessment. Code publicly available at https://github.com/dani-capellan/pTB_LungRegionExtractor.
Computer Aided Detection for Pulmonary Embolism Challenge (CAD-PE)
Mar 30, 2020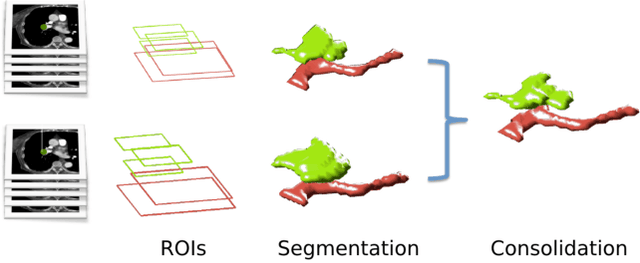
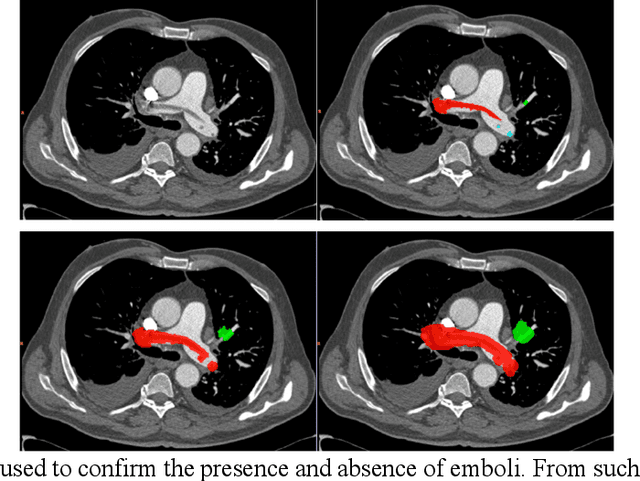
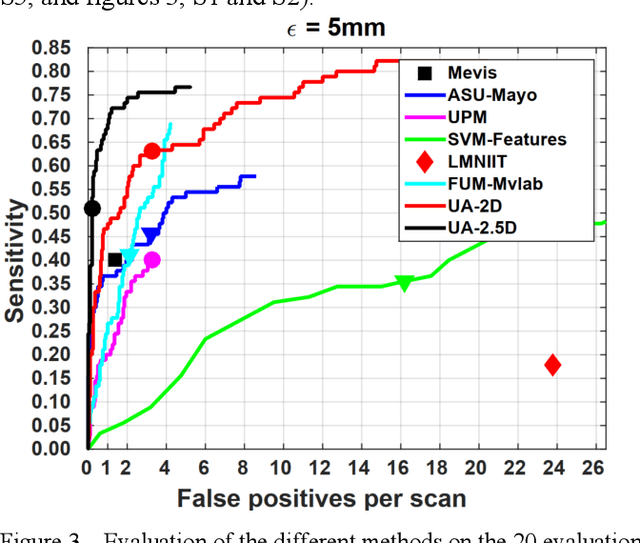
Abstract:Rationale: Computer aided detection (CAD) algorithms for Pulmonary Embolism (PE) algorithms have been shown to increase radiologists' sensitivity with a small increase in specificity. However, CAD for PE has not been adopted into clinical practice, likely because of the high number of false positives current CAD software produces. Objective: To generate a database of annotated computed tomography pulmonary angiographies, use it to compare the sensitivity and false positive rate of current algorithms and to develop new methods that improve such metrics. Methods: 91 Computed tomography pulmonary angiography scans were annotated by at least one radiologist by segmenting all pulmonary emboli visible on the study. 20 annotated CTPAs were open to the public in the form of a medical image analysis challenge. 20 more were kept for evaluation purposes. 51 were made available post-challenge. 8 submissions, 6 of them novel, were evaluated on the 20 evaluation CTPAs. Performance was measured as per embolus sensitivity vs. false positives per scan curve. Results: The best algorithms achieved a per-embolus sensitivity of 75% at 2 false positives per scan (fps) or of 70% at 1 fps, outperforming the state of the art. Deep learning approaches outperformed traditional machine learning ones, and their performance improved with the number of training cases. Significance: Through this work and challenge we have improved the state-of-the art of computer aided detection algorithms for pulmonary embolism. An open database and an evaluation benchmark for such algorithms have been generated, easing the development of further improvements. Implications on clinical practice will need further research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge