Syed Muhammad Anwar
FeTTL: Federated Template and Task Learning for Multi-Institutional Medical Imaging
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Federated learning enables collaborative model training across geographically distributed medical centers while preserving data privacy. However, domain shifts and heterogeneity in data often lead to a degradation in model performance. Medical imaging applications are particularly affected by variations in acquisition protocols, scanner types, and patient populations. To address these issues, we introduce Federated Template and Task Learning (FeTTL), a novel framework designed to harmonize multi-institutional medical imaging data in federated environments. FeTTL learns a global template together with a task model to align data distributions among clients. We evaluated FeTTL on two challenging and diverse multi-institutional medical imaging tasks: retinal fundus optical disc segmentation and histopathological metastasis classification. Experimental results show that FeTTL significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art federated learning baselines (p-values <0.002) for optical disc segmentation and classification of metastases from multi-institutional data. Our experiments further highlight the importance of jointly learning the template and the task. These findings suggest that FeTTL offers a principled and extensible solution for mitigating distribution shifts in federated learning, supporting robust model deployment in real-world, multi-institutional environments.
MRI-to-CT Synthesis With Cranial Suture Segmentations Using A Variational Autoencoder Framework
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Quantifying normative pediatric cranial development and suture ossification is crucial for diagnosing and treating growth-related cephalic disorders. Computed tomography (CT) is widely used to evaluate cranial and sutural deformities; however, its ionizing radiation is contraindicated in children without significant abnormalities. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) offers radiation free scans with superior soft tissue contrast, but unlike CT, MRI cannot elucidate cranial sutures, estimate skull bone density, or assess cranial vault growth. This study proposes a deep learning driven pipeline for transforming T1 weighted MRIs of children aged 0.2 to 2 years into synthetic CTs (sCTs), predicting detailed cranial bone segmentation, generating suture probability heatmaps, and deriving direct suture segmentation from the heatmaps. With our in-house pediatric data, sCTs achieved 99% structural similarity and a Frechet inception distance of 1.01 relative to real CTs. Skull segmentation attained an average Dice coefficient of 85% across seven cranial bones, and sutures achieved 80% Dice. Equivalence of skull and suture segmentation between sCTs and real CTs was confirmed using two one sided tests (TOST p < 0.05). To our knowledge, this is the first pediatric cranial CT synthesis framework to enable suture segmentation on sCTs derived from MRI, despite MRI's limited depiction of bone and sutures. By combining robust, domain specific variational autoencoders, our method generates perceptually indistinguishable cranial sCTs from routine pediatric MRIs, bridging critical gaps in non invasive cranial evaluation.
Foundation Models in Biomedical Imaging: Turning Hype into Reality
Dec 17, 2025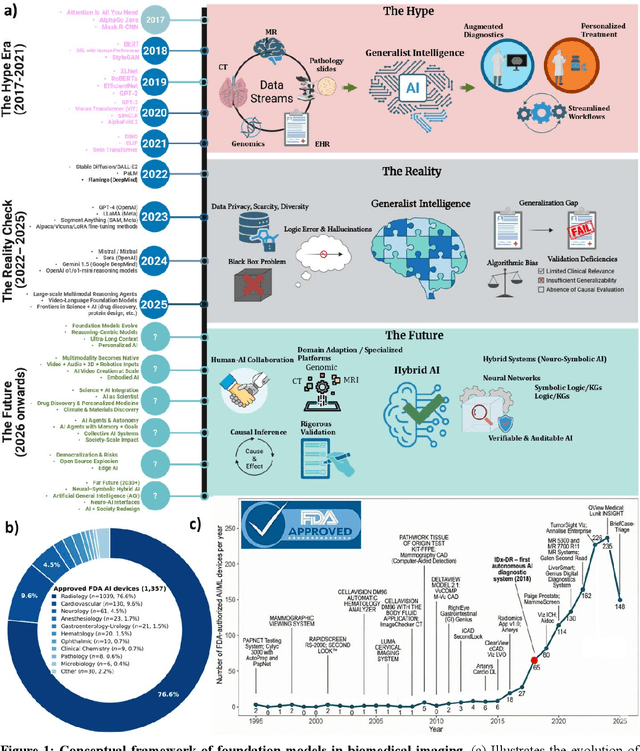
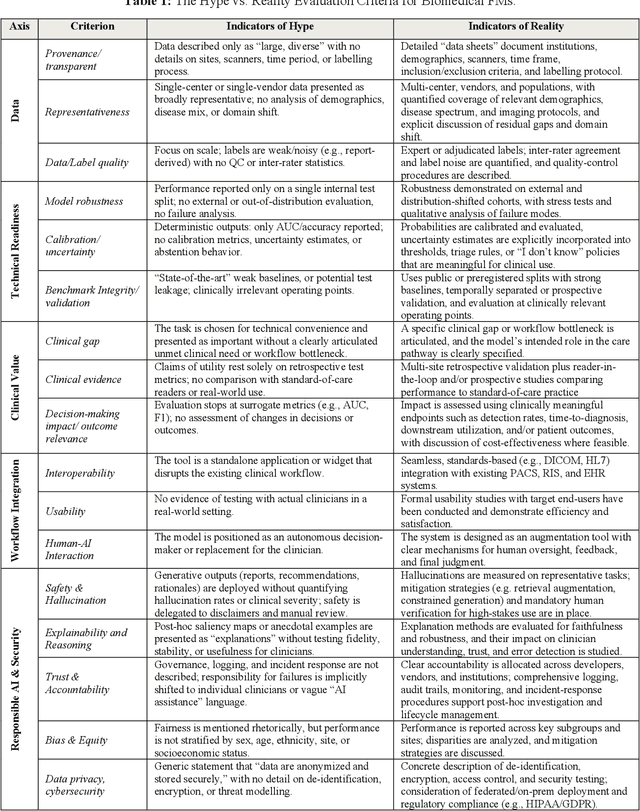
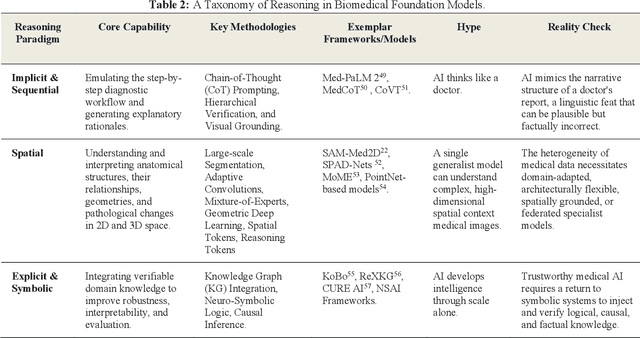
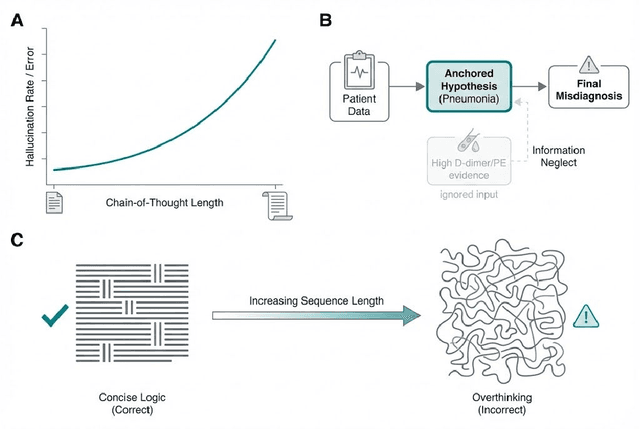
Abstract:Foundation models (FMs) are driving a prominent shift in artificial intelligence across different domains, including biomedical imaging. These models are designed to move beyond narrow pattern recognition towards emulating sophisticated clinical reasoning, understanding complex spatial relationships, and integrating multimodal data with unprecedented flexibility. However, a critical gap exists between this potential and the current reality, where the clinical evaluation and deployment of FMs are hampered by significant challenges. Herein, we critically assess the current state-of-the-art, analyzing hype by examining the core capabilities and limitations of FMs in the biomedical domain. We also provide a taxonomy of reasoning, ranging from emulated sequential logic and spatial understanding to the integration of explicit symbolic knowledge, to evaluate whether these models exhibit genuine cognition or merely mimic surface-level patterns. We argue that a critical frontier lies beyond statistical correlation, in the pursuit of causal inference, which is essential for building robust models that understand cause and effect. Furthermore, we discuss the paramount issues in deployment stemming from trustworthiness, bias, and safety, dissecting the challenges of algorithmic bias, data bias and privacy, and model hallucinations. We also draw attention to the need for more inclusive, rigorous, and clinically relevant validation frameworks to ensure their safe and ethical application. We conclude that while the vision of autonomous AI-doctors remains distant, the immediate reality is the emergence of powerful technology and assistive tools that would benefit clinical practice. The future of FMs in biomedical imaging hinges not on scale alone, but on developing hybrid, causally aware, and verifiably safe systems that augment, rather than replace, human expertise.
Improving Pre-trained Segmentation Models using Post-Processing
Dec 16, 2025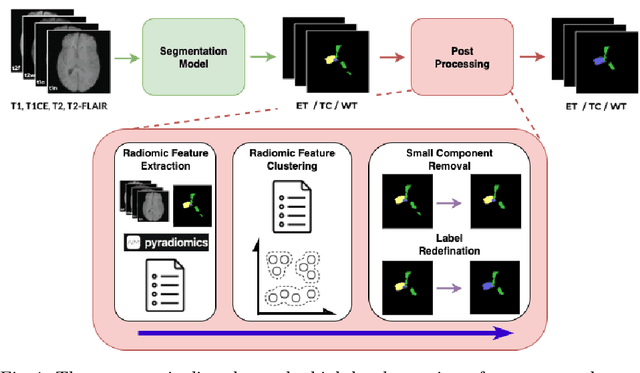
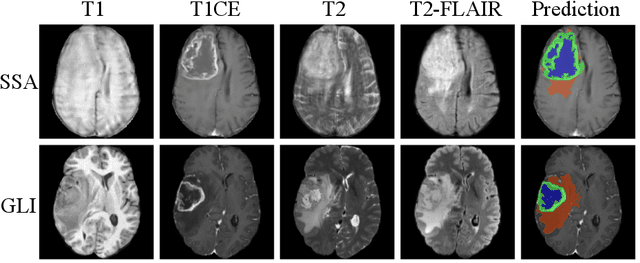
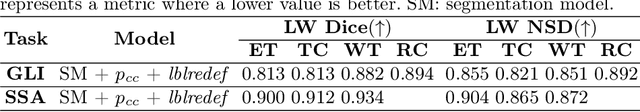
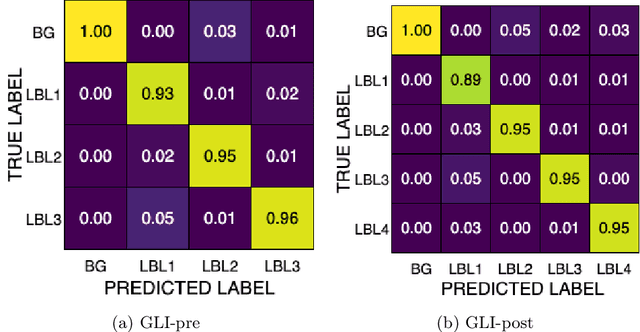
Abstract:Gliomas are the most common malignant brain tumors in adults and are among the most lethal. Despite aggressive treatment, the median survival rate is less than 15 months. Accurate multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) tumor segmentation is critical for surgical planning, radiotherapy, and disease monitoring. While deep learning models have improved the accuracy of automated segmentation, large-scale pre-trained models generalize poorly and often underperform, producing systematic errors such as false positives, label swaps, and slice discontinuities in slices. These limitations are further compounded by unequal access to GPU resources and the growing environmental cost of large-scale model training. In this work, we propose adaptive post-processing techniques to refine the quality of glioma segmentations produced by large-scale pretrained models developed for various types of tumors. We demonstrated the techniques in multiple BraTS 2025 segmentation challenge tasks, with the ranking metric improving by 14.9 % for the sub-Saharan Africa challenge and 0.9% for the adult glioma challenge. This approach promotes a shift in brain tumor segmentation research from increasingly complex model architectures to efficient, clinically aligned post-processing strategies that are precise, computationally fair, and sustainable.
Adaptable Segmentation Pipeline for Diverse Brain Tumors with Radiomic-guided Subtyping and Lesion-Wise Model Ensemble
Dec 16, 2025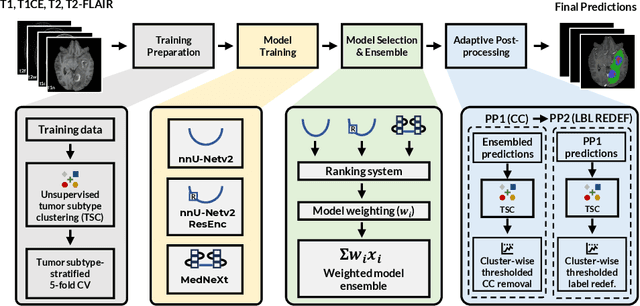
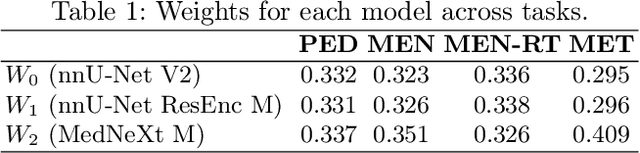
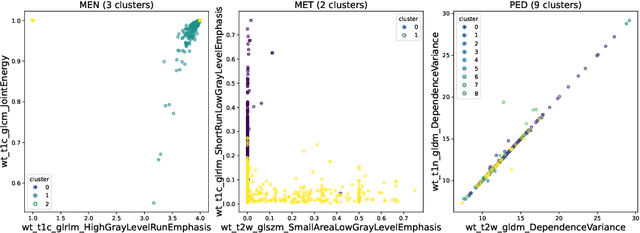
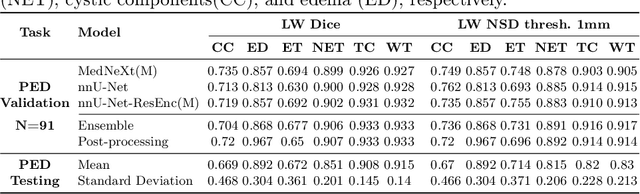
Abstract:Robust and generalizable segmentation of brain tumors on multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) remains difficult because tumor types differ widely. The BraTS 2025 Lighthouse Challenge benchmarks segmentation methods on diverse high-quality datasets of adult and pediatric tumors: multi-consortium international pediatric brain tumor segmentation (PED), preoperative meningioma tumor segmentation (MEN), meningioma radiotherapy segmentation (MEN-RT), and segmentation of pre- and post-treatment brain metastases (MET). We present a flexible, modular, and adaptable pipeline that improves segmentation performance by selecting and combining state-of-the-art models and applying tumor- and lesion-specific processing before and after training. Radiomic features extracted from MRI help detect tumor subtype, ensuring a more balanced training. Custom lesion-level performance metrics determine the influence of each model in the ensemble and optimize post-processing that further refines the predictions, enabling the workflow to tailor every step to each case. On the BraTS testing sets, our pipeline achieved performance comparable to top-ranked algorithms across multiple challenges. These findings confirm that custom lesion-aware processing and model selection yield robust segmentations yet without locking the method to a specific network architecture. Our method has the potential for quantitative tumor measurement in clinical practice, supporting diagnosis and prognosis.
Dual-Task Graph Neural Network for Joint Seizure Onset Zone Localization and Outcome Prediction using Stereo EEG
May 29, 2025Abstract:Accurately localizing the brain regions that triggers seizures and predicting whether a patient will be seizure-free after surgery are vital for surgical planning and patient management in drug-resistant epilepsy. Stereo-electroencephalography (sEEG) delivers high-fidelity intracranial recordings that enable clinicians to precisely locate epileptogenic networks. However, the clinical identification is subjective and dependent on the expertise of the clinical team. Data driven approaches in this domain are sparse, despite the fact that sEEG offers high temporal-fidelity related to seizure dynamics that can be leveraged using graph structures ideal for imitating brain networks. In this study, we introduce a dual-task graph-neural network (GNN) framework that operates on windowed sEEG recordings to jointly predict seizure-freedom outcomes and identify seizure-onset-zone (SOZ) channels. We assemble non-overlapping 10 second windows from 51 clinical seizures spread across 20 pediatric patients, with sEEG data annotated by clinical experts. For each temporal window we construct a functional connectivity graph via thresholded Pearson correlations and extract rich node features (spectral, statistical, wavelet, Hjorth and local graph features), alongside six global graph descriptors. We optimize a combined cross-entropy loss with a tunable task-weight, and select model hyper-parameters via Optuna. Under window-level 10-fold cross-validation, the model achieves a mean graph-level accuracy of $89.31 \pm 0.0976 \%$ for seizure-freedom prediction and a node-level SOZ localization accuracy of $94.72. \pm 0.0041 \%$. For the best performing model, we ran additive and leave-one-out ablation studies to explore feature importance for graph and node-level accuracy.
Analysis of the MICCAI Brain Tumor Segmentation -- Metastases (BraTS-METS) 2025 Lighthouse Challenge: Brain Metastasis Segmentation on Pre- and Post-treatment MRI
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Despite continuous advancements in cancer treatment, brain metastatic disease remains a significant complication of primary cancer and is associated with an unfavorable prognosis. One approach for improving diagnosis, management, and outcomes is to implement algorithms based on artificial intelligence for the automated segmentation of both pre- and post-treatment MRI brain images. Such algorithms rely on volumetric criteria for lesion identification and treatment response assessment, which are still not available in clinical practice. Therefore, it is critical to establish tools for rapid volumetric segmentations methods that can be translated to clinical practice and that are trained on high quality annotated data. The BraTS-METS 2025 Lighthouse Challenge aims to address this critical need by establishing inter-rater and intra-rater variability in dataset annotation by generating high quality annotated datasets from four individual instances of segmentation by neuroradiologists while being recorded on video (two instances doing "from scratch" and two instances after AI pre-segmentation). This high-quality annotated dataset will be used for testing phase in 2025 Lighthouse challenge and will be publicly released at the completion of the challenge. The 2025 Lighthouse challenge will also release the 2023 and 2024 segmented datasets that were annotated using an established pipeline of pre-segmentation, student annotation, two neuroradiologists checking, and one neuroradiologist finalizing the process. It builds upon its previous edition by including post-treatment cases in the dataset. Using these high-quality annotated datasets, the 2025 Lighthouse challenge plans to test benchmark algorithms for automated segmentation of pre-and post-treatment brain metastases (BM), trained on diverse and multi-institutional datasets of MRI images obtained from patients with brain metastases.
Graph-Based Deep Learning on Stereo EEG for Predicting Seizure Freedom in Epilepsy Patients
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Predicting seizure freedom is essential for tailoring epilepsy treatment. But accurate prediction remains challenging with traditional methods, especially with diverse patient populations. This study developed a deep learning-based graph neural network (GNN) model to predict seizure freedom from stereo electroencephalography (sEEG) data in patients with refractory epilepsy. We utilized high-quality sEEG data from 15 pediatric patients to train a deep learning model that can accurately predict seizure freedom outcomes and advance understanding of brain connectivity at the seizure onset zone. Our model integrates local and global connectivity using graph convolutions with multi-scale attention mechanisms to capture connections between difficult-to-study regions such as the thalamus and motor regions. The model achieved an accuracy of 92.4% in binary class analysis, 86.6% in patient-wise analysis, and 81.4% in multi-class analysis. Node and edge-level feature analysis highlighted the anterior cingulate and frontal pole regions as key contributors to seizure freedom outcomes. The nodes identified by our model were also more likely to coincide with seizure onset zones. Our findings underscore the potential of new connectivity-based deep learning models such as GNNs for enhancing the prediction of seizure freedom, predicting seizure onset zones, connectivity analysis of the brain during seizure, as well as informing AI-assisted personalized epilepsy treatment planning.
Geometric Deep Learning for Automated Landmarking of Maxillary Arches on 3D Oral Scans from Newborns with Cleft Lip and Palate
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:Rapid advances in 3D model scanning have enabled the mass digitization of dental clay models. However, most clinicians and researchers continue to use manual morphometric analysis methods on these models such as landmarking. This is a significant step in treatment planning for craniomaxillofacial conditions. We aimed to develop and test a geometric deep learning model that would accurately and reliably label landmarks on a complicated and specialized patient population -- infants, as accurately as a human specialist without a large amount of training data. Our developed pipeline demonstrated an accuracy of 94.44% with an absolute mean error of 1.676 +/- 0.959 mm on a set of 100 models acquired from newborn babies with cleft lip and palate. Our proposed pipeline has the potential to serve as a fast, accurate, and reliable quantifier of maxillary arch morphometric features, as well as an integral step towards a future fully automated dental treatment pipeline.
Adult Glioma Segmentation in Sub-Saharan Africa using Transfer Learning on Stratified Finetuning Data
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Gliomas, a kind of brain tumor characterized by high mortality, present substantial diagnostic challenges in low- and middle-income countries, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa. This paper introduces a novel approach to glioma segmentation using transfer learning to address challenges in resource-limited regions with minimal and low-quality MRI data. We leverage pre-trained deep learning models, nnU-Net and MedNeXt, and apply a stratified fine-tuning strategy using the BraTS2023-Adult-Glioma and BraTS-Africa datasets. Our method exploits radiomic analysis to create stratified training folds, model training on a large brain tumor dataset, and transfer learning to the Sub-Saharan context. A weighted model ensembling strategy and adaptive post-processing are employed to enhance segmentation accuracy. The evaluation of our proposed method on unseen validation cases on the BraTS-Africa 2024 task resulted in lesion-wise mean Dice scores of 0.870, 0.865, and 0.926, for enhancing tumor, tumor core, and whole tumor regions and was ranked first for the challenge. Our approach highlights the ability of integrated machine-learning techniques to bridge the gap between the medical imaging capabilities of resource-limited countries and established developed regions. By tailoring our methods to a target population's specific needs and constraints, we aim to enhance diagnostic capabilities in isolated environments. Our findings underscore the importance of approaches like local data integration and stratification refinement to address healthcare disparities, ensure practical applicability, and enhance impact.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge