Marek Wodzinski
3-D Image-to-Image Fusion in Lightsheet Microscopy by Two-Step Adversarial Network: Contribution to the FuseMyCells Challenge
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Lightsheet microscopy is a powerful 3-D imaging technique that addresses limitations of traditional optical and confocal microscopy but suffers from a low penetration depth and reduced image quality at greater depths. Multiview lightsheet microscopy improves 3-D resolution by combining multiple views but simultaneously increasing the complexity and the photon budget, leading to potential photobleaching and phototoxicity. The FuseMyCells challenge, organized in conjunction with the IEEE ISBI 2025 conference, aims to benchmark deep learning-based solutions for fusing high-quality 3-D volumes from single 3-D views, potentially simplifying procedures and conserving the photon budget. In this work, we propose a contribution to the FuseMyCells challenge based on a two-step procedure. The first step processes a downsampled version of the image to capture the entire region of interest, while the second step uses a patch-based approach for high-resolution inference, incorporating adversarial loss to enhance visual outcomes. This method addresses challenges related to high data resolution, the necessity of global context, and the preservation of high-frequency details. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, highlighting its potential to improve 3-D image fusion quality and extend the capabilities of lightsheet microscopy. The average SSIM for the nucleus and membranes is greater than 0.85 and 0.91, respectively.
Multi-Class Segmentation of Aortic Branches and Zones in Computed Tomography Angiography: The AortaSeg24 Challenge
Feb 07, 2025



Abstract:Multi-class segmentation of the aorta in computed tomography angiography (CTA) scans is essential for diagnosing and planning complex endovascular treatments for patients with aortic dissections. However, existing methods reduce aortic segmentation to a binary problem, limiting their ability to measure diameters across different branches and zones. Furthermore, no open-source dataset is currently available to support the development of multi-class aortic segmentation methods. To address this gap, we organized the AortaSeg24 MICCAI Challenge, introducing the first dataset of 100 CTA volumes annotated for 23 clinically relevant aortic branches and zones. This dataset was designed to facilitate both model development and validation. The challenge attracted 121 teams worldwide, with participants leveraging state-of-the-art frameworks such as nnU-Net and exploring novel techniques, including cascaded models, data augmentation strategies, and custom loss functions. We evaluated the submitted algorithms using the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and Normalized Surface Distance (NSD), highlighting the approaches adopted by the top five performing teams. This paper presents the challenge design, dataset details, evaluation metrics, and an in-depth analysis of the top-performing algorithms. The annotated dataset, evaluation code, and implementations of the leading methods are publicly available to support further research. All resources can be accessed at https://aortaseg24.grand-challenge.org.
Automatic Skull Reconstruction by Deep Learnable Symmetry Enforcement
Nov 26, 2024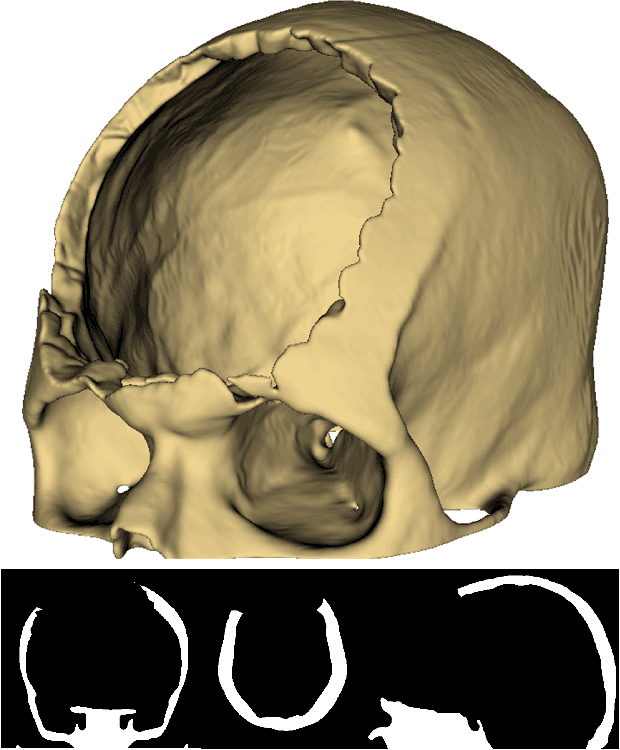
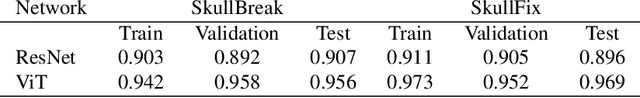
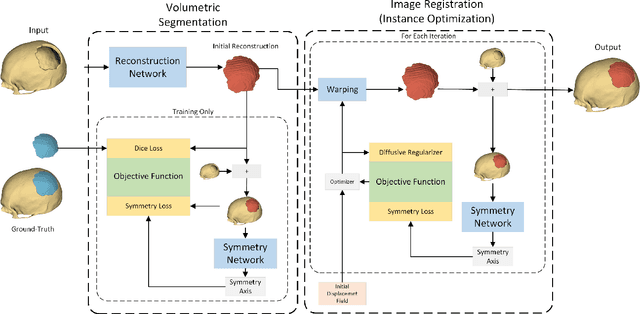
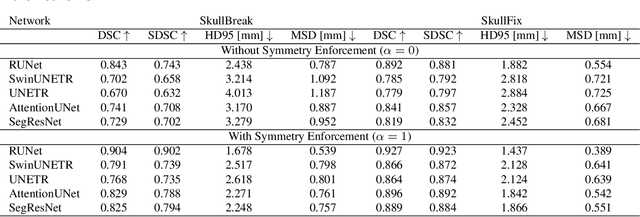
Abstract:Every year, thousands of people suffer from skull damage and require personalized implants to fill the cranial cavity. Unfortunately, the waiting time for reconstruction surgery can extend to several weeks or even months, especially in less developed countries. One factor contributing to the extended waiting period is the intricate process of personalized implant modeling. Currently, the preparation of these implants by experienced biomechanical experts is both costly and time-consuming. Recent advances in artificial intelligence, especially in deep learning, offer promising potential for automating the process. However, deep learning-based cranial reconstruction faces several challenges: (i) the limited size of training datasets, (ii) the high resolution of the volumetric data, and (iii) significant data heterogeneity. In this work, we propose a novel approach to address these challenges by enhancing the reconstruction through learnable symmetry enforcement. We demonstrate that it is possible to train a neural network dedicated to calculating skull symmetry, which can be utilized either as an additional objective function during training or as a post-reconstruction objective during the refinement step. We quantitatively evaluate the proposed method using open SkullBreak and SkullFix datasets, and qualitatively using real clinical cases. The results indicate that the symmetry-preserving reconstruction network achieves considerably better outcomes compared to the baseline (0.94/0.94/1.31 vs 0.84/0.76/2.43 in terms of DSC, bDSC, and HD95). Moreover, the results are comparable to the best-performing methods while requiring significantly fewer computational resources (< 500 vs > 100,000 GPU hours). The proposed method is a considerable contribution to the field of applied artificial intelligence in medicine and is a step toward automatic cranial defect reconstruction in clinical practice.
Unsupervised Skull Segmentation via Contrastive MR-to-CT Modality Translation
Oct 17, 2024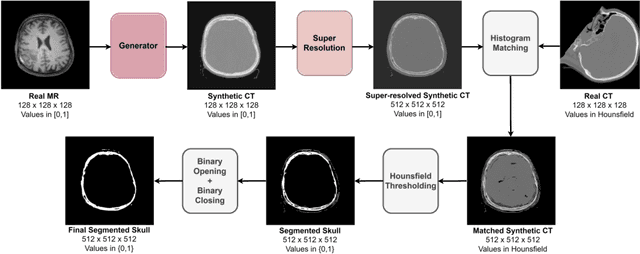
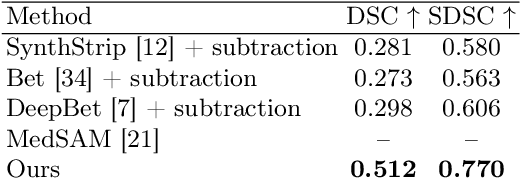
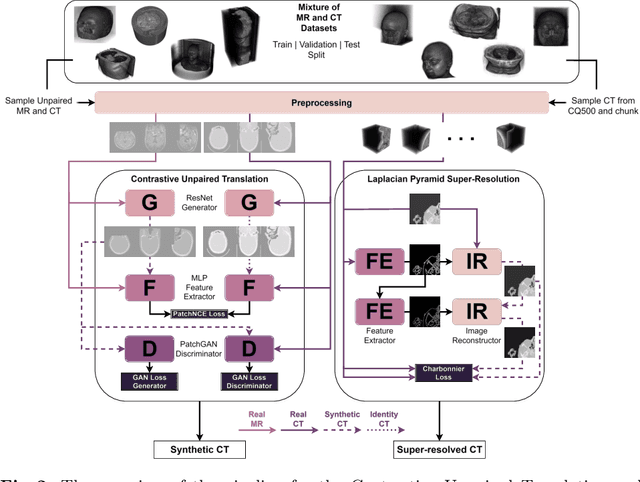
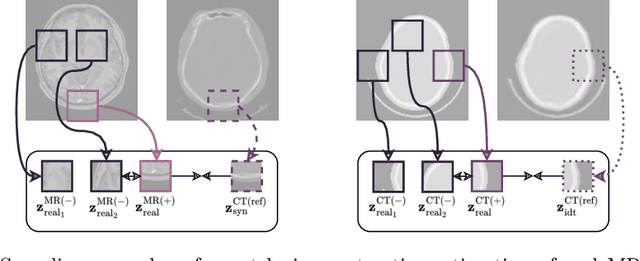
Abstract:The skull segmentation from CT scans can be seen as an already solved problem. However, in MR this task has a significantly greater complexity due to the presence of soft tissues rather than bones. Capturing the bone structures from MR images of the head, where the main visualization objective is the brain, is very demanding. The attempts that make use of skull stripping seem to not be well suited for this task and fail to work in many cases. On the other hand, supervised approaches require costly and time-consuming skull annotations. To overcome the difficulties we propose a fully unsupervised approach, where we do not perform the segmentation directly on MR images, but we rather perform a synthetic CT data generation via MR-to-CT translation and perform the segmentation there. We address many issues associated with unsupervised skull segmentation including the unpaired nature of MR and CT datasets (contrastive learning), low resolution and poor quality (super-resolution), and generalization capabilities. The research has a significant value for downstream tasks requiring skull segmentation from MR volumes such as craniectomy or surgery planning and can be seen as an important step towards the utilization of synthetic data in medical imaging.
Automatic Registration of SHG and H&E Images with Feature-based Initial Alignment and Intensity-based Instance Optimization: Contribution to the COMULIS Challenge
Sep 24, 2024Abstract:The automatic registration of noninvasive second-harmonic generation microscopy to hematoxylin and eosin slides is a highly desired, yet still unsolved problem. The task is challenging because the second-harmonic images contain only partial information, in contrast to the stained H&E slides that provide more information about the tissue morphology. Moreover, both imaging methods have different intensity distributions. Therefore, the task can be formulated as a multi-modal registration problem with missing data. In this work, we propose a method based on automatic keypoint matching followed by deformable registration based on instance optimization. The method does not require any training and is evaluated using the dataset provided in the Learn2Reg challenge by the COMULIS organization. The method achieved relatively good generalizability resulting in 88% of success rate in the initial alignment and average target registration error equal to 2.48 on the external validation set. We openly release the source code and incorporate it in the DeeperHistReg image registration framework.
Automatic Labels are as Effective as Manual Labels in Biomedical Images Classification with Deep Learning
Jun 20, 2024Abstract:The increasing availability of biomedical data is helping to design more robust deep learning (DL) algorithms to analyze biomedical samples. Currently, one of the main limitations to train DL algorithms to perform a specific task is the need for medical experts to label data. Automatic methods to label data exist, however automatic labels can be noisy and it is not completely clear when automatic labels can be adopted to train DL models. This paper aims to investigate under which circumstances automatic labels can be adopted to train a DL model on the classification of Whole Slide Images (WSI). The analysis involves multiple architectures, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Vision Transformer (ViT), and over 10000 WSIs, collected from three use cases: celiac disease, lung cancer and colon cancer, which one including respectively binary, multiclass and multilabel data. The results allow identifying 10% as the percentage of noisy labels that lead to train competitive models for the classification of WSIs. Therefore, an algorithm generating automatic labels needs to fit this criterion to be adopted. The application of the Semantic Knowledge Extractor Tool (SKET) algorithm to generate automatic labels leads to performance comparable to the one obtained with manual labels, since it generates a percentage of noisy labels between 2-5%. Automatic labels are as effective as manual ones, reaching solid performance comparable to the one obtained training models with manual labels.
Improving Quality Control of Whole Slide Images by Explicit Artifact Augmentation
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:The problem of artifacts in whole slide image acquisition, prevalent in both clinical workflows and research-oriented settings, necessitates human intervention and re-scanning. Overcoming this challenge requires developing quality control algorithms, that are hindered by the limited availability of relevant annotated data in histopathology. The manual annotation of ground-truth for artifact detection methods is expensive and time-consuming. This work addresses the issue by proposing a method dedicated to augmenting whole slide images with artifacts. The tool seamlessly generates and blends artifacts from an external library to a given histopathology dataset. The augmented datasets are then utilized to train artifact classification methods. The evaluation shows their usefulness in classification of the artifacts, where they show an improvement from 0.10 to 0.01 AUROC depending on the artifact type. The framework, model, weights, and ground-truth annotations are freely released to facilitate open science and reproducible research.
Improving Deep Learning-based Automatic Cranial Defect Reconstruction by Heavy Data Augmentation: From Image Registration to Latent Diffusion Models
Jun 10, 2024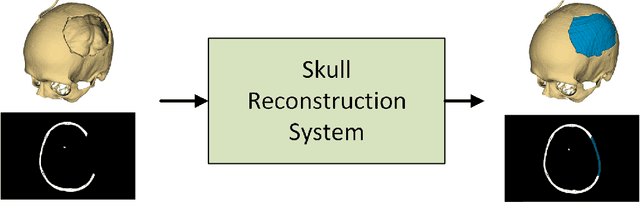
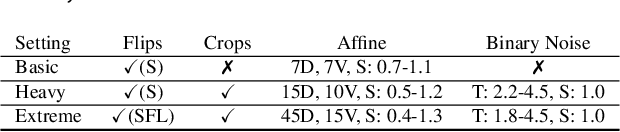
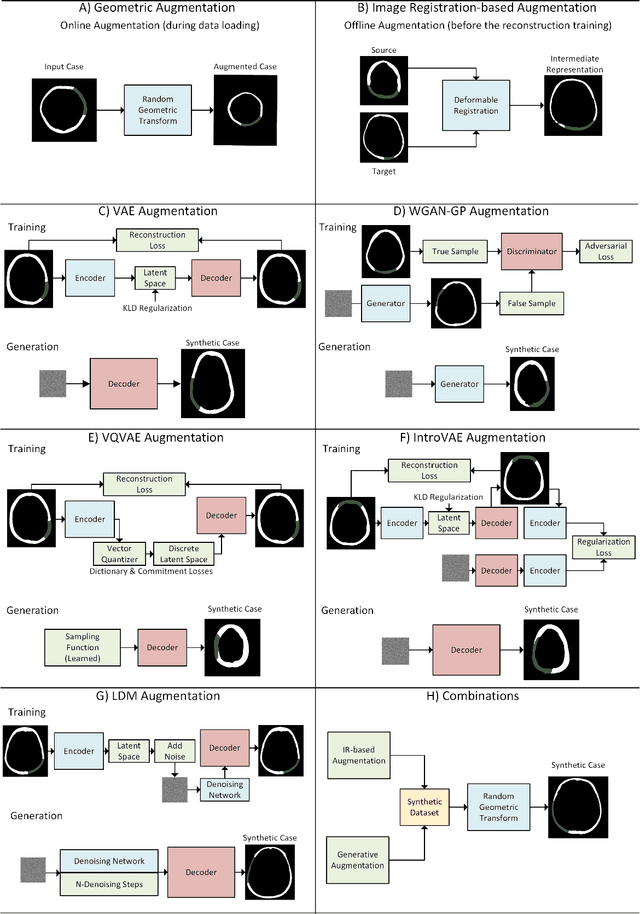

Abstract:Modeling and manufacturing of personalized cranial implants are important research areas that may decrease the waiting time for patients suffering from cranial damage. The modeling of personalized implants may be partially automated by the use of deep learning-based methods. However, this task suffers from difficulties with generalizability into data from previously unseen distributions that make it difficult to use the research outcomes in real clinical settings. Due to difficulties with acquiring ground-truth annotations, different techniques to improve the heterogeneity of datasets used for training the deep networks have to be considered and introduced. In this work, we present a large-scale study of several augmentation techniques, varying from classical geometric transformations, image registration, variational autoencoders, and generative adversarial networks, to the most recent advances in latent diffusion models. We show that the use of heavy data augmentation significantly increases both the quantitative and qualitative outcomes, resulting in an average Dice Score above 0.94 for the SkullBreak and above 0.96 for the SkullFix datasets. Moreover, we show that the synthetically augmented network successfully reconstructs real clinical defects. The work is a considerable contribution to the field of artificial intelligence in the automatic modeling of personalized cranial implants.
Patch-Based Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Automatic Transmitted Light to Fluorescence Imaging Transition: Contribution to the LightMyCells Challenge
Jun 03, 2024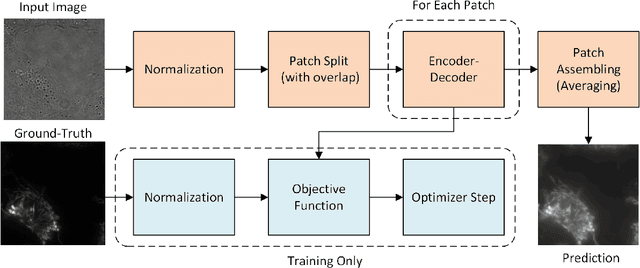
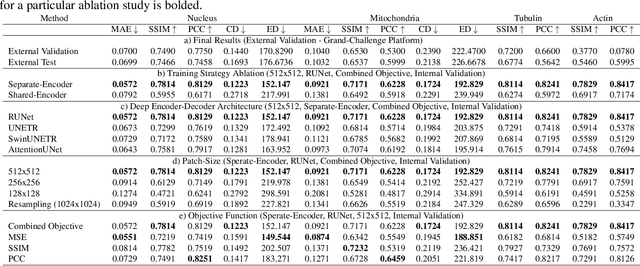
Abstract:Automatic prediction of fluorescently labeled organelles from label-free transmitted light input images is an important, yet difficult task. The traditional way to obtain fluorescence images is related to performing biochemical labeling which is time-consuming and costly. Therefore, an automatic algorithm to perform the task based on the label-free transmitted light microscopy could be strongly beneficial. The importance of the task motivated researchers from the France-BioImaging to organize the LightMyCells challenge where the goal is to propose an algorithm that automatically predicts the fluorescently labeled nucleus, mitochondria, tubulin, and actin, based on the input consisting of bright field, phase contrast, or differential interference contrast microscopic images. In this work, we present the contribution of the AGHSSO team based on a carefully prepared and trained encoder-decoder deep neural network that achieves a considerable score in the challenge, being placed among the best-performing teams.
RegWSI: Whole Slide Image Registration using Combined Deep Feature- and Intensity-Based Methods: Winner of the ACROBAT 2023 Challenge
Apr 26, 2024



Abstract:The automatic registration of differently stained whole slide images (WSIs) is crucial for improving diagnosis and prognosis by fusing complementary information emerging from different visible structures. It is also useful to quickly transfer annotations between consecutive or restained slides, thus significantly reducing the annotation time and associated costs. Nevertheless, the slide preparation is different for each stain and the tissue undergoes complex and large deformations. Therefore, a robust, efficient, and accurate registration method is highly desired by the scientific community and hospitals specializing in digital pathology. We propose a two-step hybrid method consisting of (i) deep learning- and feature-based initial alignment algorithm, and (ii) intensity-based nonrigid registration using the instance optimization. The proposed method does not require any fine-tuning to a particular dataset and can be used directly for any desired tissue type and stain. The method scored 1st place in the ACROBAT 2023 challenge. We evaluated using three open datasets: (i) ANHIR, (ii) ACROBAT, and (iii) HyReCo, and performed several ablation studies concerning the resolution used for registration and the initial alignment robustness and stability. The method achieves the most accurate results for the ACROBAT dataset, the cell-level registration accuracy for the restained slides from the HyReCo dataset, and is among the best methods evaluated on the ANHIR dataset. The method does not require any fine-tuning to a new datasets and can be used out-of-the-box for other types of microscopic images. The method is incorporated into the DeeperHistReg framework, allowing others to directly use it to register, transform, and save the WSIs at any desired pyramid level. The proposed method is a significant contribution to the WSI registration, thus advancing the field of digital pathology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge