Unsupervised Skull Segmentation via Contrastive MR-to-CT Modality Translation
Paper and Code
Oct 17, 2024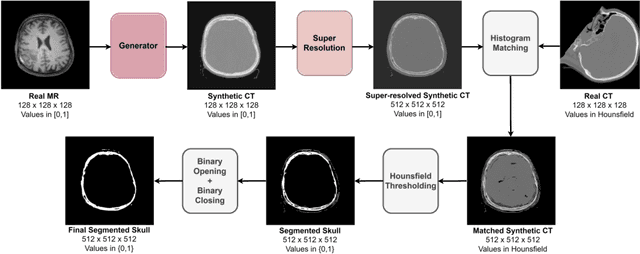
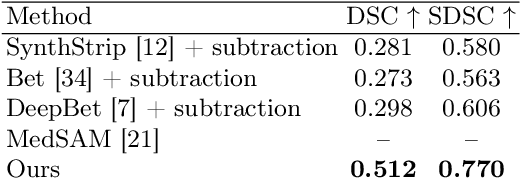
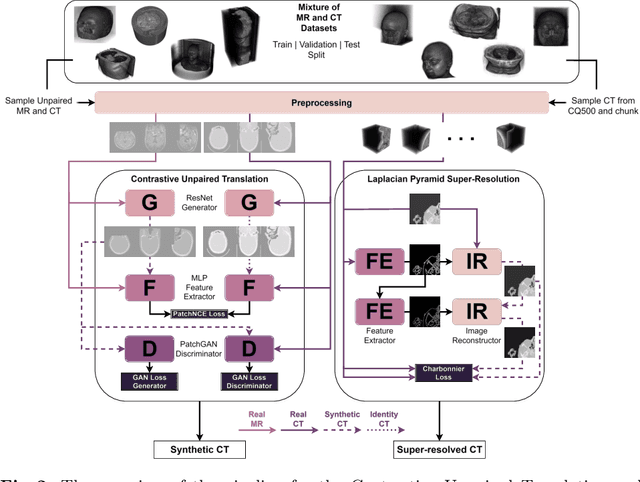
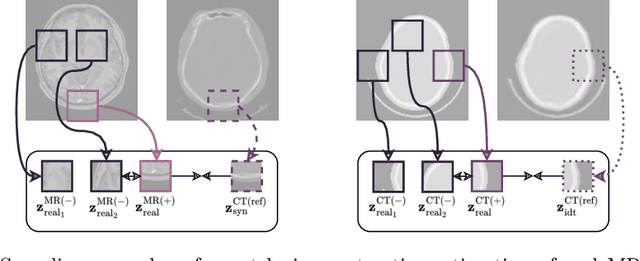
The skull segmentation from CT scans can be seen as an already solved problem. However, in MR this task has a significantly greater complexity due to the presence of soft tissues rather than bones. Capturing the bone structures from MR images of the head, where the main visualization objective is the brain, is very demanding. The attempts that make use of skull stripping seem to not be well suited for this task and fail to work in many cases. On the other hand, supervised approaches require costly and time-consuming skull annotations. To overcome the difficulties we propose a fully unsupervised approach, where we do not perform the segmentation directly on MR images, but we rather perform a synthetic CT data generation via MR-to-CT translation and perform the segmentation there. We address many issues associated with unsupervised skull segmentation including the unpaired nature of MR and CT datasets (contrastive learning), low resolution and poor quality (super-resolution), and generalization capabilities. The research has a significant value for downstream tasks requiring skull segmentation from MR volumes such as craniectomy or surgery planning and can be seen as an important step towards the utilization of synthetic data in medical imaging.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge