Magnus Sahlgren
SWEb: A Large Web Dataset for the Scandinavian Languages
Oct 06, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents the hitherto largest pretraining dataset for the Scandinavian languages: the Scandinavian WEb (SWEb), comprising over one trillion tokens. The paper details the collection and processing pipeline, and introduces a novel model-based text extractor that significantly reduces complexity in comparison with rule-based approaches. We also introduce a new cloze-style benchmark for evaluating language models in Swedish, and use this test to compare models trained on the SWEb data to models trained on FineWeb, with competitive results. All data, models and code are shared openly.
GPT-SW3: An Autoregressive Language Model for the Nordic Languages
May 23, 2023Abstract:This paper details the process of developing the first native large generative language model for the Nordic languages, GPT-SW3. We cover all parts of the development process, from data collection and processing, training configuration and instruction finetuning, to evaluation and considerations for release strategies. We hope that this paper can serve as a guide and reference for other researchers that undertake the development of large generative models for smaller languages.
The Nordic Pile: A 1.2TB Nordic Dataset for Language Modeling
Mar 30, 2023Abstract:Pre-training Large Language Models (LLMs) require massive amounts of text data, and the performance of the LLMs typically correlates with the scale and quality of the datasets. This means that it may be challenging to build LLMs for smaller languages such as Nordic ones, where the availability of text corpora is limited. In order to facilitate the development of the LLMS in the Nordic languages, we curate a high-quality dataset consisting of 1.2TB of text, in all of the major North Germanic languages (Danish, Icelandic, Norwegian, and Swedish), as well as some high-quality English data. This paper details our considerations and processes for collecting, cleaning, and filtering the dataset.
We Need to Talk About Data: The Importance of Data Readiness in Natural Language Processing
Oct 11, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, we identify the state of data as being an important reason for failure in applied Natural Language Processing (NLP) projects. We argue that there is a gap between academic research in NLP and its application to problems outside academia, and that this gap is rooted in poor mutual understanding between academic researchers and their non-academic peers who seek to apply research results to their operations. To foster transfer of research results from academia to non-academic settings, and the corresponding influx of requirements back to academia, we propose a method for improving the communication between researchers and external stakeholders regarding the accessibility, validity, and utility of data based on Data Readiness Levels \cite{lawrence2017data}. While still in its infancy, the method has been iterated on and applied in multiple innovation and research projects carried out with stakeholders in both the private and public sectors. Finally, we invite researchers and practitioners to share their experiences, and thus contributing to a body of work aimed at raising awareness of the importance of data readiness for NLP.
Cross-lingual Transfer of Monolingual Models
Sep 15, 2021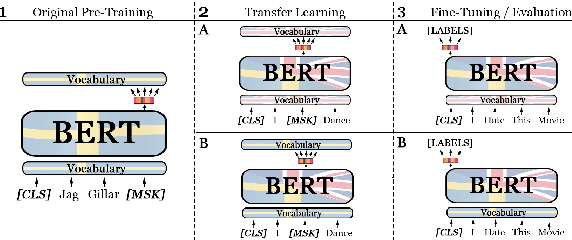
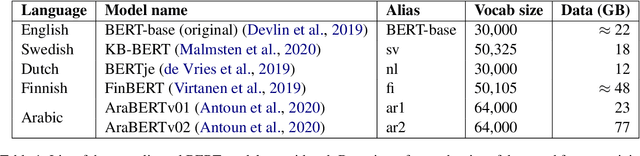
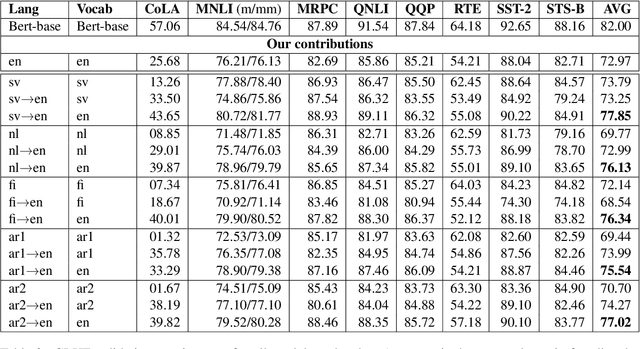
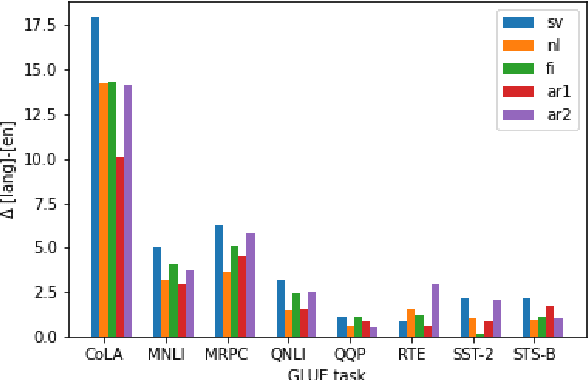
Abstract:Recent studies in zero-shot cross-lingual learning using multilingual models have falsified the previous hypothesis that shared vocabulary and joint pre-training are the keys to cross-lingual generalization. Inspired by this advancement, we introduce a cross-lingual transfer method for monolingual models based on domain adaptation. We study the effects of such transfer from four different languages to English. Our experimental results on GLUE show that the transferred models outperform the native English model independently of the source language. After probing the English linguistic knowledge encoded in the representations before and after transfer, we find that semantic information is retained from the source language, while syntactic information is learned during transfer. Additionally, the results of evaluating the transferred models in source language tasks reveal that their performance in the source domain deteriorates after transfer.
A comprehensive comparative evaluation and analysis of Distributional Semantic Models
May 20, 2021
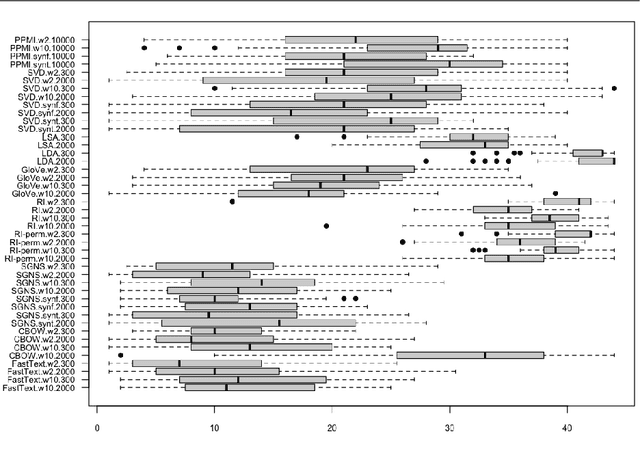
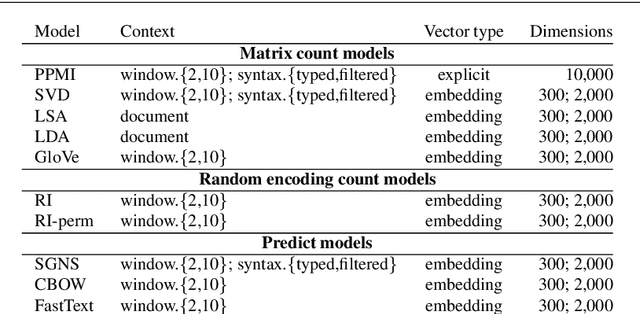
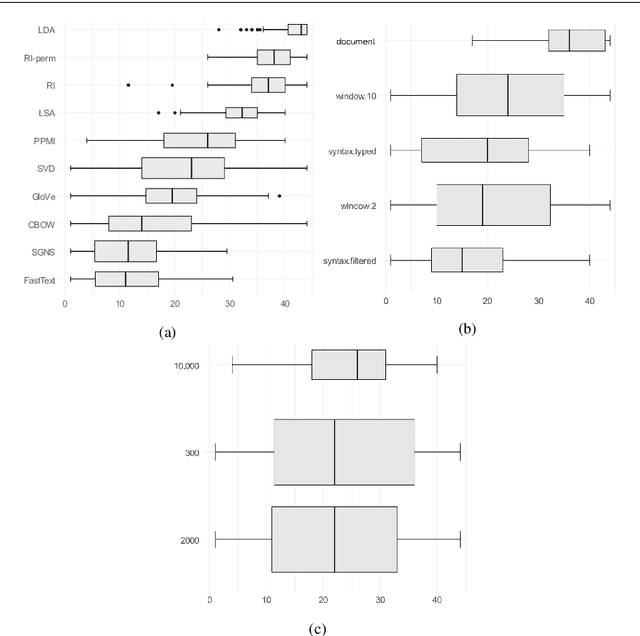
Abstract:Distributional semantics has deeply changed in the last decades. First, predict models stole the thunder from traditional count ones, and more recently both of them were replaced in many NLP applications by contextualized vectors produced by Transformer neural language models. Although an extensive body of research has been devoted to Distributional Semantic Model (DSM) evaluation, we still lack a thorough comparison with respect to tested models, semantic tasks, and benchmark datasets. Moreover, previous work has mostly focused on task-driven evaluation, instead of exploring the differences between the way models represent the lexical semantic space. In this paper, we perform a comprehensive evaluation of type distributional vectors, either produced by static DSMs or obtained by averaging the contextualized vectors generated by BERT. First of all, we investigate the performance of embeddings in several semantic tasks, carrying out an in-depth statistical analysis to identify the major factors influencing the behavior of DSMs. The results show that i.) the alleged superiority of predict based models is more apparent than real, and surely not ubiquitous and ii.) static DSMs surpass contextualized representations in most out-of-context semantic tasks and datasets. Furthermore, we borrow from cognitive neuroscience the methodology of Representational Similarity Analysis (RSA) to inspect the semantic spaces generated by distributional models. RSA reveals important differences related to the frequency and part-of-speech of lexical items.
Should we Stop Training More Monolingual Models, and Simply Use Machine Translation Instead?
Apr 21, 2021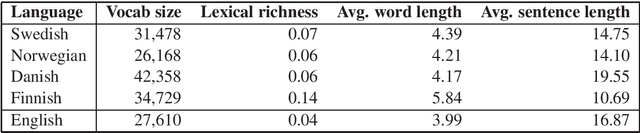


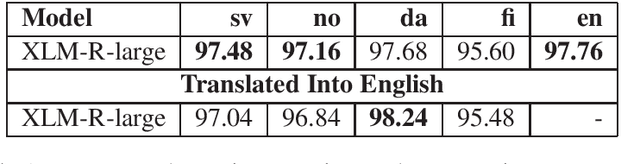
Abstract:Most work in NLP makes the assumption that it is desirable to develop solutions in the native language in question. There is consequently a strong trend towards building native language models even for low-resource languages. This paper questions this development, and explores the idea of simply translating the data into English, thereby enabling the use of pretrained, and large-scale, English language models. We demonstrate empirically that a large English language model coupled with modern machine translation outperforms native language models in most Scandinavian languages. The exception to this is Finnish, which we assume is due to inferior translation quality. Our results suggest that machine translation is a mature technology, which raises a serious counter-argument for training native language models for low-resource languages. This paper therefore strives to make a provocative but important point. As English language models are improving at an unprecedented pace, which in turn improves machine translation, it is from an empirical and environmental stand-point more effective to translate data from low-resource languages into English, than to build language models for such languages.
Federated Word2Vec: Leveraging Federated Learning to Encourage Collaborative Representation Learning
Apr 19, 2021
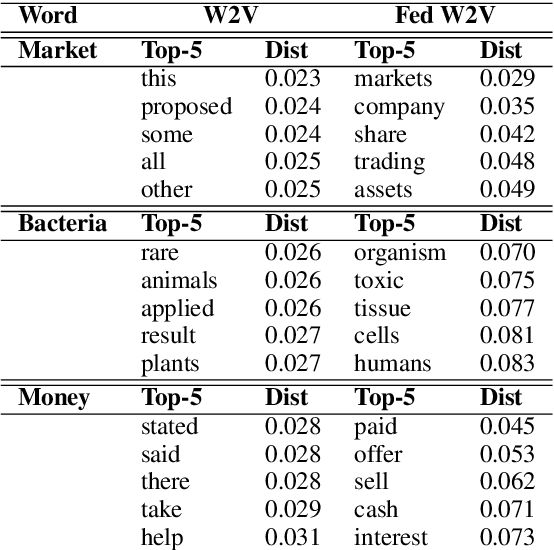
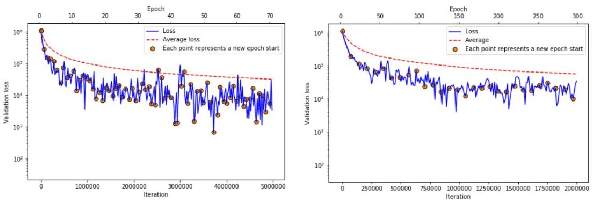
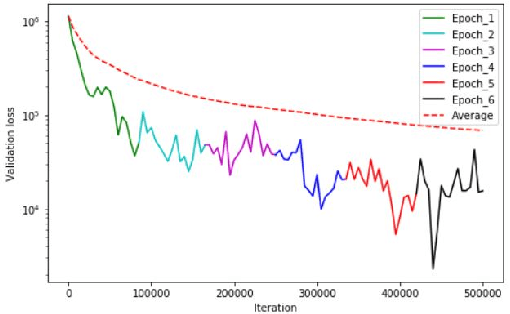
Abstract:Large scale contextual representation models have significantly advanced NLP in recent years, understanding the semantics of text to a degree never seen before. However, they need to process large amounts of data to achieve high-quality results. Joining and accessing all these data from multiple sources can be extremely challenging due to privacy and regulatory reasons. Federated Learning can solve these limitations by training models in a distributed fashion, taking advantage of the hardware of the devices that generate the data. We show the viability of training NLP models, specifically Word2Vec, with the Federated Learning protocol. In particular, we focus on a scenario in which a small number of organizations each hold a relatively large corpus. The results show that neither the quality of the results nor the convergence time in Federated Word2Vec deteriorates as compared to centralised Word2Vec.
The Singleton Fallacy: Why Current Critiques of Language Models Miss the Point
Feb 08, 2021Abstract:This paper discusses the current critique against neural network-based Natural Language Understanding (NLU) solutions known as language models. We argue that much of the current debate rests on an argumentation error that we will refer to as the singleton fallacy: the assumption that language, meaning, and understanding are single and uniform phenomena that are unobtainable by (current) language models. By contrast, we will argue that there are many different types of language use, meaning and understanding, and that (current) language models are build with the explicit purpose of acquiring and representing one type of structural understanding of language. We will argue that such structural understanding may cover several different modalities, and as such can handle several different types of meaning. Our position is that we currently see no theoretical reason why such structural knowledge would be insufficient to count as "real" understanding.
Data Readiness for Natural Language Processing
Sep 30, 2020
Abstract:This document concerns data readiness in the context of machine learning and Natural Language Processing. It describes how an organization may proceed to identify, make available, validate, and prepare data to facilitate automated analysis methods. The contents of the document is based on the practical challenges and frequently asked questions we have encountered in our work as an applied research institute with helping organizations and companies, both in the public and private sectors, to use data in their business processes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge