Lingyu Sun
TADS: Task-Aware Data Selection for Multi-Task Multimodal Pre-Training
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Large-scale multimodal pre-trained models like CLIP rely heavily on high-quality training data, yet raw web-crawled datasets are often noisy, misaligned, and redundant, leading to inefficient training and suboptimal generalization. Existing data selection methods are either heuristic-based, suffering from bias and limited diversity, or data-driven but task-agnostic, failing to optimize for multi-task scenarios. To address these gaps, we introduce TADS (Task-Aware Data Selection), a novel framework for multi-task multimodal pre-training that integrates Intrinsic Quality, Task Relevance, and Distributional Diversity into a learnable value function. TADS employs a comprehensive quality assessment system with unimodal and cross-modal operators, quantifies task relevance via interpretable similarity vectors, and optimizes diversity through cluster-based weighting. A feedback-driven meta-learning mechanism adaptively refines the selection strategy based on proxy model performance across multiple downstream tasks. Experiments on CC12M demonstrate that TADS achieves superior zero-shot performance on benchmarks like ImageNet, CIFAR-100, MS-COCO, and Flickr30K, using only 36% of the data while outperforming baselines by an average of 1.0%. This highlights that TADS significantly enhances data efficiency by curating a high-utility subset that yields a much higher performance ceiling within the same computational constraints.
HyperSIGMA: Hyperspectral Intelligence Comprehension Foundation Model
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Foundation models (FMs) are revolutionizing the analysis and understanding of remote sensing (RS) scenes, including aerial RGB, multispectral, and SAR images. However, hyperspectral images (HSIs), which are rich in spectral information, have not seen much application of FMs, with existing methods often restricted to specific tasks and lacking generality. To fill this gap, we introduce HyperSIGMA, a vision transformer-based foundation model for HSI interpretation, scalable to over a billion parameters. To tackle the spectral and spatial redundancy challenges in HSIs, we introduce a novel sparse sampling attention (SSA) mechanism, which effectively promotes the learning of diverse contextual features and serves as the basic block of HyperSIGMA. HyperSIGMA integrates spatial and spectral features using a specially designed spectral enhancement module. In addition, we construct a large-scale hyperspectral dataset, HyperGlobal-450K, for pre-training, which contains about 450K hyperspectral images, significantly surpassing existing datasets in scale. Extensive experiments on various high-level and low-level HSI tasks demonstrate HyperSIGMA's versatility and superior representational capability compared to current state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, HyperSIGMA shows significant advantages in scalability, robustness, cross-modal transferring capability, and real-world applicability.
Improving Global Forest Mapping by Semi-automatic Sample Labeling with Deep Learning on Google Earth Images
Aug 06, 2021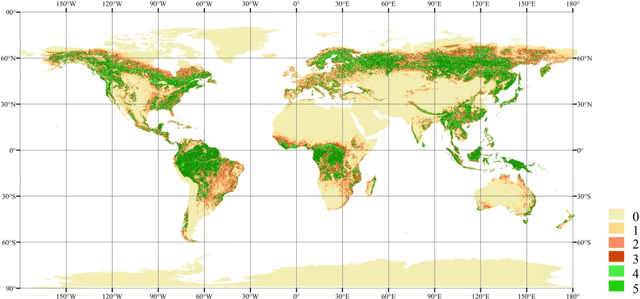
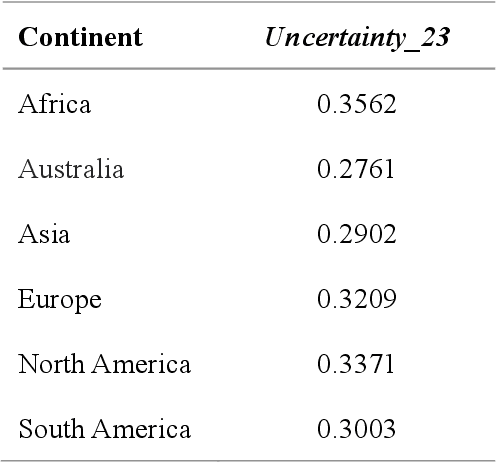
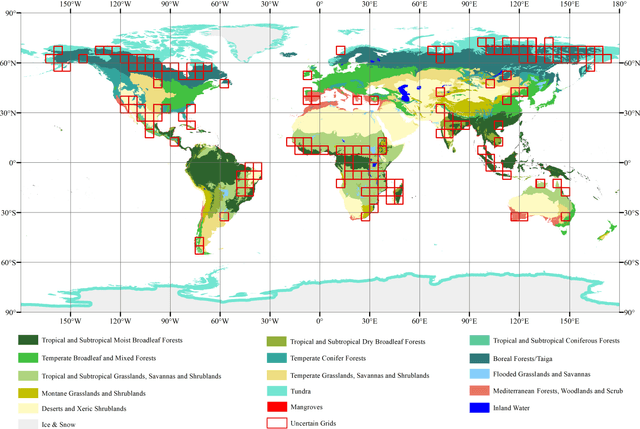
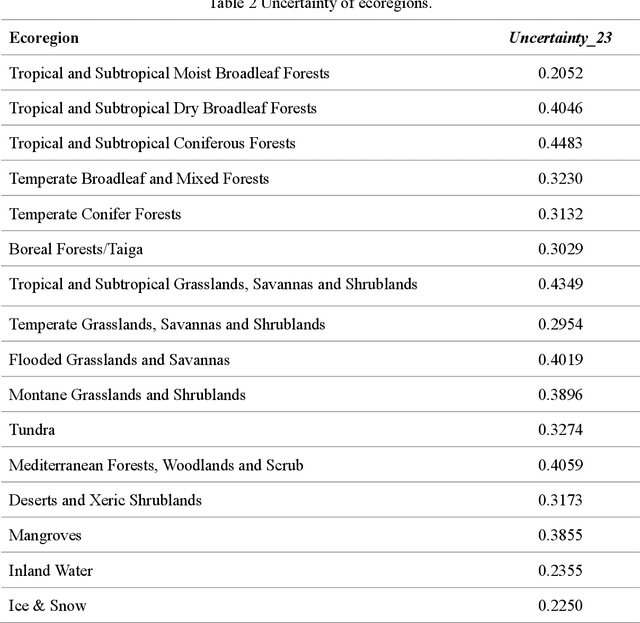
Abstract:Global forest cover is critical to the provision of certain ecosystem services. With the advent of the google earth engine cloud platform, fine resolution global land cover mapping task could be accomplished in a matter of days instead of years. The amount of global forest cover (GFC) products has been steadily increasing in the last decades. However, it's hard for users to select suitable one due to great differences between these products, and the accuracy of these GFC products has not been verified on global scale. To provide guidelines for users and producers, it is urgent to produce a validation sample set at the global level. However, this labeling task is time and labor consuming, which has been the main obstacle to the progress of global land cover mapping. In this research, a labor-efficient semi-automatic framework is introduced to build a biggest ever Forest Sample Set (FSS) contained 395280 scattered samples categorized as forest, shrubland, grassland, impervious surface, etc. On the other hand, to provide guidelines for the users, we comprehensively validated the local and global mapping accuracy of all existing 30m GFC products, and analyzed and mapped the agreement of them. Moreover, to provide guidelines for the producers, optimal sampling strategy was proposed to improve the global forest classification. Furthermore, a new global forest cover named GlobeForest2020 has been generated, which proved to improve the previous highest state-of-the-art accuracies (obtained by Gong et al., 2017) by 2.77% in uncertain grids and by 1.11% in certain grids.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge