Leyu Lin
Improving Multi-modal Recommender Systems by Denoising and Aligning Multi-modal Content and User Feedback
Jun 18, 2024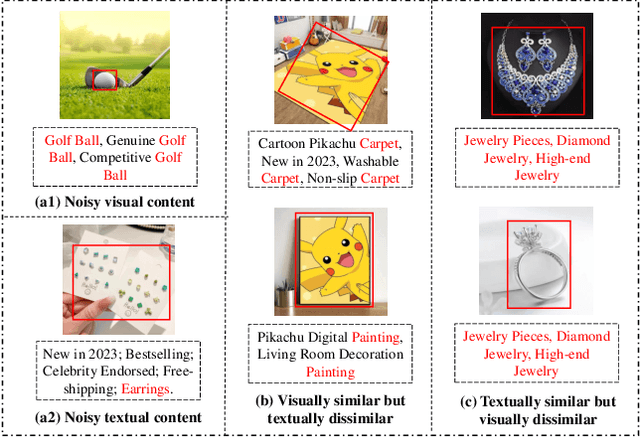
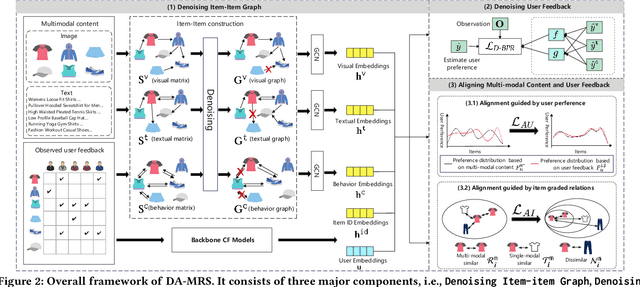
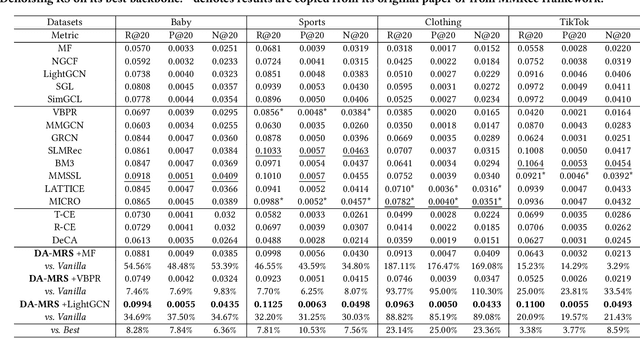
Abstract:Multi-modal recommender systems (MRSs) are pivotal in diverse online web platforms and have garnered considerable attention in recent years. However, previous studies overlook the challenges of (1) noisy multi-modal content, (2) noisy user feedback, and (3) aligning multi-modal content with user feedback. In order to tackle these challenges, we propose Denoising and Aligning Multi-modal Recommender System (DA-MRS). To mitigate multi-modal noise, DA-MRS first constructs item-item graphs determined by consistent content similarity across modalities. To denoise user feedback, DA-MRS associates the probability of observed feedback with multi-modal content and devises a denoised BPR loss. Furthermore, DA-MRS implements Alignment guided by User preference to enhance task-specific item representation and Alignment guided by graded Item relations to provide finer-grained alignment. Extensive experiments verify that DA-MRS is a plug-and-play framework and achieves significant and consistent improvements across various datasets, backbone models, and noisy scenarios.
DFGNN: Dual-frequency Graph Neural Network for Sign-aware Feedback
May 24, 2024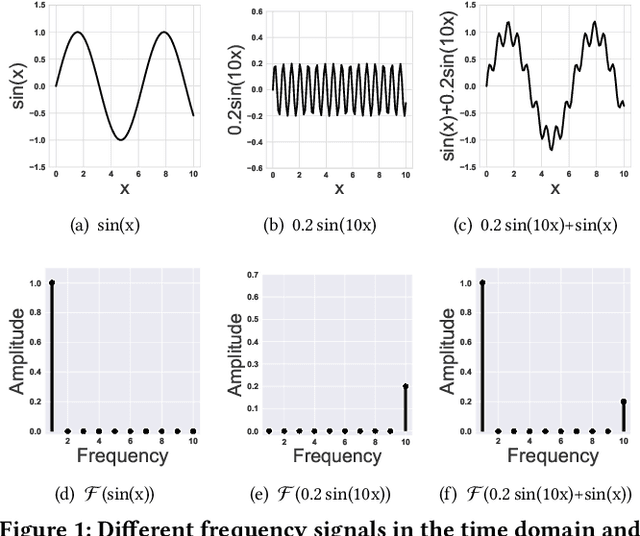
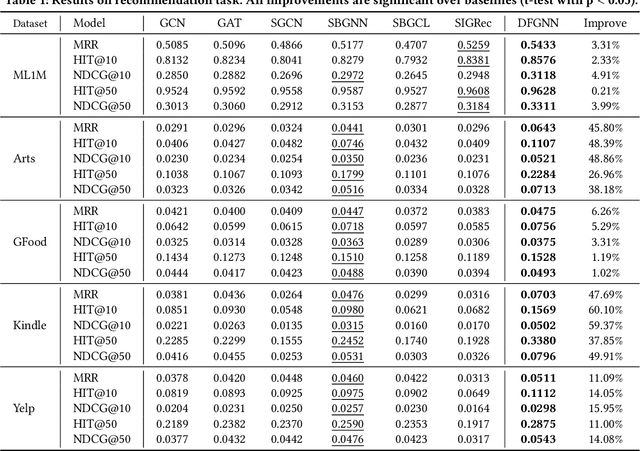
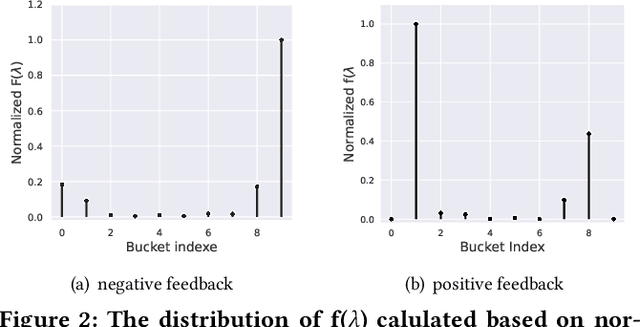
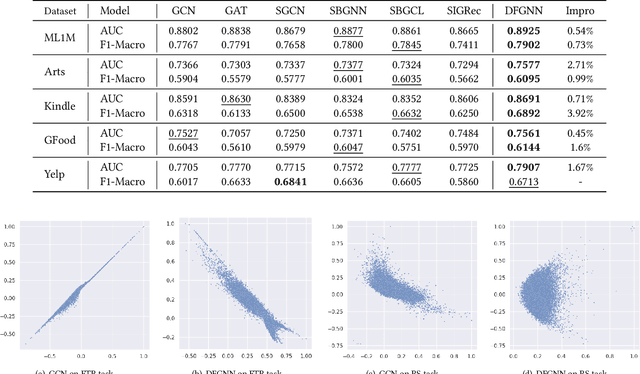
Abstract:The graph-based recommendation has achieved great success in recent years. However, most existing graph-based recommendations focus on capturing user preference based on positive edges/feedback, while ignoring negative edges/feedback (e.g., dislike, low rating) that widely exist in real-world recommender systems. How to utilize negative feedback in graph-based recommendations still remains underexplored. In this study, we first conducted a comprehensive experimental analysis and found that (1) existing graph neural networks are not well-suited for modeling negative feedback, which acts as a high-frequency signal in a user-item graph. (2) The graph-based recommendation suffers from the representation degeneration problem. Based on the two observations, we propose a novel model that models positive and negative feedback from a frequency filter perspective called Dual-frequency Graph Neural Network for Sign-aware Recommendation (DFGNN). Specifically, in DFGNN, the designed dual-frequency graph filter (DGF) captures both low-frequency and high-frequency signals that contain positive and negative feedback. Furthermore, the proposed signed graph regularization is applied to maintain the user/item embedding uniform in the embedding space to alleviate the representation degeneration problem. Additionally, we conduct extensive experiments on real-world datasets and demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed model. Codes of our model will be released upon acceptance.
ID-centric Pre-training for Recommendation
May 07, 2024



Abstract:Classical sequential recommendation models generally adopt ID embeddings to store knowledge learned from user historical behaviors and represent items. However, these unique IDs are challenging to be transferred to new domains. With the thriving of pre-trained language model (PLM), some pioneer works adopt PLM for pre-trained recommendation, where modality information (e.g., text) is considered universal across domains via PLM. Unfortunately, the behavioral information in ID embeddings is still verified to be dominating in PLM-based recommendation models compared to modality information and thus limits these models' performance. In this work, we propose a novel ID-centric recommendation pre-training paradigm (IDP), which directly transfers informative ID embeddings learned in pre-training domains to item representations in new domains. Specifically, in pre-training stage, besides the ID-based sequential model for recommendation, we also build a Cross-domain ID-matcher (CDIM) learned by both behavioral and modality information. In the tuning stage, modality information of new domain items is regarded as a cross-domain bridge built by CDIM. We first leverage the textual information of downstream domain items to retrieve behaviorally and semantically similar items from pre-training domains using CDIM. Next, these retrieved pre-trained ID embeddings, rather than certain textual embeddings, are directly adopted to generate downstream new items' embeddings. Through extensive experiments on real-world datasets, both in cold and warm settings, we demonstrate that our proposed model significantly outperforms all baselines. Codes will be released upon acceptance.
Plug-in Diffusion Model for Sequential Recommendation
Jan 05, 2024Abstract:Pioneering efforts have verified the effectiveness of the diffusion models in exploring the informative uncertainty for recommendation. Considering the difference between recommendation and image synthesis tasks, existing methods have undertaken tailored refinements to the diffusion and reverse process. However, these approaches typically use the highest-score item in corpus for user interest prediction, leading to the ignorance of the user's generalized preference contained within other items, thereby remaining constrained by the data sparsity issue. To address this issue, this paper presents a novel Plug-in Diffusion Model for Recommendation (PDRec) framework, which employs the diffusion model as a flexible plugin to jointly take full advantage of the diffusion-generating user preferences on all items. Specifically, PDRec first infers the users' dynamic preferences on all items via a time-interval diffusion model and proposes a Historical Behavior Reweighting (HBR) mechanism to identify the high-quality behaviors and suppress noisy behaviors. In addition to the observed items, PDRec proposes a Diffusion-based Positive Augmentation (DPA) strategy to leverage the top-ranked unobserved items as the potential positive samples, bringing in informative and diverse soft signals to alleviate data sparsity. To alleviate the false negative sampling issue, PDRec employs Noise-free Negative Sampling (NNS) to select stable negative samples for ensuring effective model optimization. Extensive experiments and analyses on four datasets have verified the superiority of the proposed PDRec over the state-of-the-art baselines and showcased the universality of PDRec as a flexible plugin for commonly-used sequential encoders in different recommendation scenarios. The code is available in https://github.com/hulkima/PDRec.
Distillation is All You Need for Practically Using Different Pre-trained Recommendation Models
Jan 01, 2024Abstract:Pre-trained recommendation models (PRMs) have attracted widespread attention recently. However, their totally different model structure, huge model size and computation cost hinder their application in practical recommender systems. Hence, it is highly essential to explore how to practically utilize PRMs in real-world recommendations. In this paper, we propose a novel joint knowledge distillation from different pre-trained recommendation models named PRM-KD for recommendation, which takes full advantages of diverse PRMs as teacher models for enhancing student models efficiently. Specifically, PRM-KD jointly distills diverse informative knowledge from multiple representative PRMs such as UniSRec, Recformer, and UniM^2Rec. The knowledge from the above PRMs are then smartly integrated into the student recommendation model considering their confidence and consistency. We further verify the universality of PRM-KD with various types of student models, including sequential recommendation, feature interaction, and graph-based models. Extensive experiments on five real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and efficacy of PRM-KD, which could be viewed as an economical shortcut in practically and conveniently making full use of different PRMs in online systems.
AgentCF: Collaborative Learning with Autonomous Language Agents for Recommender Systems
Oct 13, 2023Abstract:Recently, there has been an emergence of employing LLM-powered agents as believable human proxies, based on their remarkable decision-making capability. However, existing studies mainly focus on simulating human dialogue. Human non-verbal behaviors, such as item clicking in recommender systems, although implicitly exhibiting user preferences and could enhance the modeling of users, have not been deeply explored. The main reasons lie in the gap between language modeling and behavior modeling, as well as the incomprehension of LLMs about user-item relations. To address this issue, we propose AgentCF for simulating user-item interactions in recommender systems through agent-based collaborative filtering. We creatively consider not only users but also items as agents, and develop a collaborative learning approach that optimizes both kinds of agents together. Specifically, at each time step, we first prompt the user and item agents to interact autonomously. Then, based on the disparities between the agents' decisions and real-world interaction records, user and item agents are prompted to reflect on and adjust the misleading simulations collaboratively, thereby modeling their two-sided relations. The optimized agents can also propagate their preferences to other agents in subsequent interactions, implicitly capturing the collaborative filtering idea. Overall, the optimized agents exhibit diverse interaction behaviors within our framework, including user-item, user-user, item-item, and collective interactions. The results show that these agents can demonstrate personalized behaviors akin to those of real-world individuals, sparking the development of next-generation user behavior simulation.
Multi-Granularity Click Confidence Learning via Self-Distillation in Recommendation
Sep 28, 2023



Abstract:Recommendation systems rely on historical clicks to learn user interests and provide appropriate items. However, current studies tend to treat clicks equally, which may ignore the assorted intensities of user interests in different clicks. In this paper, we aim to achieve multi-granularity Click confidence Learning via Self-Distillation in recommendation (CLSD). Due to the lack of supervised signals in click confidence, we first apply self-supervised learning to obtain click confidence scores via a global self-distillation method. After that, we define a local confidence function to adapt confidence scores at the user group level, since the confidence distributions can be varied among user groups. With the combination of multi-granularity confidence learning, we can distinguish the quality of clicks and model user interests more accurately without involving extra data and model structures. The significant improvements over different backbones on industrial offline and online experiments in a real-world recommender system prove the effectiveness of our model. Recently, CLSD has been deployed on a large-scale recommender system, affecting over 400 million users.
Learning from All Sides: Diversified Positive Augmentation via Self-distillation in Recommendation
Aug 15, 2023



Abstract:Personalized recommendation relies on user historical behaviors to provide user-interested items, and thus seriously struggles with the data sparsity issue. A powerful positive item augmentation is beneficial to address the sparsity issue, while few works could jointly consider both the accuracy and diversity of these augmented training labels. In this work, we propose a novel model-agnostic Diversified self-distillation guided positive augmentation (DivSPA) for accurate and diverse positive item augmentations. Specifically, DivSPA first conducts three types of retrieval strategies to collect high-quality and diverse positive item candidates according to users' overall interests, short-term intentions, and similar users. Next, a self-distillation module is conducted to double-check and rerank these candidates as the final positive augmentations. Extensive offline and online evaluations verify the effectiveness of our proposed DivSPA on both accuracy and diversity. DivSPA is simple and effective, which could be conveniently adapted to other base models and systems. Currently, DivSPA has been deployed on multiple widely-used real-world recommender systems.
Graph Exploration Matters: Improving both individual-level and system-level diversity in WeChat Feed Recommender
May 29, 2023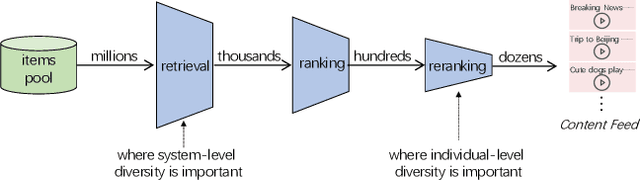
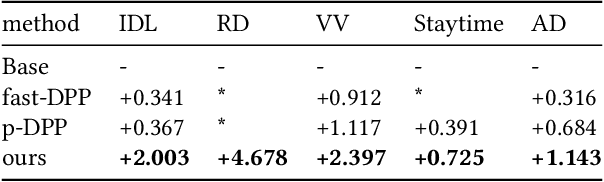
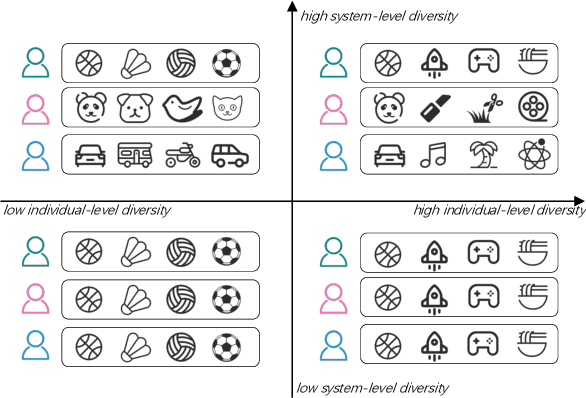
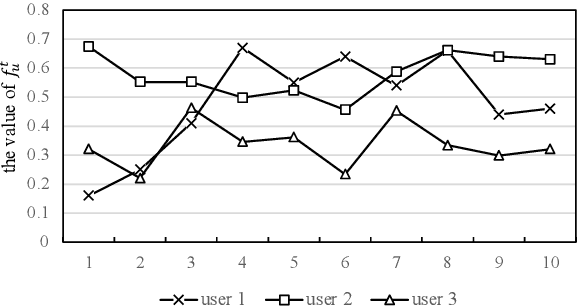
Abstract:There are roughly three stages in real industrial recommendation systems, candidates generation (retrieval), ranking and reranking. Individual-level diversity and system-level diversity are both important for industrial recommender systems. The former focus on each single user's experience, while the latter focus on the difference among users. Graph-based retrieval strategies are inevitably hijacked by heavy users and popular items, leading to the convergence of candidates for users and the lack of system-level diversity. Meanwhile, in the reranking phase, Determinantal Point Process (DPP) is deployed to increase individual-level diverisity. Heavily relying on the semantic information of items, DPP suffers from clickbait and inaccurate attributes. Besides, most studies only focus on one of the two levels of diversity, and ignore the mutual influence among different stages in real recommender systems. We argue that individual-level diversity and system-level diversity should be viewed as an integrated problem, and we provide an efficient and deployable solution for web-scale recommenders. Generally, we propose to employ the retrieval graph information in diversity-based reranking, by which to weaken the hidden similarity of items exposed to users, and consequently gain more graph explorations to improve the system-level diveristy. Besides, we argue that users' propensity for diversity changes over time in content feed recommendation. Therefore, with the explored graph, we also propose to capture the user's real-time personalized propensity to the diversity. We implement and deploy the combined system in WeChat App's Top Stories used by hundreds of millions of users. Offline simulations and online A/B tests show our solution can effectively improve both user engagement and system revenue.
Recommendation as Instruction Following: A Large Language Model Empowered Recommendation Approach
May 11, 2023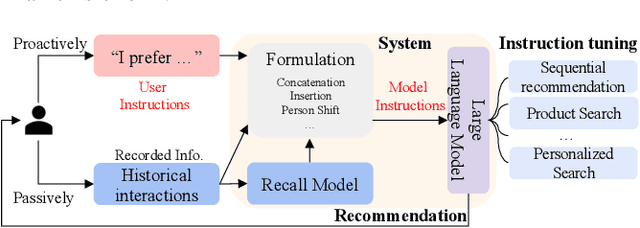

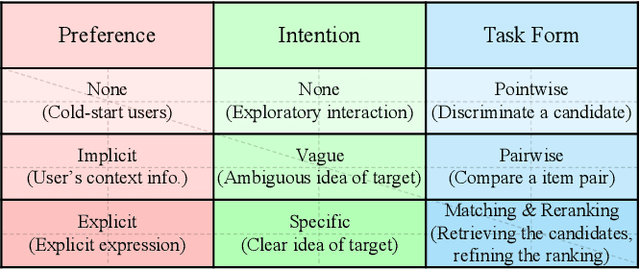
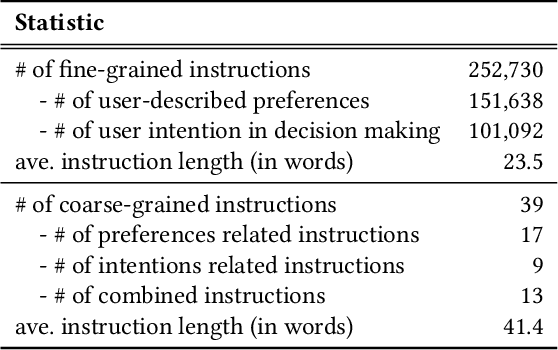
Abstract:In the past decades, recommender systems have attracted much attention in both research and industry communities, and a large number of studies have been devoted to developing effective recommendation models. Basically speaking, these models mainly learn the underlying user preference from historical behavior data, and then estimate the user-item matching relationships for recommendations. Inspired by the recent progress on large language models (LLMs), we take a different approach to developing the recommendation models, considering recommendation as instruction following by LLMs. The key idea is that the preferences or needs of a user can be expressed in natural language descriptions (called instructions), so that LLMs can understand and further execute the instruction for fulfilling the recommendation task. Instead of using public APIs of LLMs, we instruction tune an open-source LLM (3B Flan-T5-XL), in order to better adapt LLMs to recommender systems. For this purpose, we first design a general instruction format for describing the preference, intention, task form and context of a user in natural language. Then we manually design 39 instruction templates and automatically generate a large amount of user-personalized instruction data (252K instructions) with varying types of preferences and intentions. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, we instantiate the instruction templates into several widely-studied recommendation (or search) tasks, and conduct extensive experiments on these tasks with real-world datasets. Experiment results show that the proposed approach can outperform several competitive baselines, including the powerful GPT-3.5, on these evaluation tasks. Our approach sheds light on developing more user-friendly recommender systems, in which users can freely communicate with the system and obtain more accurate recommendations via natural language instructions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge