Keping Yu
Waseda University
Generative Adversarial Learning for Intelligent Trust Management in 6G Wireless Networks
Aug 02, 2022



Abstract:Emerging six generation (6G) is the integration of heterogeneous wireless networks, which can seamlessly support anywhere and anytime networking. But high Quality-of-Trust should be offered by 6G to meet mobile user expectations. Artificial intelligence (AI) is considered as one of the most important components in 6G. Then AI-based trust management is a promising paradigm to provide trusted and reliable services. In this article, a generative adversarial learning-enabled trust management method is presented for 6G wireless networks. Some typical AI-based trust management schemes are first reviewed, and then a potential heterogeneous and intelligent 6G architecture is introduced. Next, the integration of AI and trust management is developed to optimize the intelligence and security. Finally, the presented AI-based trust management method is applied to secure clustering to achieve reliable and real-time communications. Simulation results have demonstrated its excellent performance in guaranteeing network security and service quality.
An Intelligent Trust Cloud Management Method for Secure Clustering in 5G enabled Internet of Medical Things
Jul 19, 2022



Abstract:5G edge computing enabled Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is an efficient technology to provide decentralized medical services while Device-to-device (D2D) communication is a promising paradigm for future 5G networks. To assure secure and reliable communication in 5G edge computing and D2D enabled IoMT systems, this paper presents an intelligent trust cloud management method. Firstly, an active training mechanism is proposed to construct the standard trust clouds. Secondly, individual trust clouds of the IoMT devices can be established through fuzzy trust inferring and recommending. Thirdly, a trust classification scheme is proposed to determine whether an IoMT device is malicious. Finally, a trust cloud update mechanism is presented to make the proposed trust management method adaptive and intelligent under an open wireless medium. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method can effectively address the trust uncertainty issue and improve the detection accuracy of malicious devices.
An Intelligent Deterministic Scheduling Method for Ultra-Low Latency Communication in Edge Enabled Industrial Internet of Things
Jul 17, 2022



Abstract:Edge enabled Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platform is of great significance to accelerate the development of smart industry. However, with the dramatic increase in real-time IIoT applications, it is a great challenge to support fast response time, low latency, and efficient bandwidth utilization. To address this issue, Time Sensitive Network (TSN) is recently researched to realize low latency communication via deterministic scheduling. To the best of our knowledge, the combinability of multiple flows, which can significantly affect the scheduling performance, has never been systematically analyzed before. In this article, we first analyze the combinability problem. Then a non-collision theory based deterministic scheduling (NDS) method is proposed to achieve ultra-low latency communication for the time-sensitive flows. Moreover, to improve bandwidth utilization, a dynamic queue scheduling (DQS) method is presented for the best-effort flows. Experiment results demonstrate that NDS/DQS can well support deterministic ultra-low latency services and guarantee efficient bandwidth utilization.
Integration of Blockchain and Edge Computing in Internet of Things: A Survey
May 26, 2022Abstract:As an important technology to ensure data security, consistency, traceability, etc., blockchain has been increasingly used in Internet of Things (IoT) applications. The integration of blockchain and edge computing can further improve the resource utilization in terms of network, computing, storage, and security. This paper aims to present a survey on the integration of blockchain and edge computing. In particular, we first give an overview of blockchain and edge computing. We then present a general architecture of an integration of blockchain and edge computing system. We next study how to utilize blockchain to benefit edge computing, as well as how to use edge computing to benefit blockchain. We also discuss the issues brought by the integration of blockchain and edge computing system and solutions from perspectives of resource management, joint optimization, data management, computation offloading and security mechanism. Finally, we analyze and summarize the existing challenges posed by the integration of blockchain and edge computing system and the potential solutions in the future.
Question-Aware Memory Network for Multi-hop Question Answering in Human-Robot Interaction
Apr 27, 2021
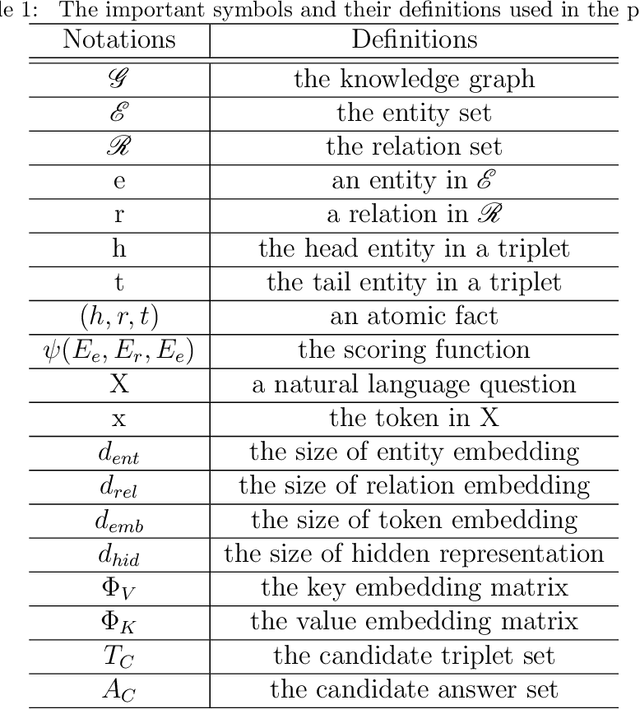

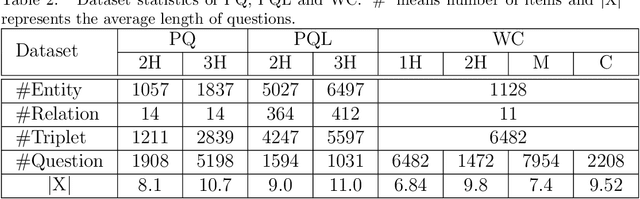
Abstract:Knowledge graph question answering is an important technology in intelligent human-robot interaction, which aims at automatically giving answer to human natural language question with the given knowledge graph. For the multi-relation question with higher variety and complexity, the tokens of the question have different priority for the triples selection in the reasoning steps. Most existing models take the question as a whole and ignore the priority information in it. To solve this problem, we propose question-aware memory network for multi-hop question answering, named QA2MN, to update the attention on question timely in the reasoning process. In addition, we incorporate graph context information into knowledge graph embedding model to increase the ability to represent entities and relations. We use it to initialize the QA2MN model and fine-tune it in the training process. We evaluate QA2MN on PathQuestion and WorldCup2014, two representative datasets for complex multi-hop question answering. The result demonstrates that QA2MN achieves state-of-the-art Hits@1 accuracy on the two datasets, which validates the effectiveness of our model.
Secure Artificial Intelligence of Things for Implicit Group Recommendations
Apr 23, 2021



Abstract:The emergence of Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) has provided novel insights for many social computing applications such as group recommender systems. As distance among people has been greatly shortened, it has been a more general demand to provide personalized services to groups instead of individuals. In order to capture group-level preference features from individuals, existing methods were mostly established via aggregation and face two aspects of challenges: secure data management workflow is absent, and implicit preference feedbacks is ignored. To tackle current difficulties, this paper proposes secure Artificial Intelligence of Things for implicit Group Recommendations (SAIoT-GR). As for hardware module, a secure IoT structure is developed as the bottom support platform. As for software module, collaborative Bayesian network model and non-cooperative game are can be introduced as algorithms. Such a secure AIoT architecture is able to maximize the advantages of the two modules. In addition, a large number of experiments are carried out to evaluate the performance of the SAIoT-GR in terms of efficiency and robustness.
Implicit Feedback-based Group Recommender System for Internet of Thing Applications
Jan 29, 2021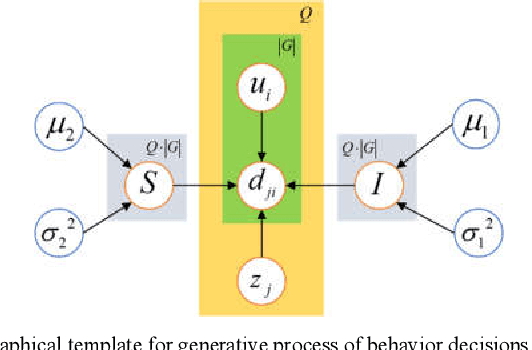
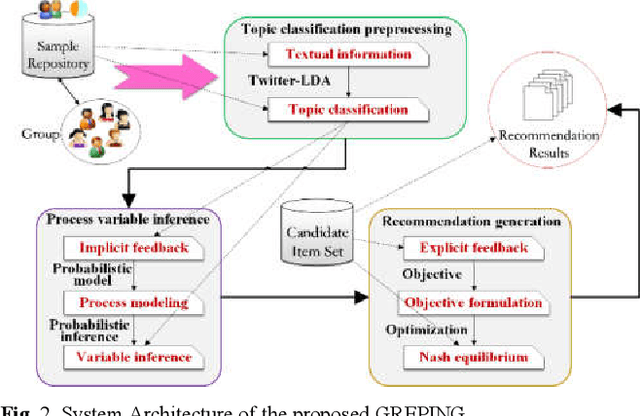
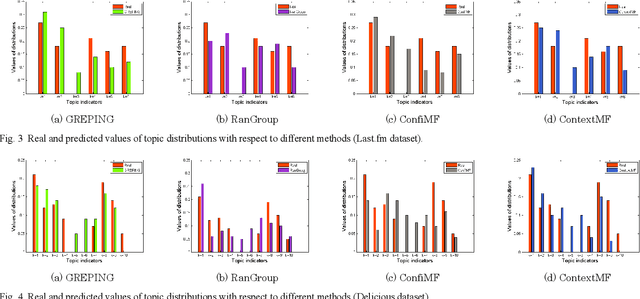
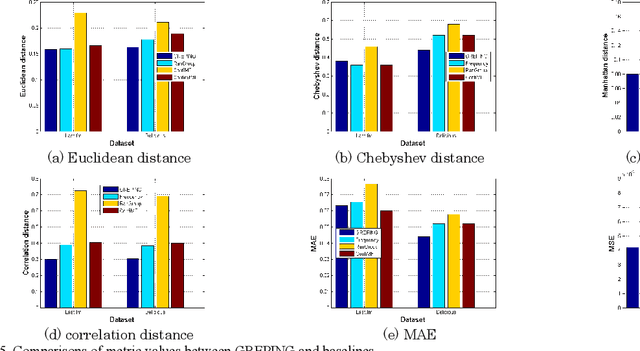
Abstract:With the prevalence of Internet of Things (IoT)-based social media applications, the distance among people has been greatly shortened. As a result, recommender systems in IoT-based social media need to be developed oriented to groups of users rather than individual users. However, existing methods were highly dependent on explicit preference feedbacks, ignoring scenarios of implicit feedback. To remedy such gap, this paper proposes an implicit feedback-based group recommender system using probabilistic inference and non-cooperative game(GREPING) for IoT-based social media. Particularly, unknown process variables can be estimated from observable implicit feedbacks via Bayesian posterior probability inference. In addition, the globally optimal recommendation results can be calculated with the aid of non-cooperative game. Two groups of experiments are conducted to assess the GREPING from two aspects: efficiency and robustness. Experimental results show obvious promotion and considerable stability of the GREPING compared to baseline methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge