Jerry Chun-Wei Lin
Enhancing Psychologists' Understanding through Explainable Deep Learning Framework for ADHD Diagnosis
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that is challenging to diagnose and requires advanced approaches for reliable and transparent identification and classification. It is characterized by a pattern of inattention, hyperactivity and impulsivity that is more severe and more frequent than in individuals with a comparable level of development. In this paper, an explainable framework based on a fine-tuned hybrid Deep Neural Network (DNN) and Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) called HyExDNN-RNN model is proposed for ADHD detection, multi-class categorization, and decision interpretation. This framework not only detects ADHD, but also provides interpretable insights into the diagnostic process so that psychologists can better understand and trust the results of the diagnosis. We use the Pearson correlation coefficient for optimal feature selection and machine and deep learning models for experimental analysis and comparison. We use a standardized technique for feature reduction, model selection and interpretation to accurately determine the diagnosis rate and ensure the interpretability of the proposed framework. Our framework provided excellent results on binary classification, with HyExDNN-RNN achieving an F1 score of 99% and 94.2% on multi-class categorization. XAI approaches, in particular SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) and Permutation Feature Importance (PFI), provided important insights into the importance of features and the decision logic of models. By combining AI with human expertise, we aim to bridge the gap between advanced computational techniques and practical psychological applications. These results demonstrate the potential of our framework to assist in ADHD diagnosis and interpretation.
Heterogeneous Federated Learning Systems for Time-Series Power Consumption Prediction with Multi-Head Embedding Mechanism
Jan 21, 2025Abstract:Time-series prediction is increasingly popular in a variety of applications, such as smart factories and smart transportation. Researchers have used various techniques to predict power consumption, but existing models lack discussion of collaborative learning and privacy issues among multiple clients. To address these issues, we propose Multi-Head Heterogeneous Federated Learning (MHHFL) systems that consist of multiple head networks, which independently act as carriers for federated learning. In the federated period, each head network is embedded into 2-dimensional vectors and shared with the centralized source pool. MHHFL then selects appropriate source networks and blends the head networks as knowledge transfer in federated learning. The experimental results show that the proposed MHHFL systems significantly outperform the benchmark and state-of-the-art systems and reduce the prediction error by 24.9% to 94.1%. The ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed mechanisms in the MHHFL (head network embedding and selection mechanisms), which significantly outperforms traditional federated average and random transfer.
Heterogeneous Federated Learning System for Sparse Healthcare Time-Series Prediction
Jan 21, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a heterogeneous federated learning (HFL) system for sparse time series prediction in healthcare, which is a decentralized federated learning algorithm with heterogeneous transfers. We design dense and sparse feature tensors to deal with the sparsity of data sources. Heterogeneous federated learning is developed to share asynchronous parts of networks and select appropriate models for knowledge transfer. Experimental results show that the proposed HFL achieves the lowest prediction error among all benchmark systems on eight out of ten prediction tasks, with MSE reduction of 94.8%, 48.3%, and 52.1% compared to the benchmark systems. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of HFL in transferring knowledge from heterogeneous domains, especially in the smaller target domain. Ablation studies then demonstrate the effectiveness of the designed mechanisms for heterogeneous domain selection and switching in predicting healthcare time series with privacy, model security, and heterogeneous knowledge transfer.
Distributed Multi-Head Learning Systems for Power Consumption Prediction
Jan 21, 2025Abstract:As more and more automatic vehicles, power consumption prediction becomes a vital issue for task scheduling and energy management. Most research focuses on automatic vehicles in transportation, but few focus on automatic ground vehicles (AGVs) in smart factories, which face complex environments and generate large amounts of data. There is an inevitable trade-off between feature diversity and interference. In this paper, we propose Distributed Multi-Head learning (DMH) systems for power consumption prediction in smart factories. Multi-head learning mechanisms are proposed in DMH to reduce noise interference and improve accuracy. Additionally, DMH systems are designed as distributed and split learning, reducing the client-to-server transmission cost, sharing knowledge without sharing local data and models, and enhancing the privacy and security levels. Experimental results show that the proposed DMH systems rank in the top-2 on most datasets and scenarios. DMH-E system reduces the error of the state-of-the-art systems by 14.5% to 24.0%. Effectiveness studies demonstrate the effectiveness of Pearson correlation-based feature engineering, and feature grouping with the proposed multi-head learning further enhances prediction performance.
Explainability of Highly Associated Fuzzy Churn Patterns in Binary Classification
Oct 21, 2024Abstract:Customer churn, particularly in the telecommunications sector, influences both costs and profits. As the explainability of models becomes increasingly important, this study emphasizes not only the explainability of customer churn through machine learning models, but also the importance of identifying multivariate patterns and setting soft bounds for intuitive interpretation. The main objective is to use a machine learning model and fuzzy-set theory with top-\textit{k} HUIM to identify highly associated patterns of customer churn with intuitive identification, referred to as Highly Associated Fuzzy Churn Patterns (HAFCP). Moreover, this method aids in uncovering association rules among multiple features across low, medium, and high distributions. Such discoveries are instrumental in enhancing the explainability of findings. Experiments show that when the top-5 HAFCPs are included in five datasets, a mixture of performance results is observed, with some showing notable improvements. It becomes clear that high importance features enhance explanatory power through their distribution and patterns associated with other features. As a result, the study introduces an innovative approach that improves the explainability and effectiveness of customer churn prediction models.
A Utility-Mining-Driven Active Learning Approach for Analyzing Clickstream Sequences
Oct 09, 2024Abstract:In rapidly evolving e-commerce industry, the capability of selecting high-quality data for model training is essential. This study introduces the High-Utility Sequential Pattern Mining using SHAP values (HUSPM-SHAP) model, a utility mining-based active learning strategy to tackle this challenge. We found that the parameter settings for positive and negative SHAP values impact the model's mining outcomes, introducing a key consideration into the active learning framework. Through extensive experiments aimed at predicting behaviors that do lead to purchases or not, the designed HUSPM-SHAP model demonstrates its superiority across diverse scenarios. The model's ability to mitigate labeling needs while maintaining high predictive performance is highlighted. Our findings demonstrate the model's capability to refine e-commerce data processing, steering towards more streamlined, cost-effective prediction modeling.
Human-free Prompted Based Anomaly Detection: prompt optimization with Meta-guiding prompt scheme
Jun 26, 2024Abstract:Pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs) are highly adaptable to various downstream tasks through few-shot learning, making prompt-based anomaly detection a promising approach. Traditional methods depend on human-crafted prompts that require prior knowledge of specific anomaly types. Our goal is to develop a human-free prompt-based anomaly detection framework that optimally learns prompts through data-driven methods, eliminating the need for human intervention. The primary challenge in this approach is the lack of anomalous samples during the training phase. Additionally, the Vision Transformer (ViT)-based image encoder in VLMs is not ideal for pixel-wise anomaly segmentation due to a locality feature mismatch between the original image and the output feature map. To tackle the first challenge, we have developed the Object-Attention Anomaly Generation Module (OAGM) to synthesize anomaly samples for training. Furthermore, our Meta-Guiding Prompt-Tuning Scheme (MPTS) iteratively adjusts the gradient-based optimization direction of learnable prompts to avoid overfitting to the synthesized anomalies. For the second challenge, we propose Locality-Aware Attention, which ensures that each local patch feature attends only to nearby patch features, preserving the locality features corresponding to their original locations. This framework allows for the optimal prompt embeddings by searching in the continuous latent space via backpropagation, free from human semantic constraints. Additionally, the modified locality-aware attention improves the precision of pixel-wise anomaly segmentation.
Large Language Models in Education: Vision and Opportunities
Nov 22, 2023


Abstract:With the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, large language models (LLMs) have become a hot research topic. Education plays an important role in human social development and progress. Traditional education faces challenges such as individual student differences, insufficient allocation of teaching resources, and assessment of teaching effectiveness. Therefore, the applications of LLMs in the field of digital/smart education have broad prospects. The research on educational large models (EduLLMs) is constantly evolving, providing new methods and approaches to achieve personalized learning, intelligent tutoring, and educational assessment goals, thereby improving the quality of education and the learning experience. This article aims to investigate and summarize the application of LLMs in smart education. It first introduces the research background and motivation of LLMs and explains the essence of LLMs. It then discusses the relationship between digital education and EduLLMs and summarizes the current research status of educational large models. The main contributions are the systematic summary and vision of the research background, motivation, and application of large models for education (LLM4Edu). By reviewing existing research, this article provides guidance and insights for educators, researchers, and policy-makers to gain a deep understanding of the potential and challenges of LLM4Edu. It further provides guidance for further advancing the development and application of LLM4Edu, while still facing technical, ethical, and practical challenges requiring further research and exploration.
HTPS: Heterogeneous Transferring Prediction System for Healthcare Datasets
May 02, 2023Abstract:Medical internet of things leads to revolutionary improvements in medical services, also known as smart healthcare. With the big healthcare data, data mining and machine learning can assist wellness management and intelligent diagnosis, and achieve the P4-medicine. However, healthcare data has high sparsity and heterogeneity. In this paper, we propose a Heterogeneous Transferring Prediction System (HTPS). Feature engineering mechanism transforms the dataset into sparse and dense feature matrices, and autoencoders in the embedding networks not only embed features but also transfer knowledge from heterogeneous datasets. Experimental results show that the proposed HTPS outperforms the benchmark systems on various prediction tasks and datasets, and ablation studies present the effectiveness of each designed mechanism. Experimental results demonstrate the negative impact of heterogeneous data on benchmark systems and the high transferability of the proposed HTPS.
Itemset Utility Maximization with Correlation Measure
Aug 26, 2022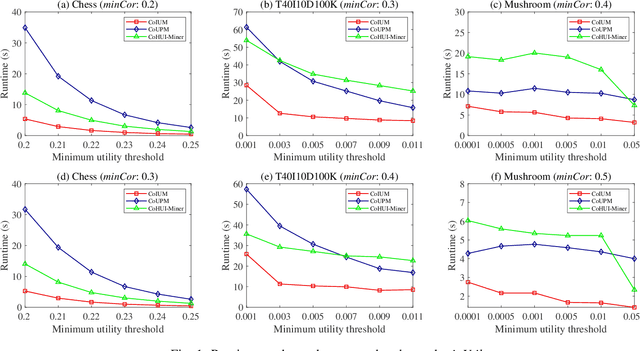
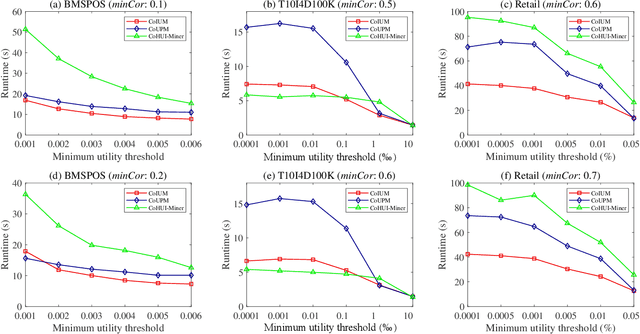
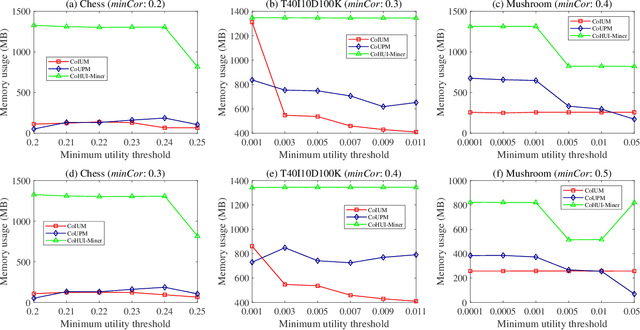
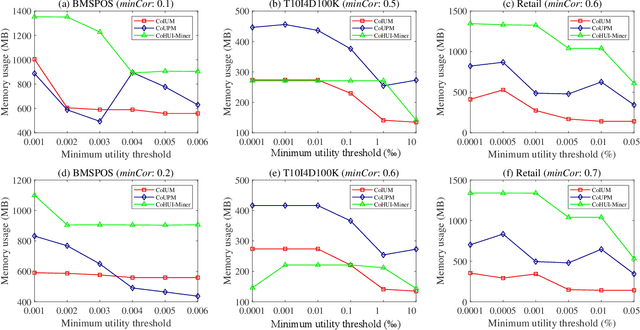
Abstract:As an important data mining technology, high utility itemset mining (HUIM) is used to find out interesting but hidden information (e.g., profit and risk). HUIM has been widely applied in many application scenarios, such as market analysis, medical detection, and web click stream analysis. However, most previous HUIM approaches often ignore the relationship between items in an itemset. Therefore, many irrelevant combinations (e.g., \{gold, apple\} and \{notebook, book\}) are discovered in HUIM. To address this limitation, many algorithms have been proposed to mine correlated high utility itemsets (CoHUIs). In this paper, we propose a novel algorithm called the Itemset Utility Maximization with Correlation Measure (CoIUM), which considers both a strong correlation and the profitable values of the items. Besides, the novel algorithm adopts a database projection mechanism to reduce the cost of database scanning. Moreover, two upper bounds and four pruning strategies are utilized to effectively prune the search space. And a concise array-based structure named utility-bin is used to calculate and store the adopted upper bounds in linear time and space. Finally, extensive experimental results on dense and sparse datasets demonstrate that CoIUM significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art algorithms in terms of runtime and memory consumption.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge