Justin K. Yim
Steerable rolling of a 1-DoF robot using an internal pendulum
Apr 16, 2025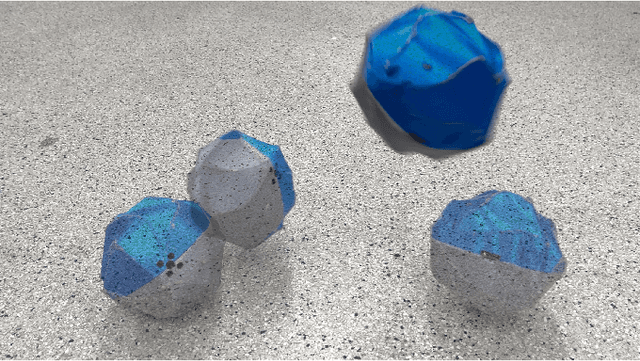
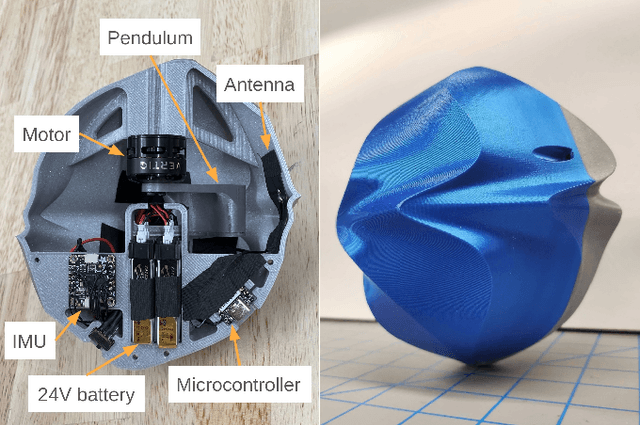
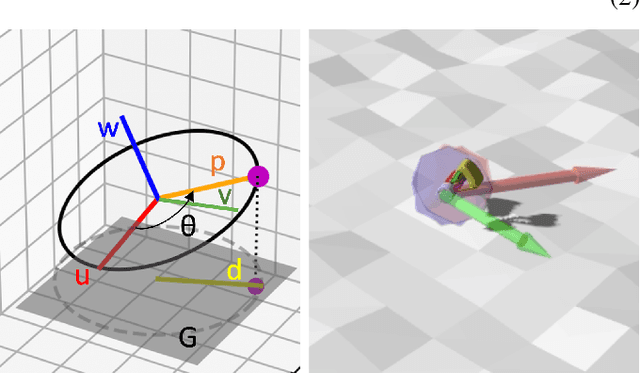
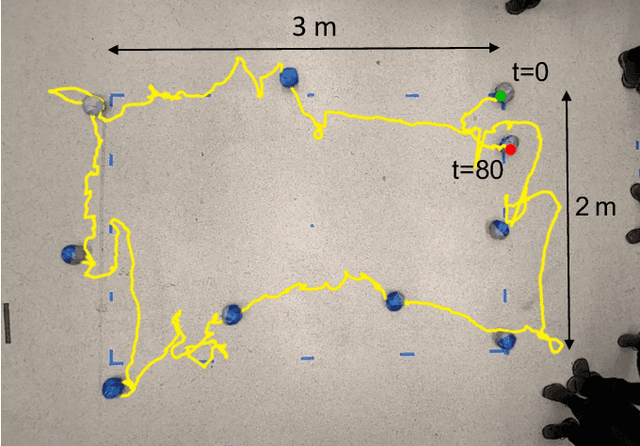
Abstract:We present ROCK (Rolling One-motor Controlled rocK), a 1 degree-of-freedom robot consisting of a round shell and an internal pendulum. An uneven shell surface enables steering by using only the movement of the pendulum, allowing for mechanically simple designs that may be feasible to scale to large quantities or small sizes. We train a control policy using reinforcement learning in simulation and deploy it onto the robot to complete a rectangular trajectory.
Pinto: A latched spring actuated robot for jumping and perching
Sep 13, 2024Abstract:Arboreal environments challenge current robots but are deftly traversed by many familiar animal locomotors such as squirrels. We present a small, 450 g robot "Pinto" developed for tree-jumping, a behavior seen in squirrels but rarely in legged robots: jumping from the ground onto a vertical tree trunk. We develop a powerful and lightweight latched series-elastic actuator using a twisted string and carbon fiber springs. We consider the effects of scaling down conventional quadrupeds and experimentally show how storing energy in a parallel-elastic fashion using a latch increases jump energy compared to series-elastic or springless strategies. By switching between series and parallel-elastic modes with our latched 5-bar leg mechanism, Pinto executes energetic jumps as well as maintains continuous control during shorter bounding motions. We also develop sprung 2-DoF arms equipped with spined grippers to grasp tree bark for high-speed perching following a jump.
Double-Anonymous Review for Robotics
Jun 14, 2024Abstract:Prior research has investigated the benefits and costs of double-anonymous review (DAR, also known as double-blind review) in comparison to single-anonymous review (SAR) and open review (OR). Several review papers have attempted to compile experimental results in peer review research both broadly and in engineering and computer science. This document summarizes prior research in peer review that may inform decisions about the format of peer review in the field of robotics and makes some recommendations for potential next steps for robotics publication.
Cooperative Modular Manipulation with Numerous Cable-Driven Robots for Assistive Construction and Gap Crossing
Mar 19, 2024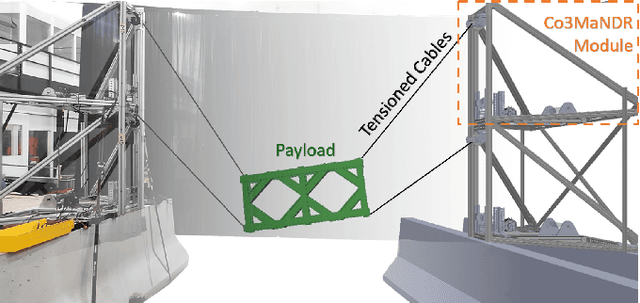
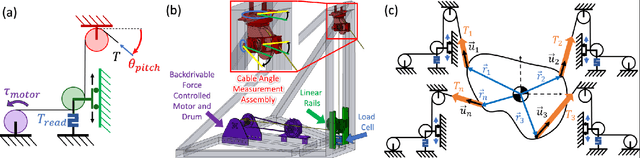
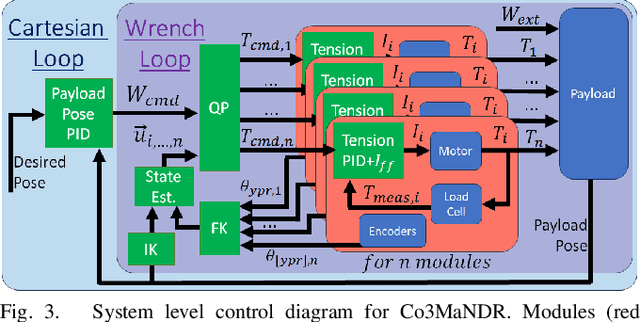
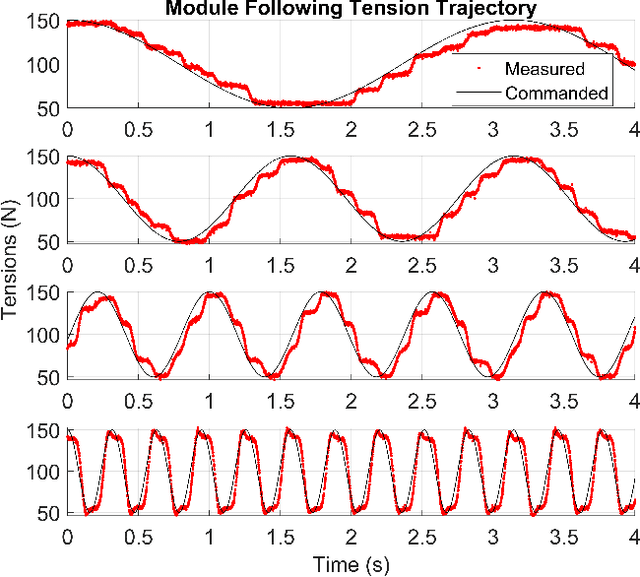
Abstract:Soldiers in the field often need to cross negative obstacles, such as rivers or canyons, to reach goals or safety. Military gap crossing involves on-site temporary bridges construction. However, this procedure is conducted with dangerous, time and labor intensive operations, and specialized machinery. We envision a scalable robotic solution inspired by advancements in force-controlled and Cable Driven Parallel Robots (CDPRs); this solution can address the challenges inherent in this transportation problem, achieving fast, efficient, and safe deployment and field operations. We introduce the embodied vision in Co3MaNDR, a solution to the military gap crossing problem, a distributed robot consisting of several modules simultaneously pulling on a central payload, controlling the cables' tensions to achieve complex objectives, such as precise trajectory tracking or force amplification. Hardware experiments demonstrate teleoperation of a payload, trajectory following, and the sensing and amplification of operators' applied physical forces during slow operations. An operator was shown to manipulate a 27.2 kg (60 lb) payload with an average force utilization of 14.5\% of its weight. Results indicate that the system can be scaled up to heavier payloads without compromising performance or introducing superfluous complexity. This research lays a foundation to expand CDPR technology to uncoordinated and unstable mobile platforms in unknown environments.
The Simplest Walking Robot: A bipedal robot with one actuator and two rigid bodies
Aug 16, 2023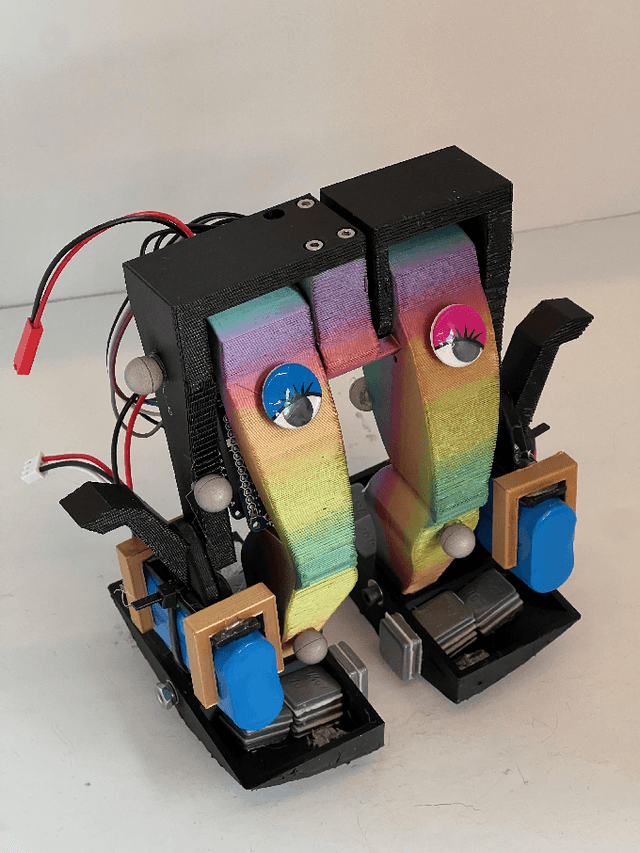
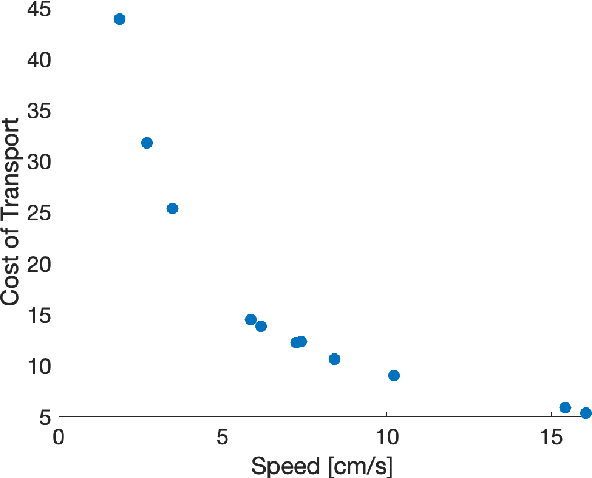
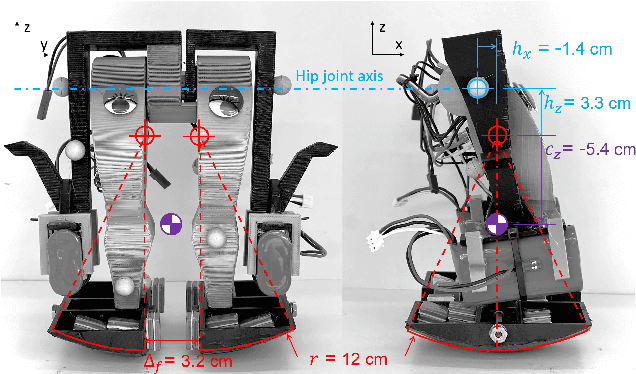
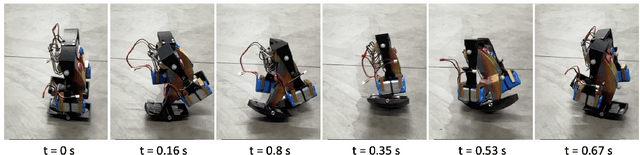
Abstract:We present the design and experimental results of the first 1-DOF, hip-actuated bipedal robot. While passive dynamic walking is simple by nature, many existing bipeds inspired by this form of walking are complex in control, mechanical design, or both. Our design using only two rigid bodies connected by a single motor aims to enable exploration of walking at smaller sizes where more complex designs cannot be constructed. The walker, "Mugatu", is self-contained and autonomous, open-loop stable over a range of input parameters, able to stop and start from standing, and able to control its heading left and right. We analyze the mechanical design and distill down a set of design rules that enable these behaviors. Experimental evaluations measure speed, energy consumption, and steering.
Proprioception and reaction for walking among entanglements
Apr 04, 2023



Abstract:Entanglements like vines and branches in natural settings or cords and pipes in human spaces prevent mobile robots from accessing many environments. Legged robots should be effective in these settings, and more so than wheeled or tracked platforms, but naive controllers quickly become entangled and stuck. In this paper we present a method for proprioception aimed specifically at the task of sensing entanglements of a robot's legs as well as a reaction strategy to disentangle legs during their swing phase as they advance to their next foothold. We demonstrate our proprioception and reaction strategy enables traversal of entanglements of many stiffnesses and geometries succeeding in 14 out of 16 trials in laboratory tests, as well as a natural outdoor environment.
Proprioception and Tail Control Enable Extreme Terrain Traversal by Quadruped Robots
Mar 08, 2023



Abstract:Legged robots leverage ground contacts and the reaction forces they provide to achieve agile locomotion. However, uncertainty coupled with contact discontinuities can lead to failure, especially in real-world environments with unexpected height variations such as rocky hills or curbs. To enable dynamic traversal of extreme terrain, this work introduces 1) a proprioception-based gait planner for estimating unknown hybrid events due to elevation changes and responding by modifying contact schedules and planned footholds online, and 2) a two-degree-of-freedom tail for improving contact-independent control and a corresponding decoupled control scheme for better versatility and efficiency. Simulation results show that the gait planner significantly improves stability under unforeseen terrain height changes compared to methods that assume fixed contact schedules and footholds. Further, testing shows the tail is most effective at maintaining stability when encountering a terrain change with an initial angular disturbance. The results show that these approaches work synergistically to stabilize locomotion with elevation changes up to 1.5 times the leg length and tilted initial states.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge