Junting Wang
Multi-modal Relational Item Representation Learning for Inferring Substitutable and Complementary Items
Jul 29, 2025Abstract:We introduce a novel self-supervised multi-modal relational item representation learning framework designed to infer substitutable and complementary items. Existing approaches primarily focus on modeling item-item associations deduced from user behaviors using graph neural networks (GNNs) or leveraging item content information. However, these methods often overlook critical challenges, such as noisy user behavior data and data sparsity due to the long-tailed distribution of these behaviors. In this paper, we propose MMSC, a self-supervised multi-modal relational item representation learning framework to address these challenges. Specifically, MMSC consists of three main components: (1) a multi-modal item representation learning module that leverages a multi-modal foundational model and learns from item metadata, (2) a self-supervised behavior-based representation learning module that denoises and learns from user behavior data, and (3) a hierarchical representation aggregation mechanism that integrates item representations at both the semantic and task levels. Additionally, we leverage LLMs to generate augmented training data, further enhancing the denoising process during training. We conduct extensive experiments on five real-world datasets, showing that MMSC outperforms existing baselines by 26.1% for substitutable recommendation and 39.2% for complementary recommendation. In addition, we empirically show that MMSC is effective in modeling cold-start items.
A Multimodal Data Fusion Generative Adversarial Network for Real Time Underwater Sound Speed Field Construction
Jul 16, 2025



Abstract:Sound speed profiles (SSPs) are essential parameters underwater that affects the propagation mode of underwater signals and has a critical impact on the energy efficiency of underwater acoustic communication and accuracy of underwater acoustic positioning. Traditionally, SSPs can be obtained by matching field processing (MFP), compressive sensing (CS), and deep learning (DL) methods. However, existing methods mainly rely on on-site underwater sonar observation data, which put forward strict requirements on the deployment of sonar observation systems. To achieve high-precision estimation of sound velocity distribution in a given sea area without on-site underwater data measurement, we propose a multi-modal data-fusion generative adversarial network model with residual attention block (MDF-RAGAN) for SSP construction. To improve the model's ability for capturing global spatial feature correlations, we embedded the attention mechanisms, and use residual modules for deeply capturing small disturbances in the deep ocean sound velocity distribution caused by changes of SST. Experimental results on real open dataset show that the proposed model outperforms other state-of-the-art methods, which achieves an accuracy with an error of less than 0.3m/s. Specifically, MDF-RAGAN not only outperforms convolutional neural network (CNN) and spatial interpolation (SITP) by nearly a factor of two, but also achieves about 65.8\% root mean square error (RMSE) reduction compared to mean profile, which fully reflects the enhancement of overall profile matching by multi-source fusion and cross-modal attention.
A Zero-Shot Generalization Framework for LLM-Driven Cross-Domain Sequential Recommendation
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:Zero-shot cross-domain sequential recommendation (ZCDSR) enables predictions in unseen domains without the need for additional training or fine-tuning, making it particularly valuable in data-sparse environments where traditional models struggle. Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have greatly improved ZCDSR by leveraging rich pretrained representations to facilitate cross-domain knowledge transfer. However, a key challenge persists: domain semantic bias, which arises from variations in vocabulary and content focus across domains. This misalignment leads to inconsistencies in item embeddings and hinders generalization. To address this issue, we propose a novel framework designed to enhance LLM-based ZCDSR by improving cross-domain alignment at both the item and sequential levels. At the item level, we introduce a generalization loss that promotes inter-domain compactness by aligning embeddings of similar items across domains while maintaining intra-domain diversity to preserve unique item characteristics. This prevents embeddings from becoming overly generic while ensuring effective transferability. At the sequential level, we develop a method for transferring user behavioral patterns by clustering user sequences in the source domain and applying attention-based aggregation for target domain inference. This dynamic adaptation of user embeddings allows effective zero-shot recommendations without requiring target-domain interactions. Comprehensive experiments across multiple datasets and domains demonstrate that our framework significantly improves sequential recommendation performance in the ZCDSR setting. By mitigating domain bias and enhancing the transferability of sequential patterns, our method provides a scalable and robust approach for achieving more effective zero-shot recommendations across domains.
A Pre-trained Sequential Recommendation Framework: Popularity Dynamics for Zero-shot Transfer
Jan 03, 2024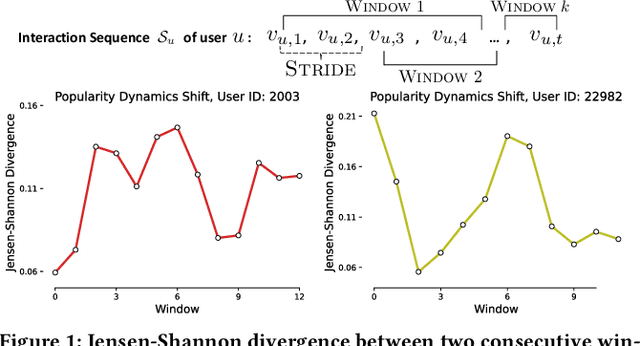
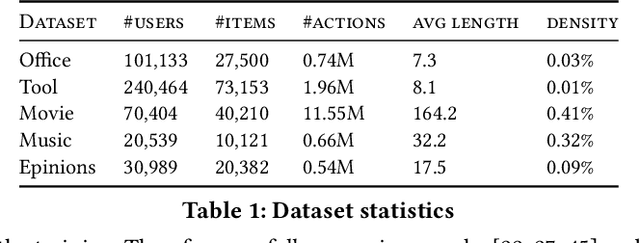
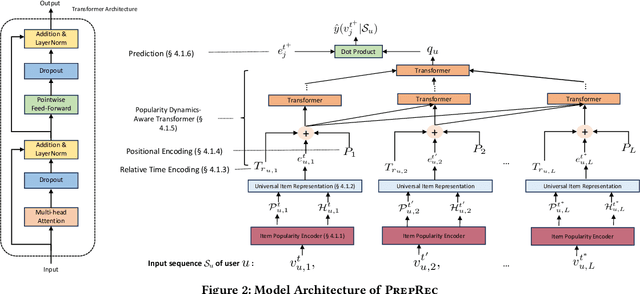
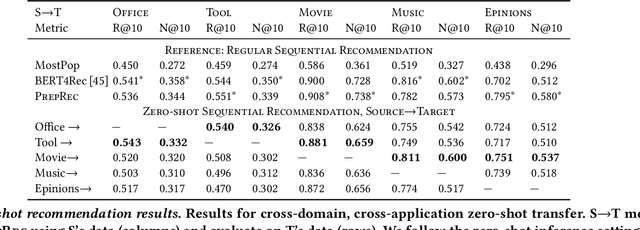
Abstract:Sequential recommenders are crucial to the success of online applications, \eg e-commerce, video streaming, and social media. While model architectures continue to improve, for every new application domain, we still have to train a new model from scratch for high quality recommendations. On the other hand, pre-trained language and vision models have shown great success in zero-shot or few-shot adaptation to new application domains. Inspired by the success of pre-trained models in peer AI fields, we propose a novel pre-trained sequential recommendation framework: PrepRec. We learn universal item representations by modeling item popularity dynamics. Through extensive experiments on five real-world datasets, we show that PrepRec, without any auxiliary information, can not only zero-shot transfer to a new domain, but achieve competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art sequential recommender models with only a fraction of the model size. In addition, with a simple post-hoc interpolation, PrepRec can improve the performance of existing sequential recommenders on average by 13.8\% in Recall@10 and 29.5% in NDCG@10. We provide an anonymized implementation of PrepRec at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/PrepRec--2F60/
Experimental Results of Underwater Sound Speed Profile Inversion by Few-shot Multi-task Learning
Oct 18, 2023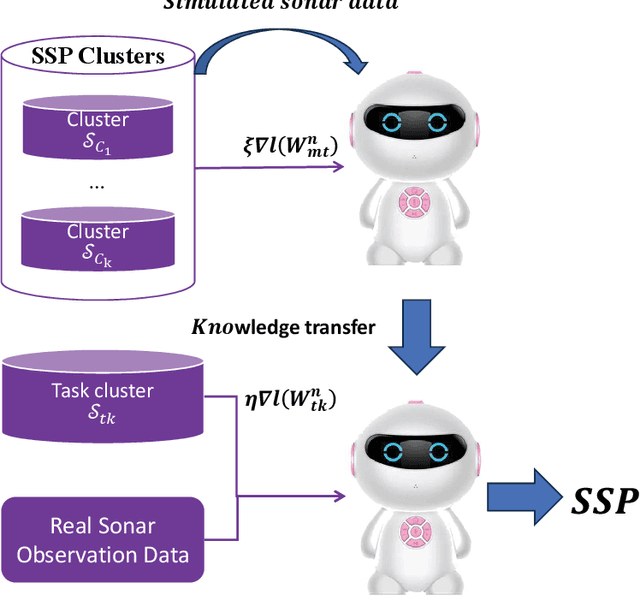
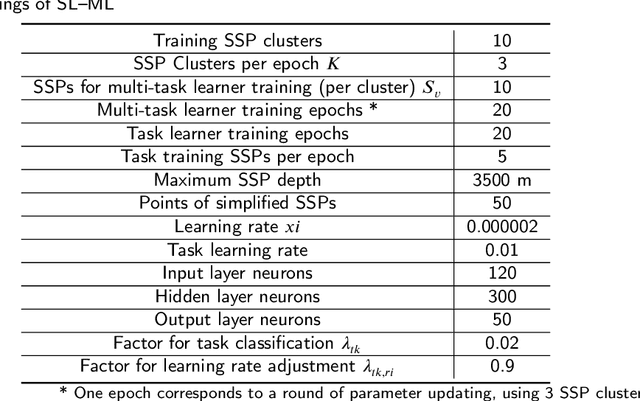
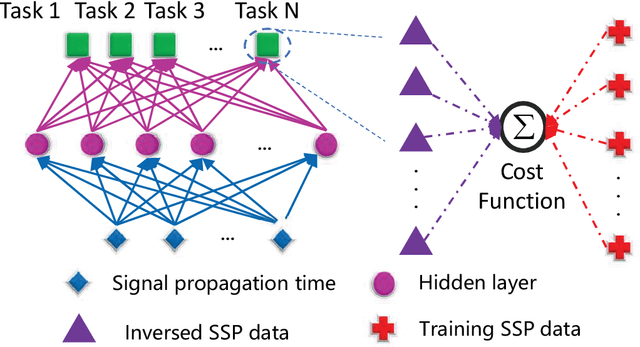
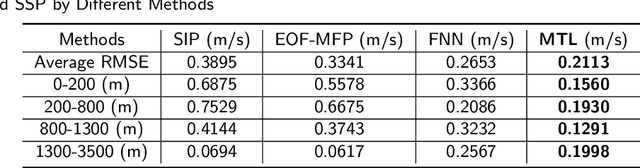
Abstract:Underwater Sound Speed Profile (SSP) distribution has great influence on the propagation mode of acoustic signal, thus the fast and accurate estimation of SSP is of great importance in building underwater observation systems. The state-of-the-art SSP inversion methods include frameworks of matched field processing (MFP), compressive sensing (CS), and feedforeward neural networks (FNN), among which the FNN shows better real-time performance while maintain the same level of accuracy. However, the training of FNN needs quite a lot historical SSP samples, which is diffcult to be satisfied in many ocean areas. This situation is called few-shot learning. To tackle this issue, we propose a multi-task learning (MTL) model with partial parameter sharing among different traning tasks. By MTL, common features could be extracted, thus accelerating the learning process on given tasks, and reducing the demand for reference samples, so as to enhance the generalization ability in few-shot learning. To verify the feasibility and effectiveness of MTL, a deep-ocean experiment was held in April 2023 at the South China Sea. Results shows that MTL outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of accuracy for SSP inversion, while inherits the real-time advantage of FNN during the inversion stage.
Underwater Sound Speed Profile Construction: A Review
Oct 12, 2023



Abstract:Real--time and accurate construction of regional sound speed profiles (SSP) is important for building underwater positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) systems as it greatly affect the signal propagation modes such as trajectory. In this paper, we summarizes and analyzes the current research status in the field of underwater SSP construction, and the mainstream methods include direct SSP measurement and SSP inversion. In the direct measurement method, we compare the performance of popular international commercial temperature, conductivity, and depth profilers (CTD). While for the inversion methods, the framework and basic principles of matched field processing (MFP), compressive sensing (CS), and deep learning (DL) for constructing SSP are introduced, and their advantages and disadvantages are compared. The traditional direct measurement method has good accuracy performance, but it usually takes a long time. The proposal of SSP inversion method greatly improves the convenience and real--time performance, but the accuracy is not as good as the direct measurement method. Currently, the SSP inversion relies on sonar observation data, making it difficult to apply to areas that couldn't be covered by underwater observation systems, and these methods are unable to predict the distribution of sound velocity at future times. How to comprehensively utilize multi-source data and provide elastic sound velocity distribution estimation services with different accuracy and real-time requirements for underwater users without sonar observation data is the mainstream trend in future research on SSP construction.
Pre-trained Neural Recommenders: A Transferable Zero-Shot Framework for Recommendation Systems
Sep 03, 2023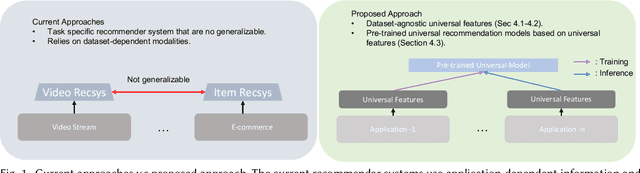
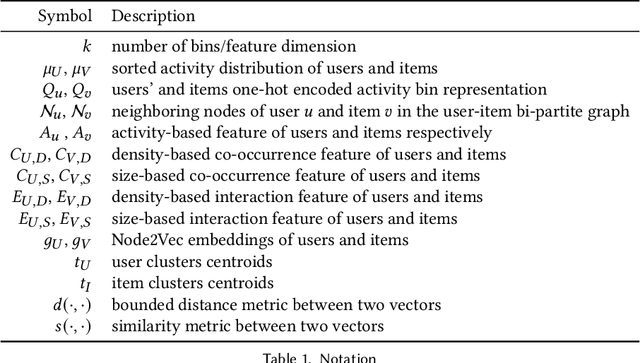
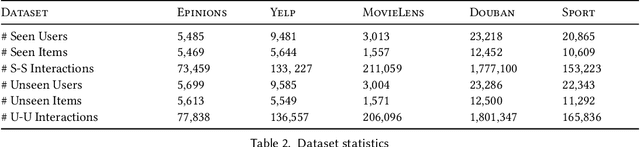
Abstract:Modern neural collaborative filtering techniques are critical to the success of e-commerce, social media, and content-sharing platforms. However, despite technical advances -- for every new application domain, we need to train an NCF model from scratch. In contrast, pre-trained vision and language models are routinely applied to diverse applications directly (zero-shot) or with limited fine-tuning. Inspired by the impact of pre-trained models, we explore the possibility of pre-trained recommender models that support building recommender systems in new domains, with minimal or no retraining, without the use of any auxiliary user or item information. Zero-shot recommendation without auxiliary information is challenging because we cannot form associations between users and items across datasets when there are no overlapping users or items. Our fundamental insight is that the statistical characteristics of the user-item interaction matrix are universally available across different domains and datasets. Thus, we use the statistical characteristics of the user-item interaction matrix to identify dataset-independent representations for users and items. We show how to learn universal (i.e., supporting zero-shot adaptation without user or item auxiliary information) representations for nodes and edges from the bipartite user-item interaction graph. We learn representations by exploiting the statistical properties of the interaction data, including user and item marginals, and the size and density distributions of their clusters.
Beyond Localized Graph Neural Networks: An Attributed Motif Regularization Framework
Sep 11, 2020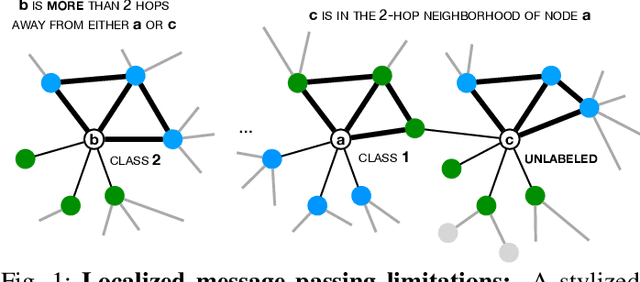
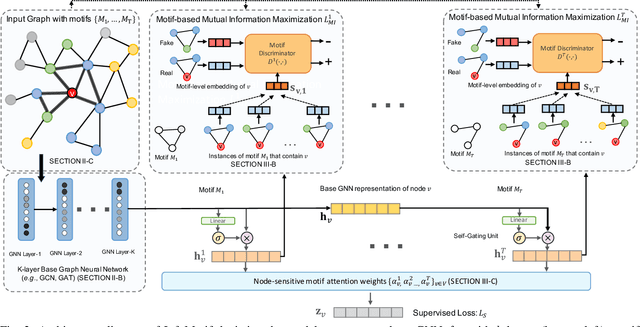
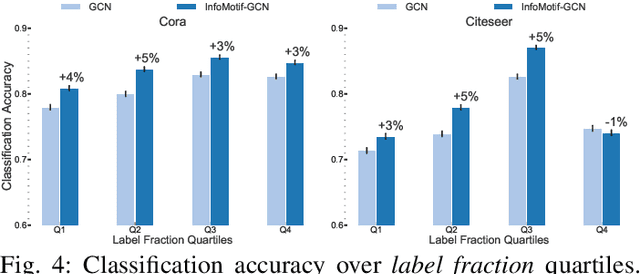
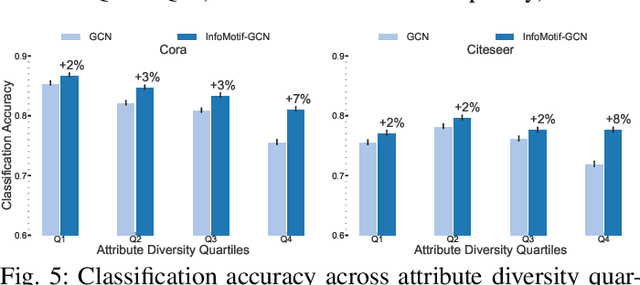
Abstract:We present InfoMotif, a new semi-supervised, motif-regularized, learning framework over graphs. We overcome two key limitations of message passing in popular graph neural networks (GNNs): localization (a k-layer GNN cannot utilize features outside the k-hop neighborhood of the labeled training nodes) and over-smoothed (structurally indistinguishable) representations. We propose the concept of attributed structural roles of nodes based on their occurrence in different network motifs, independent of network proximity. Two nodes share attributed structural roles if they participate in topologically similar motif instances over co-varying sets of attributes. Further, InfoMotif achieves architecture independence by regularizing the node representations of arbitrary GNNs via mutual information maximization. Our training curriculum dynamically prioritizes multiple motifs in the learning process without relying on distributional assumptions in the underlying graph or the learning task. We integrate three state-of-the-art GNNs in our framework, to show significant gains (3-10% accuracy) across six diverse, real-world datasets. We see stronger gains for nodes with sparse training labels and diverse attributes in local neighborhood structures.
An Induced Multi-Relational Framework for Answer Selection in Community Question Answer Platforms
Nov 16, 2019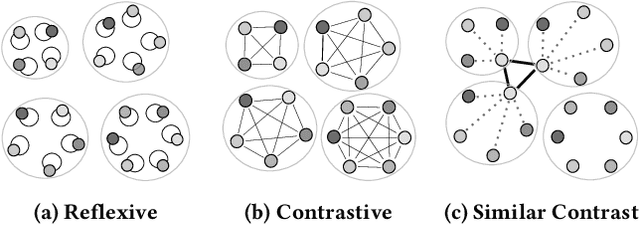
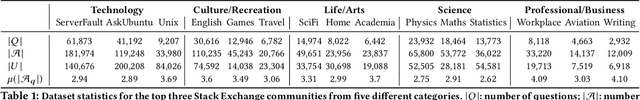
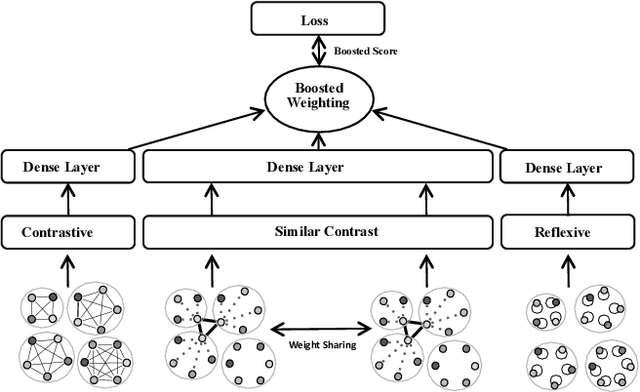
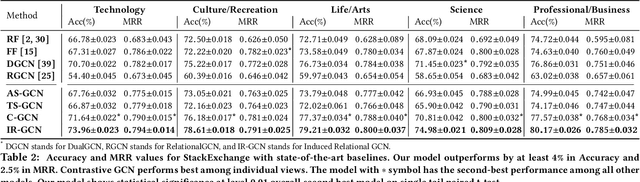
Abstract:This paper addresses the question of identifying the best candidate answer to a question on Community Question Answer (CQA) forums. The problem is important because Individuals often visit CQA forums to seek answers to nuanced questions. We develop a novel induced relational graph convolutional network (IR-GCN) framework to address the question. We make three contributions. First, we introduce a modular framework that separates the construction of the graph with the label selection mechanism. We use equivalence relations to induce a graph comprising cliques and identify two label assignment mechanisms---label contrast, label sharing. Then, we show how to encode these assignment mechanisms in GCNs. Second, we show that encoding contrast creates discriminative magnification---enhancing the separation between nodes in the embedding space. Third, we show a surprising result---boosting techniques improve learning over familiar stacking, fusion, or aggregation approaches for neural architectures. We show strong results over the state-of-the-art neural baselines in extensive experiments on 50 StackExchange communities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge