Junhao Huang
How to Set the Learning Rate for Large-Scale Pre-training?
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Optimal configuration of the learning rate (LR) is a fundamental yet formidable challenge in large-scale pre-training. Given the stringent trade-off between training costs and model performance, the pivotal question is whether the optimal LR can be accurately extrapolated from low-cost experiments. In this paper, we formalize this investigation into two distinct research paradigms: Fitting and Transfer. Within the Fitting Paradigm, we innovatively introduce a Scaling Law for search factor, effectively reducing the search complexity from O(n^3) to O(n*C_D*C_η) via predictive modeling. Within the Transfer Paradigm, we extend the principles of $μ$Transfer to the Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture, broadening its applicability to encompass model depth, weight decay, and token horizons. By pushing the boundaries of existing hyperparameter research in terms of scale, we conduct a comprehensive comparison between these two paradigms. Our empirical results challenge the scalability of the widely adopted $μ$ Transfer in large-scale pre-training scenarios. Furthermore, we provide a rigorous analysis through the dual lenses of training stability and feature learning to elucidate the underlying reasons why module-wise parameter tuning underperforms in large-scale settings. This work offers systematic practical guidelines and a fresh theoretical perspective for optimizing industrial-level pre-training.
How to Set the Batch Size for Large-Scale Pre-training?
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:The concept of Critical Batch Size, as pioneered by OpenAI, has long served as a foundational principle for large-scale pre-training. However, with the paradigm shift towards the Warmup-Stable-Decay (WSD) learning rate scheduler, we observe that the original theoretical framework and its underlying mechanisms fail to align with new pre-training dynamics. To bridge this gap between theory and practice, this paper derives a revised E(S) relationship tailored for WSD scheduler, characterizing the trade-off between training data consumption E and steps S during pre-training. Our theoretical analysis reveals two fundamental properties of WSD-based pre-training: 1) B_min, the minimum batch size threshold required to achieve a target loss, and 2) B_opt, the optimal batch size that maximizes data efficiency by minimizing total tokens. Building upon these properties, we propose a dynamic Batch Size Scheduler. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our revised formula precisely captures the dynamics of large-scale pre-training, and the resulting scheduling strategy significantly enhances both training efficiency and final model quality.
Step-GUI Technical Report
Dec 19, 2025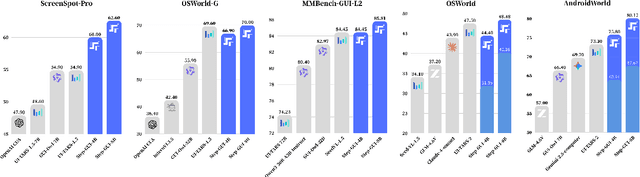
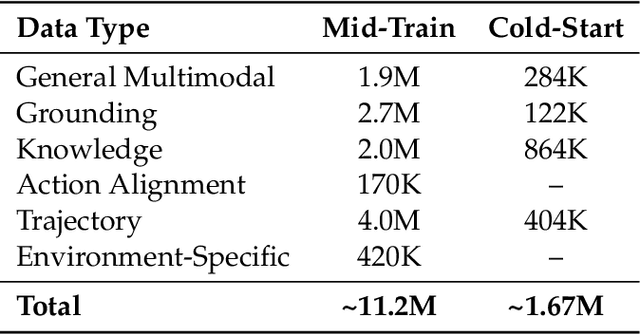
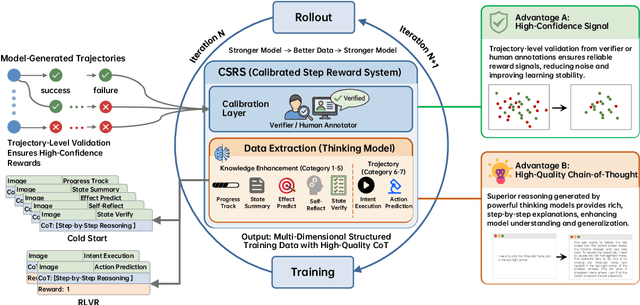

Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal large language models unlock unprecedented opportunities for GUI automation. However, a fundamental challenge remains: how to efficiently acquire high-quality training data while maintaining annotation reliability? We introduce a self-evolving training pipeline powered by the Calibrated Step Reward System, which converts model-generated trajectories into reliable training signals through trajectory-level calibration, achieving >90% annotation accuracy with 10-100x lower cost. Leveraging this pipeline, we introduce Step-GUI, a family of models (4B/8B) that achieves state-of-the-art GUI performance (8B: 80.2% AndroidWorld, 48.5% OSWorld, 62.6% ScreenShot-Pro) while maintaining robust general capabilities. As GUI agent capabilities improve, practical deployment demands standardized interfaces across heterogeneous devices while protecting user privacy. To this end, we propose GUI-MCP, the first Model Context Protocol for GUI automation with hierarchical architecture that combines low-level atomic operations and high-level task delegation to local specialist models, enabling high-privacy execution where sensitive data stays on-device. Finally, to assess whether agents can handle authentic everyday usage, we introduce AndroidDaily, a benchmark grounded in real-world mobile usage patterns with 3146 static actions and 235 end-to-end tasks across high-frequency daily scenarios (8B: static 89.91%, end-to-end 52.50%). Our work advances the development of practical GUI agents and demonstrates strong potential for real-world deployment in everyday digital interactions.
NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Day and Night Raindrop Removal for Dual-Focused Images: Methods and Results
Apr 19, 2025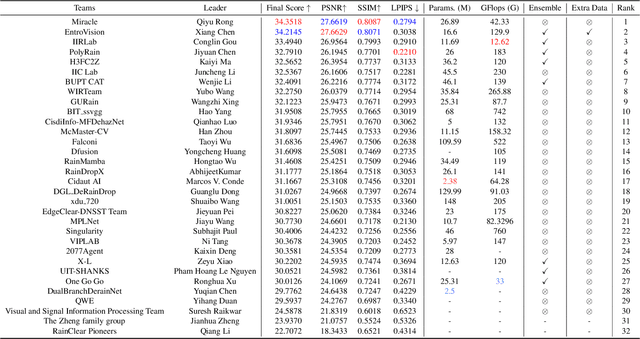
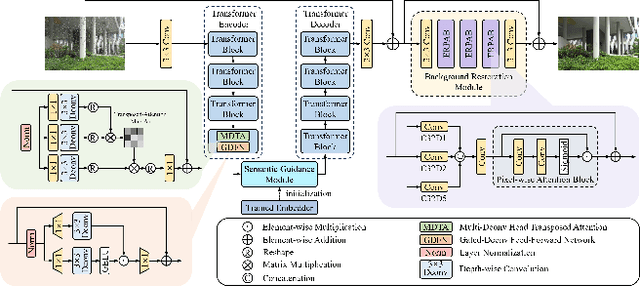
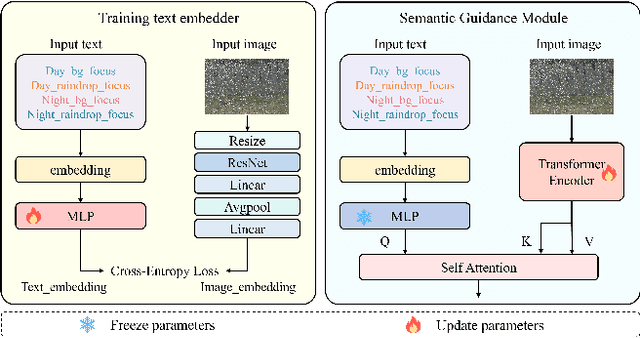
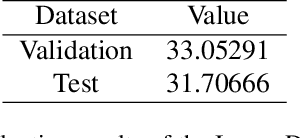
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Day and Night Raindrop Removal for Dual-Focused Images. This challenge received a wide range of impressive solutions, which are developed and evaluated using our collected real-world Raindrop Clarity dataset. Unlike existing deraining datasets, our Raindrop Clarity dataset is more diverse and challenging in degradation types and contents, which includes day raindrop-focused, day background-focused, night raindrop-focused, and night background-focused degradations. This dataset is divided into three subsets for competition: 14,139 images for training, 240 images for validation, and 731 images for testing. The primary objective of this challenge is to establish a new and powerful benchmark for the task of removing raindrops under varying lighting and focus conditions. There are a total of 361 participants in the competition, and 32 teams submitting valid solutions and fact sheets for the final testing phase. These submissions achieved state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on the Raindrop Clarity dataset. The project can be found at https://lixinustc.github.io/CVPR-NTIRE2025-RainDrop-Competition.github.io/.
Texture-Preserving Diffusion Models for High-Fidelity Virtual Try-On
Apr 01, 2024Abstract:Image-based virtual try-on is an increasingly important task for online shopping. It aims to synthesize images of a specific person wearing a specified garment. Diffusion model-based approaches have recently become popular, as they are excellent at image synthesis tasks. However, these approaches usually employ additional image encoders and rely on the cross-attention mechanism for texture transfer from the garment to the person image, which affects the try-on's efficiency and fidelity. To address these issues, we propose an Texture-Preserving Diffusion (TPD) model for virtual try-on, which enhances the fidelity of the results and introduces no additional image encoders. Accordingly, we make contributions from two aspects. First, we propose to concatenate the masked person and reference garment images along the spatial dimension and utilize the resulting image as the input for the diffusion model's denoising UNet. This enables the original self-attention layers contained in the diffusion model to achieve efficient and accurate texture transfer. Second, we propose a novel diffusion-based method that predicts a precise inpainting mask based on the person and reference garment images, further enhancing the reliability of the try-on results. In addition, we integrate mask prediction and image synthesis into a single compact model. The experimental results show that our approach can be applied to various try-on tasks, e.g., garment-to-person and person-to-person try-ons, and significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods on popular VITON, VITON-HD databases.
abess: A Fast Best Subset Selection Library in Python and R
Oct 19, 2021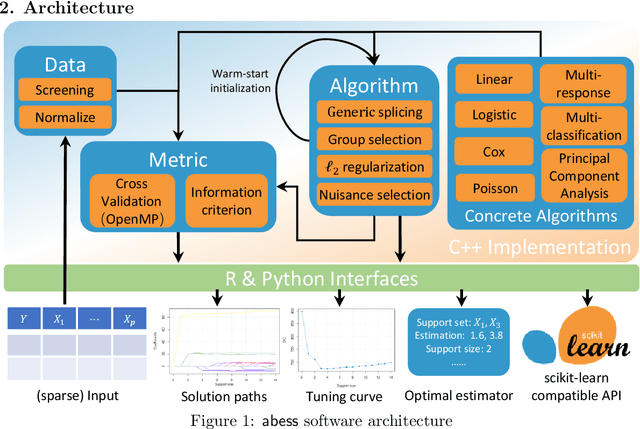


Abstract:We introduce a new library named abess that implements a unified framework of best-subset selection for solving diverse machine learning problems, e.g., linear regression, classification, and principal component analysis. Particularly, the abess certifiably gets the optimal solution within polynomial times under the linear model. Our efficient implementation allows abess to attain the solution of best-subset selection problems as fast as or even 100x faster than existing competing variable (model) selection toolboxes. Furthermore, it supports common variants like best group subset selection and $\ell_2$ regularized best-subset selection. The core of the library is programmed in C++. For ease of use, a Python library is designed for conveniently integrating with scikit-learn, and it can be installed from the Python library Index. In addition, a user-friendly R library is available at the Comprehensive R Archive Network. The source code is available at: https://github.com/abess-team/abess.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge