Jun-Wei Hsieh
Partial Ring Scan: Revisiting Scan Order in Vision State Space Models
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:State Space Models (SSMs) have emerged as efficient alternatives to attention for vision tasks, offering lineartime sequence processing with competitive accuracy. Vision SSMs, however, require serializing 2D images into 1D token sequences along a predefined scan order, a factor often overlooked. We show that scan order critically affects performance by altering spatial adjacency, fracturing object continuity, and amplifying degradation under geometric transformations such as rotation. We present Partial RIng Scan Mamba (PRISMamba), a rotation-robust traversal that partitions an image into concentric rings, performs order-agnostic aggregation within each ring, and propagates context across rings through a set of short radial SSMs. Efficiency is further improved via partial channel filtering, which routes only the most informative channels through the recurrent ring pathway while keeping the rest on a lightweight residual branch. On ImageNet-1K, PRISMamba achieves 84.5% Top-1 with 3.9G FLOPs and 3,054 img/s on A100, outperforming VMamba in both accuracy and throughput while requiring fewer FLOPs. It also maintains performance under rotation, whereas fixed-path scans drop by 1~2%. These results highlight scan-order design, together with channel filtering, as a crucial, underexplored factor for accuracy, efficiency, and rotation robustness in Vision SSMs. Code will be released upon acceptance.
RepSFNet : A Single Fusion Network with Structural Reparameterization for Crowd Counting
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Crowd counting remains challenging in variable-density scenes due to scale variations, occlusions, and the high computational cost of existing models. To address these issues, we propose RepSFNet (Reparameterized Single Fusion Network), a lightweight architecture designed for accurate and real-time crowd estimation. RepSFNet leverages a RepLK-ViT backbone with large reparameterized kernels for efficient multi-scale feature extraction. It further integrates a Feature Fusion module combining Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP) and Context-Aware Network (CAN) to achieve robust, density-adaptive context modeling. A Concatenate Fusion module is employed to preserve spatial resolution and generate high-quality density maps. By avoiding attention mechanisms and multi-branch designs, RepSFNet significantly reduces parameters and computational complexity. The training objective combines Mean Squared Error and Optimal Transport loss to improve both count accuracy and spatial distribution alignment. Experiments conducted on ShanghaiTech, NWPU, and UCF-QNRF datasets demonstrate that RepSFNet achieves competitive accuracy while reducing inference latency by up to 34 percent compared to recent state-of-the-art methods, making it suitable for real-time and low-power edge computing applications.
* 6 pages. Published in Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal-Based Surveillance (AVSS) 2025
Semantic-Guided Natural Language and Visual Fusion for Cross-Modal Interaction Based on Tiny Object Detection
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces a cutting-edge approach to cross-modal interaction for tiny object detection by combining semantic-guided natural language processing with advanced visual recognition backbones. The proposed method integrates the BERT language model with the CNN-based Parallel Residual Bi-Fusion Feature Pyramid Network (PRB-FPN-Net), incorporating innovative backbone architectures such as ELAN, MSP, and CSP to optimize feature extraction and fusion. By employing lemmatization and fine-tuning techniques, the system aligns semantic cues from textual inputs with visual features, enhancing detection precision for small and complex objects. Experimental validation using the COCO and Objects365 datasets demonstrates that the model achieves superior performance. On the COCO2017 validation set, it attains a 52.6% average precision (AP), outperforming YOLO-World significantly while maintaining half the parameter consumption of Transformer-based models like GLIP. Several test on different of backbones such ELAN, MSP, and CSP further enable efficient handling of multi-scale objects, ensuring scalability and robustness in resource-constrained environments. This study underscores the potential of integrating natural language understanding with advanced backbone architectures, setting new benchmarks in object detection accuracy, efficiency, and adaptability to real-world challenges.
Block-based Symmetric Pruning and Fusion for Efficient Vision Transformers
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Vision Transformer (ViT) has achieved impressive results across various vision tasks, yet its high computational cost limits practical applications. Recent methods have aimed to reduce ViT's $O(n^2)$ complexity by pruning unimportant tokens. However, these techniques often sacrifice accuracy by independently pruning query (Q) and key (K) tokens, leading to performance degradation due to overlooked token interactions. To address this limitation, we introduce a novel {\bf Block-based Symmetric Pruning and Fusion} for efficient ViT (BSPF-ViT) that optimizes the pruning of Q/K tokens jointly. Unlike previous methods that consider only a single direction, our approach evaluates each token and its neighbors to decide which tokens to retain by taking token interaction into account. The retained tokens are compressed through a similarity fusion step, preserving key information while reducing computational costs. The shared weights of Q/K tokens create a symmetric attention matrix, allowing pruning only the upper triangular part for speed up. BSPF-ViT consistently outperforms state-of-the-art ViT methods at all pruning levels, increasing ImageNet classification accuracy by 1.3% on DeiT-T and 2.0% on DeiT-S, while reducing computational overhead by 50%. It achieves 40% speedup with improved accuracy across various ViTs.
FaceLiVT: Face Recognition using Linear Vision Transformer with Structural Reparameterization For Mobile Device
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces FaceLiVT, a lightweight yet powerful face recognition model that integrates a hybrid Convolution Neural Network (CNN)-Transformer architecture with an innovative and lightweight Multi-Head Linear Attention (MHLA) mechanism. By combining MHLA alongside a reparameterized token mixer, FaceLiVT effectively reduces computational complexity while preserving competitive accuracy. Extensive evaluations on challenging benchmarks; including LFW, CFP-FP, AgeDB-30, IJB-B, and IJB-C; highlight its superior performance compared to state-of-the-art lightweight models. MHLA notably improves inference speed, allowing FaceLiVT to deliver high accuracy with lower latency on mobile devices. Specifically, FaceLiVT is 8.6 faster than EdgeFace, a recent hybrid CNN-Transformer model optimized for edge devices, and 21.2 faster than a pure ViT-Based model. With its balanced design, FaceLiVT offers an efficient and practical solution for real-time face recognition on resource-constrained platforms.
Fast-COS: A Fast One-Stage Object Detector Based on Reparameterized Attention Vision Transformer for Autonomous Driving
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:The perception system is a a critical role of an autonomous driving system for ensuring safety. The driving scene perception system fundamentally represents an object detection task that requires achieving a balance between accuracy and processing speed. Many contemporary methods focus on improving detection accuracy but often overlook the importance of real-time detection capabilities when computational resources are limited. Thus, it is vital to investigate efficient object detection strategies for driving scenes. This paper introduces Fast-COS, a novel single-stage object detection framework crafted specifically for driving scene applications. The research initiates with an analysis of the backbone, considering both macro and micro architectural designs, yielding the Reparameterized Attention Vision Transformer (RAViT). RAViT utilizes Reparameterized Multi-Scale Depth-Wise Convolution (RepMSDW) and Reparameterized Self-Attention (RepSA) to enhance computational efficiency and feature extraction. In extensive tests across GPU, edge, and mobile platforms, RAViT achieves 81.4% Top-1 accuracy on the ImageNet-1K dataset, demonstrating significant throughput improvements over comparable backbone models such as ResNet, FastViT, RepViT, and EfficientFormer. Additionally, integrating RepMSDW into a feature pyramid network forms RepFPN, enabling fast and multi-scale feature fusion. Fast-COS enhances object detection in driving scenes, attaining an AP50 score of 57.2% on the BDD100K dataset and 80.0% on the TJU-DHD Traffic dataset. It surpasses leading models in efficiency, delivering up to 75.9% faster GPU inference and 1.38 higher throughput on edge devices compared to FCOS, YOLOF, and RetinaNet. These findings establish Fast-COS as a highly scalable and reliable solution suitable for real-time applications, especially in resource-limited environments like autonomous driving systems
MicroViT: A Vision Transformer with Low Complexity Self Attention for Edge Device
Feb 09, 2025Abstract:The Vision Transformer (ViT) has demonstrated state-of-the-art performance in various computer vision tasks, but its high computational demands make it impractical for edge devices with limited resources. This paper presents MicroViT, a lightweight Vision Transformer architecture optimized for edge devices by significantly reducing computational complexity while maintaining high accuracy. The core of MicroViT is the Efficient Single Head Attention (ESHA) mechanism, which utilizes group convolution to reduce feature redundancy and processes only a fraction of the channels, thus lowering the burden of the self-attention mechanism. MicroViT is designed using a multi-stage MetaFormer architecture, stacking multiple MicroViT encoders to enhance efficiency and performance. Comprehensive experiments on the ImageNet-1K and COCO datasets demonstrate that MicroViT achieves competitive accuracy while significantly improving 3.6 faster inference speed and reducing energy consumption with 40% higher efficiency than the MobileViT series, making it suitable for deployment in resource-constrained environments such as mobile and edge devices.
The 8th AI City Challenge
Apr 15, 2024
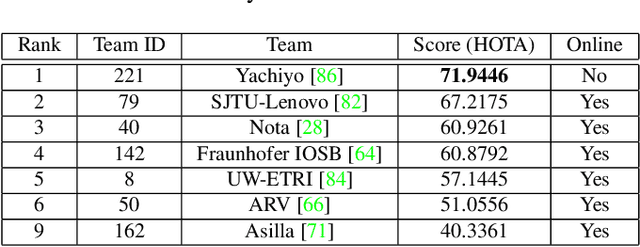
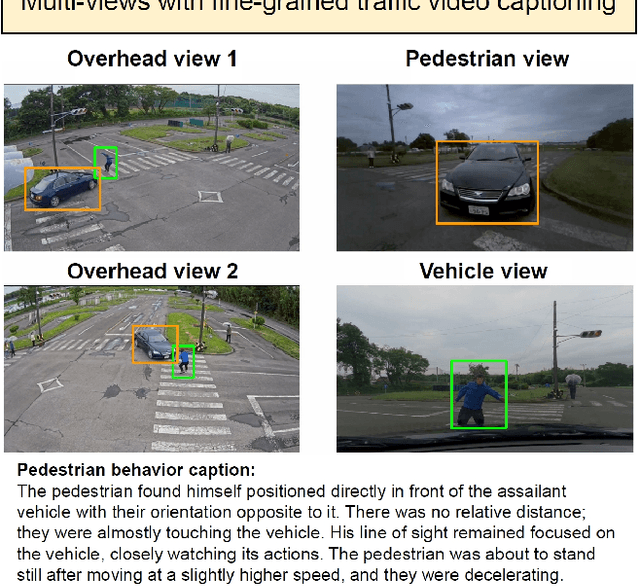
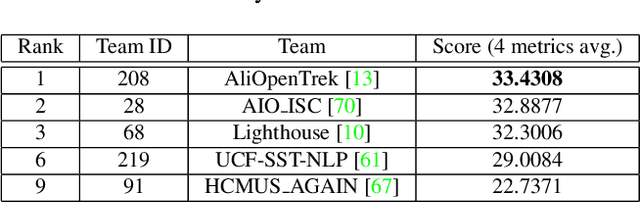
Abstract:The eighth AI City Challenge highlighted the convergence of computer vision and artificial intelligence in areas like retail, warehouse settings, and Intelligent Traffic Systems (ITS), presenting significant research opportunities. The 2024 edition featured five tracks, attracting unprecedented interest from 726 teams in 47 countries and regions. Track 1 dealt with multi-target multi-camera (MTMC) people tracking, highlighting significant enhancements in camera count, character number, 3D annotation, and camera matrices, alongside new rules for 3D tracking and online tracking algorithm encouragement. Track 2 introduced dense video captioning for traffic safety, focusing on pedestrian accidents using multi-camera feeds to improve insights for insurance and prevention. Track 3 required teams to classify driver actions in a naturalistic driving analysis. Track 4 explored fish-eye camera analytics using the FishEye8K dataset. Track 5 focused on motorcycle helmet rule violation detection. The challenge utilized two leaderboards to showcase methods, with participants setting new benchmarks, some surpassing existing state-of-the-art achievements.
ParFormer: Vision Transformer Baseline with Parallel Local Global Token Mixer and Convolution Attention Patch Embedding
Mar 22, 2024Abstract:This work presents ParFormer as an enhanced transformer architecture that allows the incorporation of different token mixers into a single stage, hence improving feature extraction capabilities. Integrating both local and global data allows for precise representation of short- and long-range spatial relationships without the need for computationally intensive methods such as shifting windows. Along with the parallel token mixer encoder, We offer the Convolutional Attention Patch Embedding (CAPE) as an enhancement of standard patch embedding to improve token mixer extraction with a convolutional attention module. Our comprehensive evaluation demonstrates that our ParFormer outperforms CNN-based and state-of-the-art transformer-based architectures in image classification and several complex tasks such as object recognition. The proposed CAPE has been demonstrated to benefit the overall MetaFormer architecture, even while utilizing the Identity Mapping Token Mixer, resulting in a 0.5\% increase in accuracy. The ParFormer models outperformed ConvNeXt and Swin Transformer for the pure convolution and transformer model in accuracy. Furthermore, our model surpasses the current leading hybrid transformer by reaching competitive Top-1 scores in the ImageNet-1K classification test. Specifically, our model variants with 11M, 23M, and 34M parameters achieve scores of 80.4\%, 82.1\%, and 83.1\%, respectively. Code: https://github.com/novendrastywn/ParFormer-CAPE-2024
Addressing Long-Tail Noisy Label Learning Problems: a Two-Stage Solution with Label Refurbishment Considering Label Rarity
Mar 04, 2024



Abstract:Real-world datasets commonly exhibit noisy labels and class imbalance, such as long-tailed distributions. While previous research addresses this issue by differentiating noisy and clean samples, reliance on information from predictions based on noisy long-tailed data introduces potential errors. To overcome the limitations of prior works, we introduce an effective two-stage approach by combining soft-label refurbishing with multi-expert ensemble learning. In the first stage of robust soft label refurbishing, we acquire unbiased features through contrastive learning, making preliminary predictions using a classifier trained with a carefully designed BAlanced Noise-tolerant Cross-entropy (BANC) loss. In the second stage, our label refurbishment method is applied to obtain soft labels for multi-expert ensemble learning, providing a principled solution to the long-tail noisy label problem. Experiments conducted across multiple benchmarks validate the superiority of our approach, Label Refurbishment considering Label Rarity (LR^2), achieving remarkable accuracies of 94.19% and 77.05% on simulated noisy CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 long-tail datasets, as well as 77.74% and 81.40% on real-noise long-tail datasets, Food-101N and Animal-10N, surpassing existing state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge