Juexiao Feng
YOLO-UniOW: Efficient Universal Open-World Object Detection
Dec 30, 2024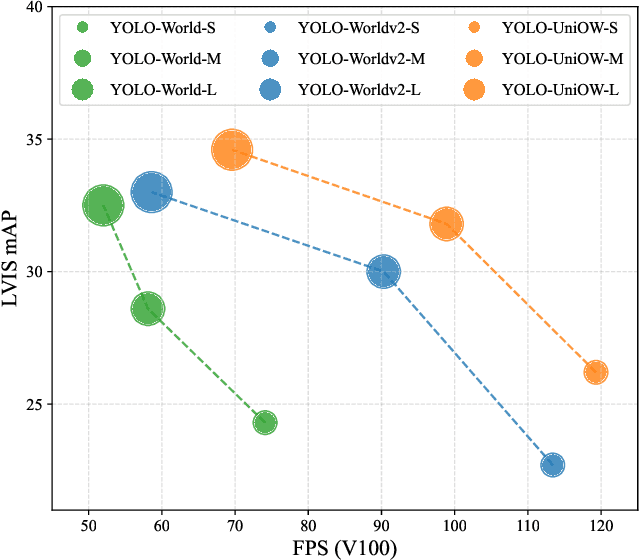
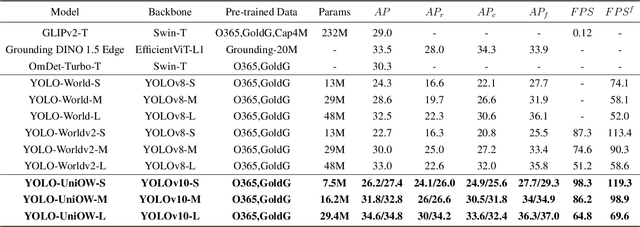
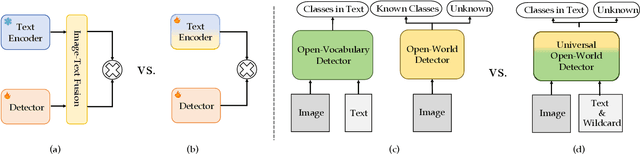
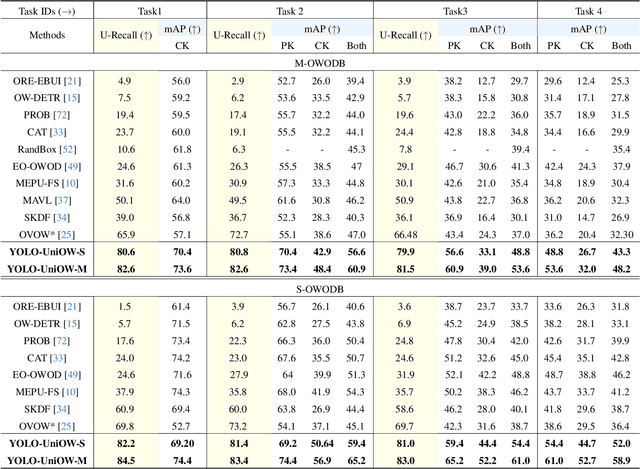
Abstract:Traditional object detection models are constrained by the limitations of closed-set datasets, detecting only categories encountered during training. While multimodal models have extended category recognition by aligning text and image modalities, they introduce significant inference overhead due to cross-modality fusion and still remain restricted by predefined vocabulary, leaving them ineffective at handling unknown objects in open-world scenarios. In this work, we introduce Universal Open-World Object Detection (Uni-OWD), a new paradigm that unifies open-vocabulary and open-world object detection tasks. To address the challenges of this setting, we propose YOLO-UniOW, a novel model that advances the boundaries of efficiency, versatility, and performance. YOLO-UniOW incorporates Adaptive Decision Learning to replace computationally expensive cross-modality fusion with lightweight alignment in the CLIP latent space, achieving efficient detection without compromising generalization. Additionally, we design a Wildcard Learning strategy that detects out-of-distribution objects as "unknown" while enabling dynamic vocabulary expansion without the need for incremental learning. This design empowers YOLO-UniOW to seamlessly adapt to new categories in open-world environments. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of YOLO-UniOW, achieving achieving 34.6 AP and 30.0 APr on LVIS with an inference speed of 69.6 FPS. The model also sets benchmarks on M-OWODB, S-OWODB, and nuScenes datasets, showcasing its unmatched performance in open-world object detection. Code and models are available at https://github.com/THU-MIG/YOLO-UniOW.
Quantized Prompt for Efficient Generalization of Vision-Language Models
Jul 15, 2024Abstract:In the past few years, large-scale pre-trained vision-language models like CLIP have achieved tremendous success in various fields. Naturally, how to transfer the rich knowledge in such huge pre-trained models to downstream tasks and datasets becomes a hot topic. During downstream adaptation, the most challenging problems are overfitting and catastrophic forgetting, which can cause the model to overly focus on the current data and lose more crucial domain-general knowledge. Existing works use classic regularization techniques to solve the problems. As solutions become increasingly complex, the ever-growing storage and inference costs are also a significant problem that urgently needs to be addressed. While in this paper, we start from an observation that proper random noise can suppress overfitting and catastrophic forgetting. Then we regard quantization error as a kind of noise, and explore quantization for regularizing vision-language model, which is quite efficiency and effective. Furthermore, to improve the model's generalization capability while maintaining its specialization capacity at minimal cost, we deeply analyze the characteristics of the weight distribution in prompts, conclude several principles for quantization module design and follow such principles to create several competitive baselines. The proposed method is significantly efficient due to its inherent lightweight nature, making it possible to adapt on extremely resource-limited devices. Our method can be fruitfully integrated into many existing approaches like MaPLe, enhancing accuracy while reducing storage overhead, making it more powerful yet versatile. Extensive experiments on 11 datasets shows great superiority of our method sufficiently. Code is available at https://github.com/beyondhtx/QPrompt.
Debiased Novel Category Discovering and Localization
Feb 29, 2024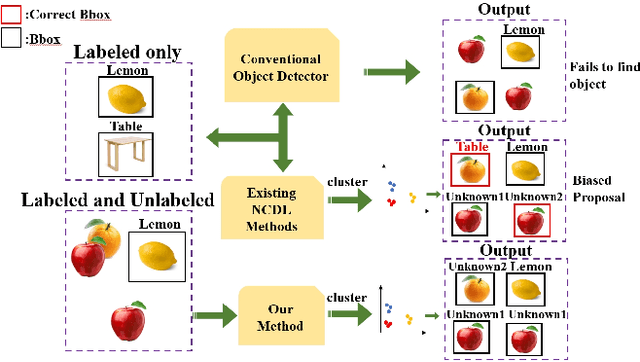
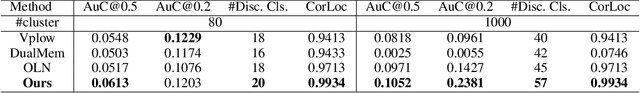
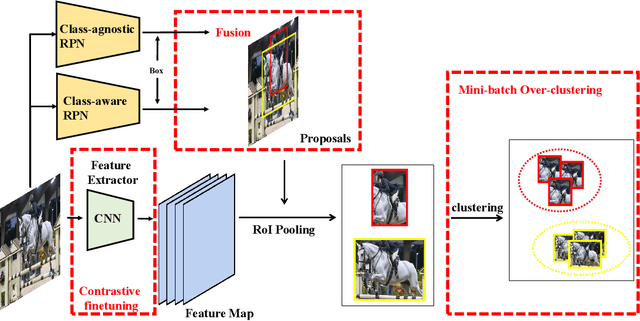

Abstract:In recent years, object detection in deep learning has experienced rapid development. However, most existing object detection models perform well only on closed-set datasets, ignoring a large number of potential objects whose categories are not defined in the training set. These objects are often identified as background or incorrectly classified as pre-defined categories by the detectors. In this paper, we focus on the challenging problem of Novel Class Discovery and Localization (NCDL), aiming to train detectors that can detect the categories present in the training data, while also actively discover, localize, and cluster new categories. We analyze existing NCDL methods and identify the core issue: object detectors tend to be biased towards seen objects, and this leads to the neglect of unseen targets. To address this issue, we first propose an Debiased Region Mining (DRM) approach that combines class-agnostic Region Proposal Network (RPN) and class-aware RPN in a complementary manner. Additionally, we suggest to improve the representation network through semi-supervised contrastive learning by leveraging unlabeled data. Finally, we adopt a simple and efficient mini-batch K-means clustering method for novel class discovery. We conduct extensive experiments on the NCDL benchmark, and the results demonstrate that the proposed DRM approach significantly outperforms previous methods, establishing a new state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge