Judy W. Gichoya
Synthetically Enhanced: Unveiling Synthetic Data's Potential in Medical Imaging Research
Nov 15, 2023



Abstract:Chest X-rays (CXR) are the most common medical imaging study and are used to diagnose multiple medical conditions. This study examines the impact of synthetic data supplementation, using diffusion models, on the performance of deep learning (DL) classifiers for CXR analysis. We employed three datasets: CheXpert, MIMIC-CXR, and Emory Chest X-ray, training conditional denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs) to generate synthetic frontal radiographs. Our approach ensured that synthetic images mirrored the demographic and pathological traits of the original data. Evaluating the classifiers' performance on internal and external datasets revealed that synthetic data supplementation enhances model accuracy, particularly in detecting less prevalent pathologies. Furthermore, models trained on synthetic data alone approached the performance of those trained on real data. This suggests that synthetic data can potentially compensate for real data shortages in training robust DL models. However, despite promising outcomes, the superiority of real data persists.
A general-purpose AI assistant embedded in an open-source radiology information system
Mar 18, 2023



Abstract:Radiology AI models have made significant progress in near-human performance or surpassing it. However, AI model's partnership with human radiologist remains an unexplored challenge due to the lack of health information standards, contextual and workflow differences, and data labeling variations. To overcome these challenges, we integrated an AI model service that uses DICOM standard SR annotations into the OHIF viewer in the open-source LibreHealth Radiology Information Systems (RIS). In this paper, we describe the novel Human-AI partnership capabilities of the platform, including few-shot learning and swarm learning approaches to retrain the AI models continuously. Building on the concept of machine teaching, we developed an active learning strategy within the RIS, so that the human radiologist can enable/disable AI annotations as well as "fix"/relabel the AI annotations. These annotations are then used to retrain the models. This helps establish a partnership between the radiologist user and a user-specific AI model. The weights of these user-specific models are then finally shared between multiple models in a swarm learning approach.
Two-step adversarial debiasing with partial learning -- medical image case-studies
Nov 16, 2021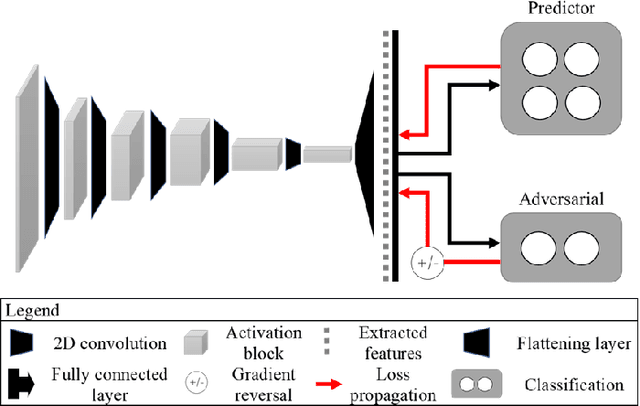
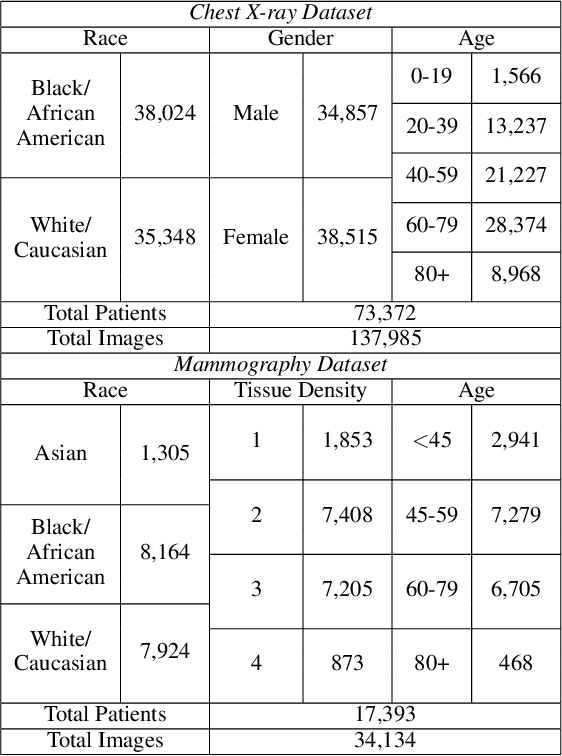
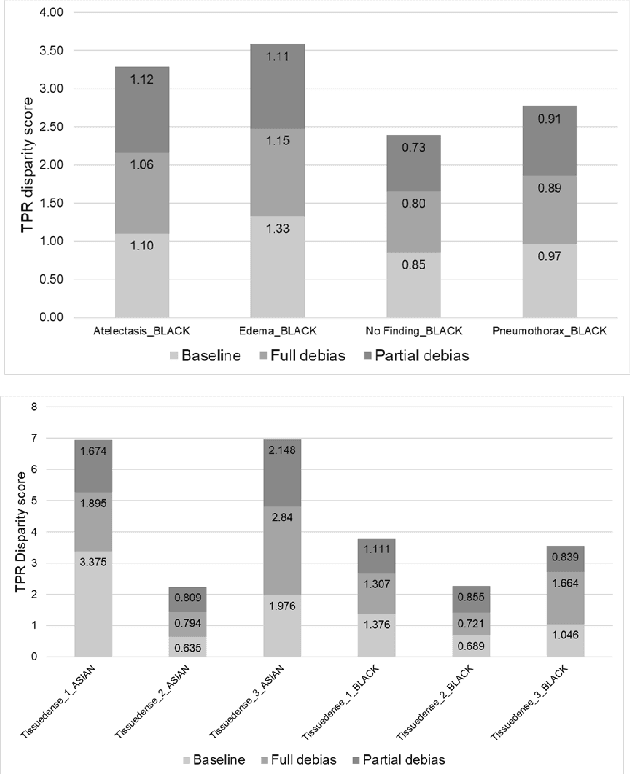
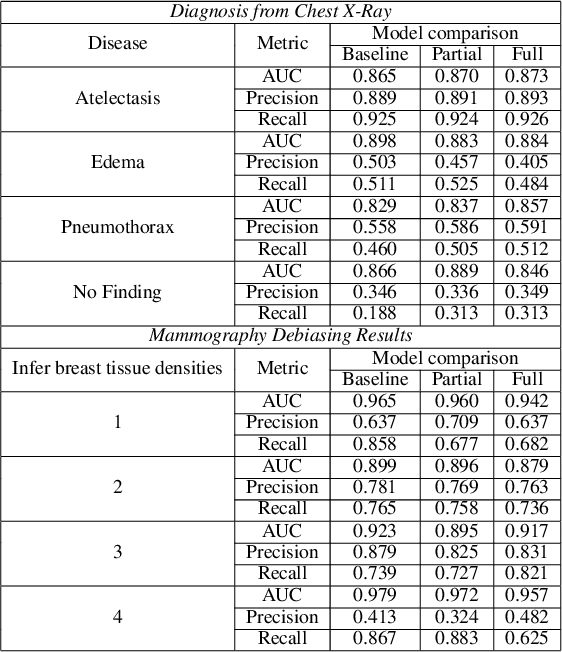
Abstract:The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare has become a very active research area in the last few years. While significant progress has been made in image classification tasks, only a few AI methods are actually being deployed in hospitals. A major hurdle in actively using clinical AI models currently is the trustworthiness of these models. More often than not, these complex models are black boxes in which promising results are generated. However, when scrutinized, these models begin to reveal implicit biases during the decision making, such as detecting race and having bias towards ethnic groups and subpopulations. In our ongoing study, we develop a two-step adversarial debiasing approach with partial learning that can reduce the racial disparity while preserving the performance of the targeted task. The methodology has been evaluated on two independent medical image case-studies - chest X-ray and mammograms, and showed promises in bias reduction while preserving the targeted performance.
Was there COVID-19 back in 2012? Challenge for AI in Diagnosis with Similar Indications
Jun 23, 2020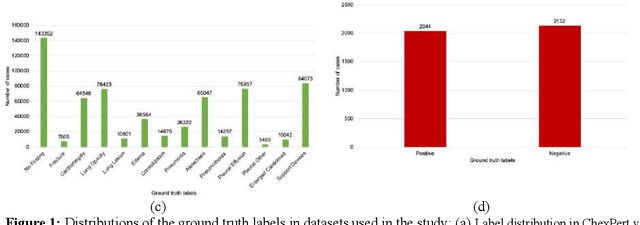
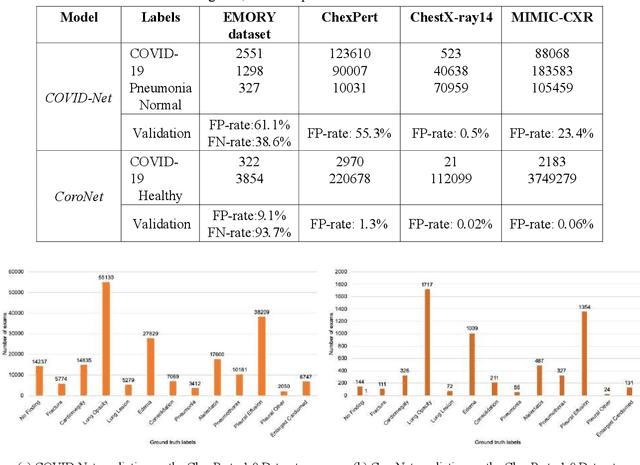
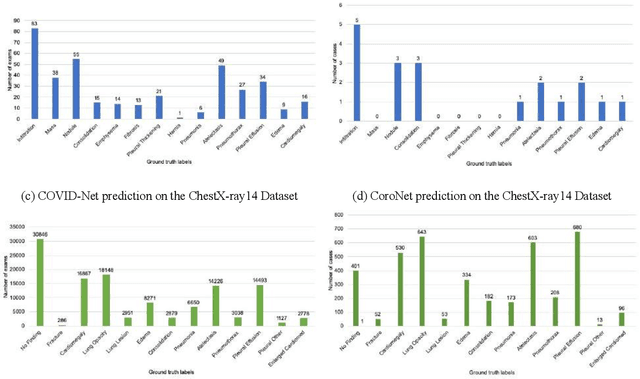

Abstract:Purpose: Since the recent COVID-19 outbreak, there has been an avalanche of research papers applying deep learning based image processing to chest radiographs for detection of the disease. To test the performance of the two top models for CXR COVID-19 diagnosis on external datasets to assess model generalizability. Methods: In this paper, we present our argument regarding the efficiency and applicability of existing deep learning models for COVID-19 diagnosis. We provide results from two popular models - COVID-Net and CoroNet evaluated on three publicly available datasets and an additional institutional dataset collected from EMORY Hospital between January and May 2020, containing patients tested for COVID-19 infection using RT-PCR. Results: There is a large false positive rate (FPR) for COVID-Net on both ChexPert (55.3%) and MIMIC-CXR (23.4%) dataset. On the EMORY Dataset, COVID-Net has 61.4% sensitivity, 0.54 F1-score and 0.49 precision value. The FPR of the CoroNet model is significantly lower across all the datasets as compared to COVID-Net - EMORY(9.1%), ChexPert (1.3%), ChestX-ray14 (0.02%), MIMIC-CXR (0.06%). Conclusion: The models reported good to excellent performance on their internal datasets, however we observed from our testing that their performance dramatically worsened on external data. This is likely from several causes including overfitting models due to lack of appropriate control patients and ground truth labels. The fourth institutional dataset was labeled using RT-PCR, which could be positive without radiographic findings and vice versa. Therefore, a fusion model of both clinical and radiographic data may have better performance and generalization.
Multi-label natural language processing to identify diagnosis and procedure codes from MIMIC-III inpatient notes
Mar 17, 2020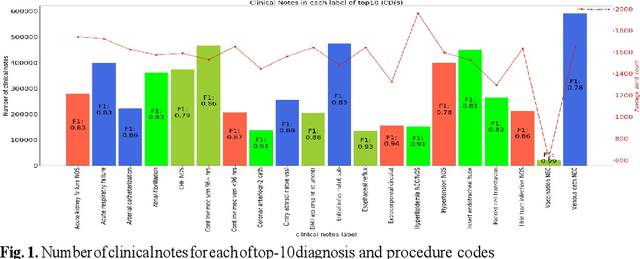
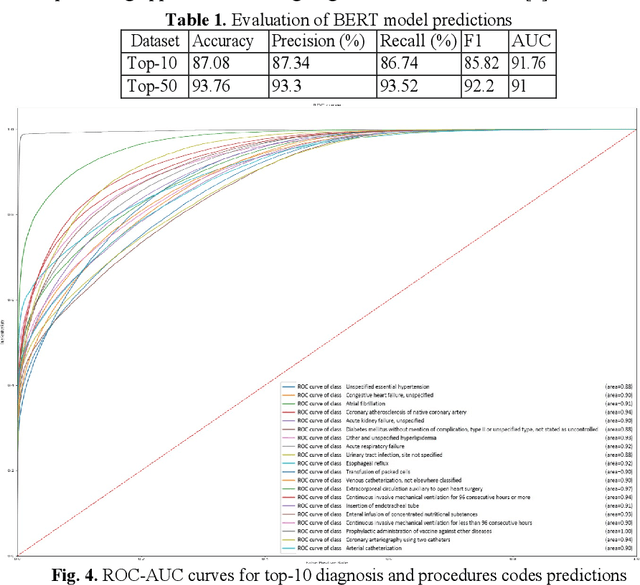
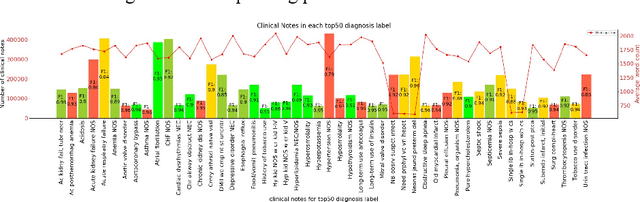
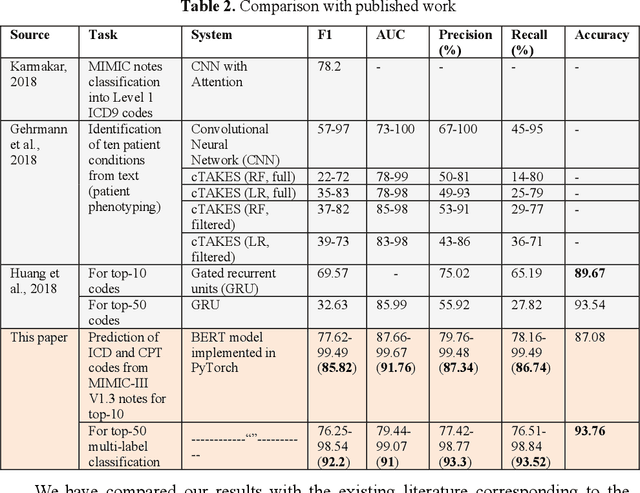
Abstract:In the United States, 25% or greater than 200 billion dollars of hospital spending accounts for administrative costs that involve services for medical coding and billing. With the increasing number of patient records, manual assignment of the codes performed is overwhelming, time-consuming and error-prone, causing billing errors. Natural language processing can automate the extraction of codes/labels from unstructured clinical notes, which can aid human coders to save time, increase productivity, and verify medical coding errors. Our objective is to identify appropriate diagnosis and procedure codes from clinical notes by performing multi-label classification. We used de-identified data of critical care patients from the MIMIC-III database and subset the data to select the ten (top-10) and fifty (top-50) most common diagnoses and procedures, which covers 47.45% and 74.12% of all admissions respectively. We implemented state-of-the-art Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) to fine-tune the language model on 80% of the data and validated on the remaining 20%. The model achieved an overall accuracy of 87.08%, an F1 score of 85.82%, and an AUC of 91.76% for top-10 codes. For the top-50 codes, our model achieved an overall accuracy of 93.76%, an F1 score of 92.24%, and AUC of 91%. When compared to previously published research, our model outperforms in predicting codes from the clinical text. We discuss approaches to generalize the knowledge discovery process of our MIMIC-BERT to other clinical notes. This can help human coders to save time, prevent backlogs, and additional costs due to coding errors.
Natural language processing of MIMIC-III clinical notes for identifying diagnosis and procedures with neural networks
Dec 28, 2019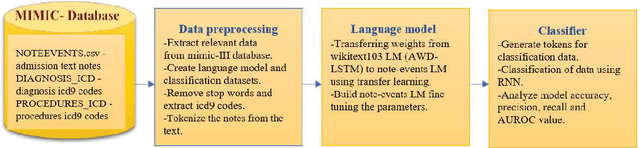
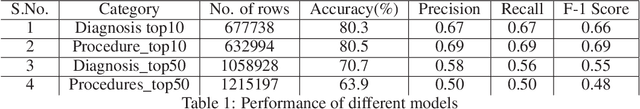
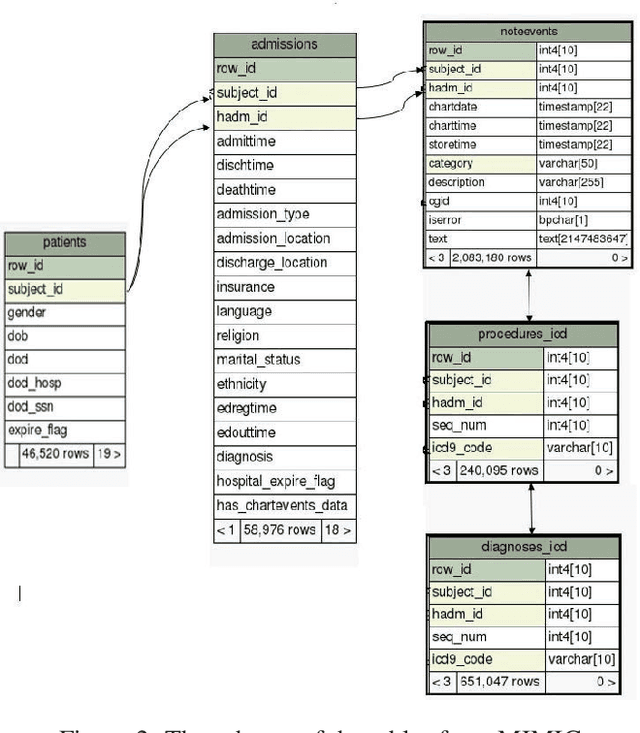
Abstract:Coding diagnosis and procedures in medical records is a crucial process in the healthcare industry, which includes the creation of accurate billings, receiving reimbursements from payers, and creating standardized patient care records. In the United States, Billing and Insurance related activities cost around $471 billion in 2012 which constitutes about 25% of all the U.S hospital spending. In this paper, we report the performance of a natural language processing model that can map clinical notes to medical codes, and predict final diagnosis from unstructured entries of history of present illness, symptoms at the time of admission, etc. Previous studies have demonstrated that deep learning models perform better at such mapping when compared to conventional machine learning models. Therefore, we employed state-of-the-art deep learning method, ULMFiT on the largest emergency department clinical notes dataset MIMIC III which has 1.2M clinical notes to select for the top-10 and top-50 diagnosis and procedure codes. Our models were able to predict the top-10 diagnoses and procedures with 80.3% and 80.5% accuracy, whereas the top-50 ICD-9 codes of diagnosis and procedures are predicted with 70.7% and 63.9% accuracy. Prediction of diagnosis and procedures from unstructured clinical notes benefit human coders to save time, eliminate errors and minimize costs. With promising scores from our present model, the next step would be to deploy this on a small-scale real-world scenario and compare it with human coders as the gold standard. We believe that further research of this approach can create highly accurate predictions that can ease the workflow in a clinical setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge