Jorge Querol
Artificial Intelligence implementation of onboard flexible payload and adaptive beamforming using commercial off-the-shelf devices
May 03, 2025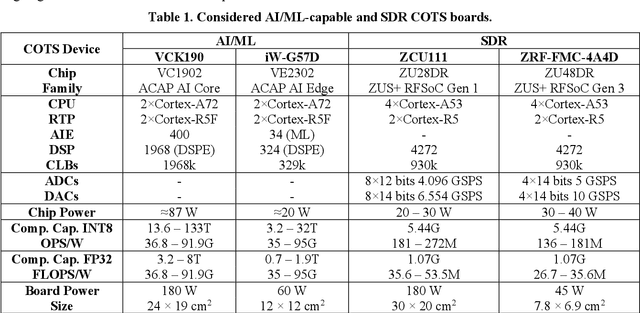
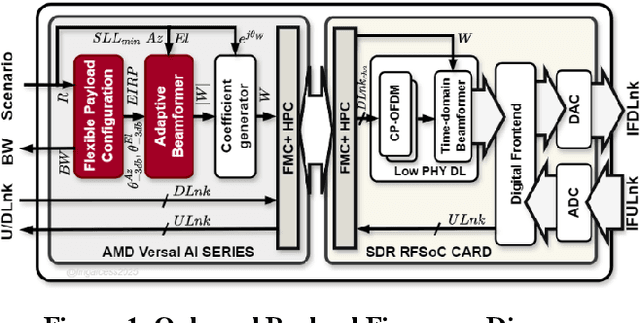
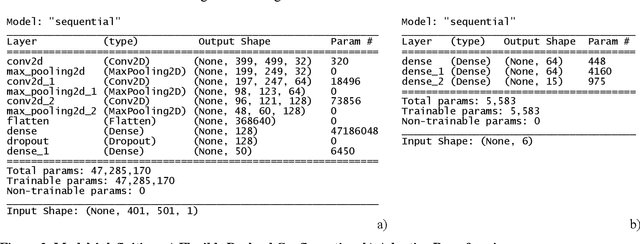
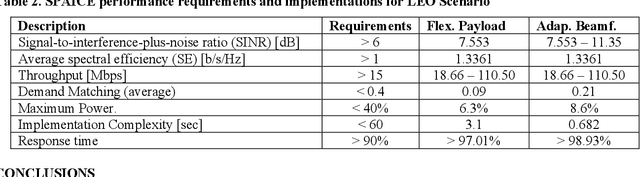
Abstract:Very High Throughput satellites typically provide multibeam coverage, however, a common problem is that there can be a mismatch between the capacity of each beam and the traffic demand: some beams may fall short, while others exceed the requirements. This challenge can be addressed by integrating machine learning with flexible payload and adaptive beamforming techniques. These methods allow for dynamic allocation of payload resources based on real-time capacity needs. As artificial intelligence advances, its ability to automate tasks, enhance efficiency, and increase precision is proving invaluable, especially in satellite communications, where traditional optimization methods are often computationally intensive. AI-driven solutions offer faster, more effective ways to handle complex satellite communication tasks. Artificial intelligence in space has more constraints than other fields, considering the radiation effects, the spaceship power capabilities, mass, and area. Current onboard processing uses legacy space-certified general-purpose processors, costly application-specific integrated circuits, or field-programmable gate arrays subjected to a highly stringent certification process. The increased performance demands of onboard processors to satisfy the accelerated data rates and autonomy requirements have rendered current space-graded processors obsolete. This work is focused on transforming the satellite payload using artificial intelligence and machine learning methodologies over available commercial off-the-shelf chips for onboard processing. The objectives include validating artificial intelligence-driven scenarios, focusing on flexible payload and adaptive beamforming as machine learning models onboard. Results show that machine learning models significantly improve signal quality, spectral efficiency, and throughput compared to conventional payload.
Survey on Beyond Diagonal RIS Enabled 6G Wireless Networks: Fundamentals, Recent Advances, and Challenges
Mar 11, 2025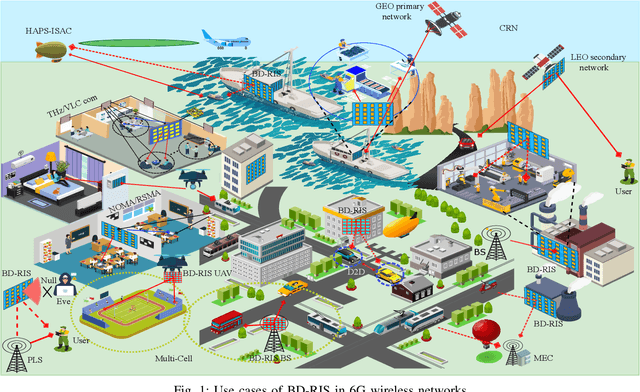
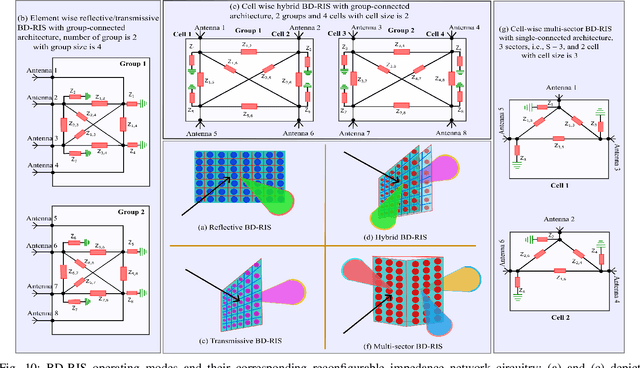
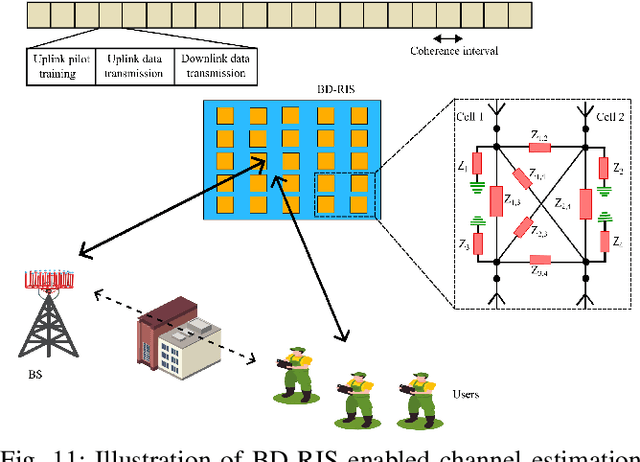
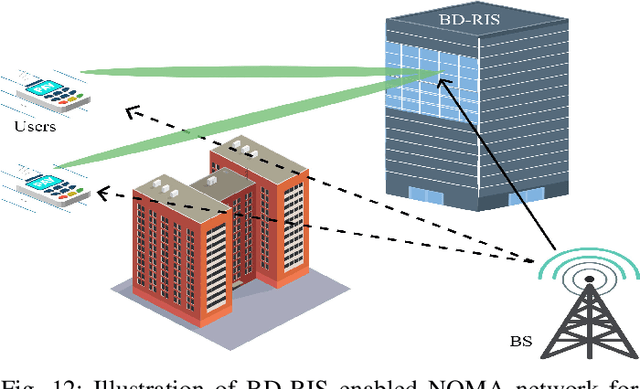
Abstract:Beyond Diagonal Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (BD-RIS) represent a groundbreaking innovation in sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks, enabling unprecedented control over wireless propagation environments compared to conventional diagonal RIS (D-RIS). This survey provides a comprehensive analysis of BD-RIS, detailing its architectures, operational principles, and mathematical modeling while highlighting its performance benefits. BD-RIS classifications, including single-connected, fully-connected, and group-connected architectures, and their reflective, transmissive, hybrid, and multi-sector operating modes are examined. Recent advances in BD-RIS-enabled 6G networks are reviewed, focusing on critical areas such as channel estimation, sum-rate and spectral efficiency optimization, energy efficiency enhancement, and security. The survey identifies fundamental challenges in BD-RIS research, including hardware design limitations, adaptive channel estimation, and the impact of non-ideal hardware effects. Future research directions for BD-RIS are proposed, emphasizing the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML), joint optimization of communication and sensing, and enhanced physical layer security (PLS). This study concludes by underscoring BD-RIS's transformative potential to redefine 6G wireless networks, offering valuable insights and lessons for future research and development.
Secrecy Rate Maximization for 6G Reconfigurable Holographic Surfaces Assisted Systems
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Reconfigurable holographic surfaces (RHS) have emerged as a transformative material technology, enabling dynamic control of electromagnetic waves to generate versatile holographic beam patterns. This paper addresses the problem of secrecy rate maximization for an RHS-assisted systems by joint designing the digital beamforming, artificial noise (AN), and the analog holographic beamforming. However, such a problem results to be non-convex and challenging. Therefore, to solve it, a novel alternating optimization algorithm based on the majorization-maximization (MM) framework for RHS-assisted systems is proposed, which rely on surrogate functions to facilitate efficient and reliable optimization. In the proposed approach, digital beamforming design ensures directed signal power toward the legitimate user while minimizing leakage to the unintended receiver. The AN generation method projects noise into the null space of the legitimate user channel, aligning it with the unintended receiver channel to degrade its signal quality. Finally, the holographic beamforming weights are optimized to refine the wavefronts for enhanced secrecy rate performance Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed framework, demonstrating significant improvements in secrecy rate compared to the benchmark method.
Joint Beamforming and 3D Location Optimization for Multi-User Holographic UAV Communications
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:This paper pioneers the field of multi-user holographic unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) communications, laying a solid foundation for future innovations in next-generation aerial wireless networks. The study focuses on the challenging problem of jointly optimizing hybrid holographic beamforming and 3D UAV positioning in scenarios where the UAV is equipped with a reconfigurable holographic surface (RHS) instead of conventional phased array antennas. Using the unique capabilities of RHSs, the system dynamically adjusts both the position of the UAV and its hybrid beamforming properties to maximize the sum rate of the network. To address this complex optimization problem, we propose an iterative algorithm combining zero-forcing digital beamforming and a gradient ascent approach for the holographic patterns and the 3D position optimization, while ensuring practical feasibility constraints. The algorithm is designed to effectively balance the trade-offs between power, beamforming, and UAV trajectory constraints, enabling adaptive and efficient communications, while assuring a monotonic increase in the sum-rate performance. Our numerical investigations demonstrate that the significant performance improvements with the proposed approach over the benchmark methods, showcasing enhanced sum rate and system adaptability under varying conditions.
Joint Holographic Beamforming and User Scheduling with Individual QoS Constraints
Feb 24, 2025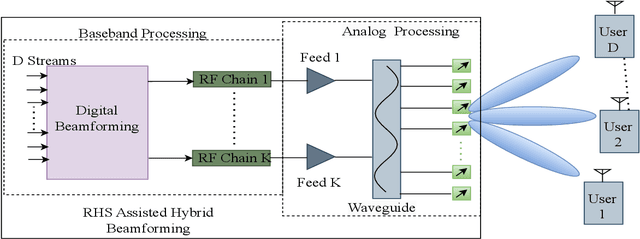
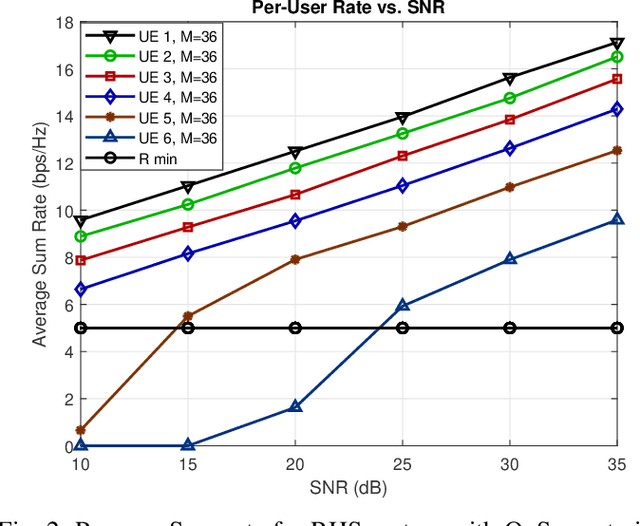
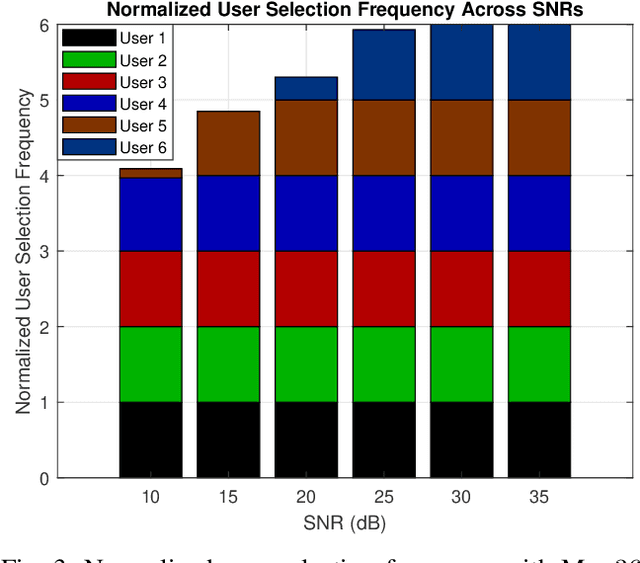
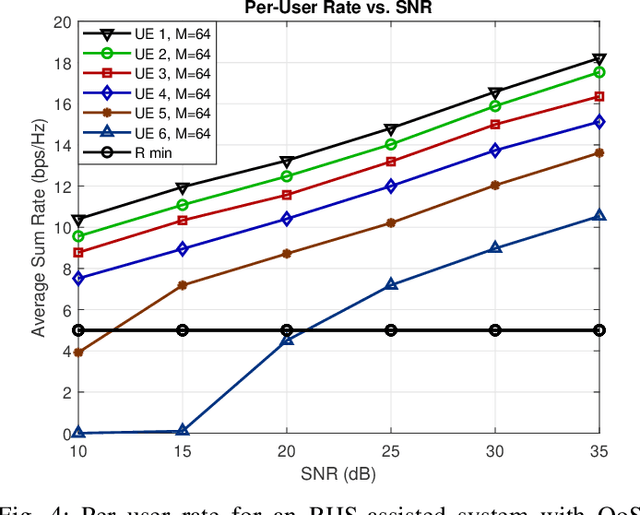
Abstract:Reconfigurable holographic surfaces (RHS) have emerged as a transformative material technology, enabling dynamic control of electromagnetic waves to generate versatile holographic beam patterns. This paper addresses the problem of joint hybrid holographic beamforming and user scheduling under per-user minimum quality-of-service (QoS) constraints, a critical challenge in resource-constrained networks. However, such a problem results in mixed-integer non-convex optimization, making it difficult to identify feasible solutions efficiently. To overcome this challenge, we propose a novel iterative optimization framework that jointly solves the problem to maximize the RHS-assisted network sum-rate, efficiently managing holographic beamforming patterns, dynamically scheduling users, and ensuring the minimum QoS requirements for each scheduled user. The proposed framework relies on zero-forcing digital beamforming, gradient-ascent-based holographic beamformer optimization, and a greedy user selection principle. Our extensive simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme, demonstrating their superior performance compared to the benchmark algorithms in terms of sum-rate performance, while meeting the minimum per-user QoS constraints
Optimizing Antenna Activation for Even Power Distribution in Multi-Beam Satellite Systems Using Genetic Algorithm
Feb 23, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in onboard satellite communication have significantly enhanced the ability to dynamically modify the radiation pattern of a Direct Radiating Array, which is essential for both conventional communication satellites like GEO and those in lower orbits such as LEO. This is particularly relevant for communication at 28 GHz, a key frequency in the mmWave spectrum, used for high-bandwidth satellite links and 5G communications. Critical design factors include the number of beams, beamwidth, and SLL for each beam. However, in multibeam scenarios, balancing these design factors can result in uneven power distribution, leading to over-saturation in centrally located antenna elements due to frequent activations. This paper introduces a GA-based approach to optimize beamforming coefficients by modulating the amplitude component of the weight matrix, while imposing a constraint on activation instances per element to avoid over-saturation in the RF chain. The proposed method, tested on an 16x16 DRA patch antenna array at 28 GHz for a CubeSat orbiting at 500 km, demonstrates how the algorithm efficiently meets beam pattern requirements and ensures uniform activation distribution. These findings are particularly relevant for emerging satellite systems and 5G networks operating in the mmWave spectrum.
Holographic Joint Communications and Sensing With Cramer-Rao Bounds
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Joint Communication and Sensing (JCAS) technology facilitates the seamless integration of communication and sensing functionalities within a unified framework, enhancing spectral efficiency, reducing hardware complexity, and enabling simultaneous data transmission and environmental perception. This paper explores the potential of holographic JCAS systems by leveraging reconfigurable holographic surfaces (RHS) to achieve high-resolution hybrid holographic beamforming while simultaneously sensing the environment. As the holographic transceivers are governed by arbitrary antenna spacing, we first derive exact Cram\'er-Rao Bounds (CRBs) for azimuth and elevation angles to rigorously characterize the three-dimensional (3D) sensing accuracy. To optimize the system performance, we propose a novel weighted multi-objective problem formulation that aims to simultaneously maximize the communication rate and minimize the CRBs. However, this formulation is highly non-convex due to the inverse dependence of the CRB on the optimization variables, making the solution extremely challenging. To address this, we propose a novel algorithmic framework based on the Majorization-Maximization (MM) principle, employing alternating optimization to efficiently solve the problem. The proposed method relies on the closed-form surrogate functions that majorize the original objective derived herein, enabling tractable optimization. Simulation results are presented to validate the effectiveness of the proposed framework under diverse system configurations, demonstrating its potential for next-generation holographic JCAS systems.
Joint Communications and Sensing for 6G Satellite Networks: Use Cases and Challenges
Jan 09, 2025



Abstract:Satellite Networks (SN) have traditionally been instrumental in providing two key services: communications and sensing. Communications satellites enable global connectivity, while sensing satellites facilitate applications such as Earth observation, navigation, and disaster management. However, the emergence of novel use cases and the exponential growth in service demands make the independent evolution of communication and sensing payloads increasingly impractical. Addressing this challenge requires innovative approaches to optimize satellite resources. Joint Communications and Sensing (JCAS) technology represents a transformative paradigm for SN. By integrating communication and sensing functionalities into unified hardware platforms, JCAS enhances spectral efficiency, reduces operational costs, and minimizes hardware redundancies. This paper explores the potential of JCAS in advancing the next-generation space era, highlighting its role in emerging applications. Furthermore, it identifies critical challenges, such as waveform design, Doppler effect mitigation, and multi-target detection, that remain open for future research. Through these discussions, we aim to stimulate further research into the transformative potential of JCAS in addressing the demands of 6G and beyond SN.
Holographic MIMO for Next Generation Non-Terrestrial Networks: Motivation, Opportunities, and Challenges
Nov 15, 2024



Abstract:In this article, we propose the integration of the Holographic Multiple Input Multiple Output (HMIMO) as a transformative solution for next generation Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTNs), addressing key challenges, such as high hardware costs, launch expenses, and energy inefficiency. Traditional NTNs are constrained by the financial and operational limitations posed by bulky, costly antenna systems, alongside the complexities of maintaining effective communications in space. HMIMO offers a novel approach utilizing compact and lightweight arrays of densely packed radiating elements with real-time reconfiguration capabilities, thus, capable of optimizing system performance under dynamic conditions such as varying orbital dynamics and Doppler shifts. By replacing conventional antenna systems with HMIMO, the complexity and cost of satellite manufacturing and launch can be substantially reduced, enabling more streamlined and cost-effective satellite designs. This advancement holds significant potential to democratize space communications, making them accessible to a broader range of stakeholders, including smaller nations and commercial enterprises. Moreover, the inherent capabilities of HMIMO in enhancing energy efficiency, scalability, and adaptability position this technology as a key enabler of new use cases and sustainable satellite operations.
Optimal Linear Precoding Under Realistic Satellite Communications Scenarios
Aug 16, 2024Abstract:In this paper, optimal linear precoding for the multibeam geostationary earth orbit (GEO) satellite with the multi-user (MU) multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) downlink scenario is addressed. Multiple-user interference is one of the major issues faced by the satellites serving the multiple users operating at the common time-frequency resource block in the downlink channel. To mitigate this issue, the optimal linear precoders are implemented at the gateways (GWs). The precoding computation is performed by utilizing the channel state information obtained at user terminals (UTs). The optimal linear precoders are derived considering beamformer update and power control with an iterative per-antenna power optimization algorithm with a limited required number of iterations. The efficacy of the proposed algorithm is validated using the In-Lab experiment for 16X16 precoding with multi-beam satellite for transmitting and receiving the precoded data with digital video broadcasting satellite-second generation extension (DVB- S2X) standard for the GW and the UTs. The software defined radio platforms are employed for emulating the GWs, UTs, and satellite links. The validation is supported by comparing the proposed optimal linear precoder with full frequency reuse (FFR), and minimum mean square error (MMSE) schemes. The experimental results demonstrate that with the optimal linear precoders it is possible to successfully cancel the inter-user interference in the simulated satellite FFR link. Thus, optimal linear precoding brings gains in terms of enhanced signal-to-noise-and-interference ratio, and increased system throughput and spectral efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge