Rakesh Palisetty
Optimal Linear Precoding Under Realistic Satellite Communications Scenarios
Aug 16, 2024Abstract:In this paper, optimal linear precoding for the multibeam geostationary earth orbit (GEO) satellite with the multi-user (MU) multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) downlink scenario is addressed. Multiple-user interference is one of the major issues faced by the satellites serving the multiple users operating at the common time-frequency resource block in the downlink channel. To mitigate this issue, the optimal linear precoders are implemented at the gateways (GWs). The precoding computation is performed by utilizing the channel state information obtained at user terminals (UTs). The optimal linear precoders are derived considering beamformer update and power control with an iterative per-antenna power optimization algorithm with a limited required number of iterations. The efficacy of the proposed algorithm is validated using the In-Lab experiment for 16X16 precoding with multi-beam satellite for transmitting and receiving the precoded data with digital video broadcasting satellite-second generation extension (DVB- S2X) standard for the GW and the UTs. The software defined radio platforms are employed for emulating the GWs, UTs, and satellite links. The validation is supported by comparing the proposed optimal linear precoder with full frequency reuse (FFR), and minimum mean square error (MMSE) schemes. The experimental results demonstrate that with the optimal linear precoders it is possible to successfully cancel the inter-user interference in the simulated satellite FFR link. Thus, optimal linear precoding brings gains in terms of enhanced signal-to-noise-and-interference ratio, and increased system throughput and spectral efficiency.
User-Centric Beam Selection and Precoding Design for Coordinated Multiple-Satellite Systems
Mar 13, 2024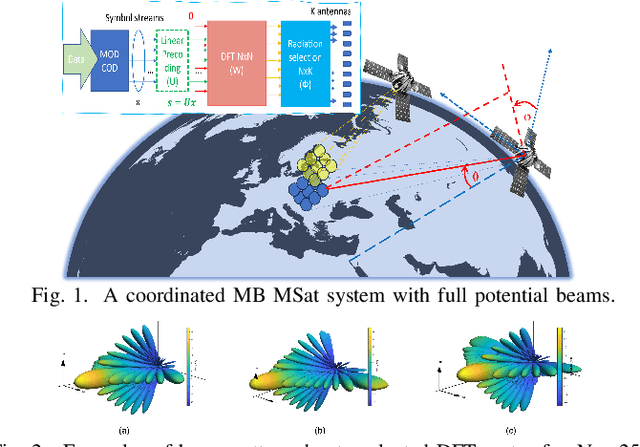
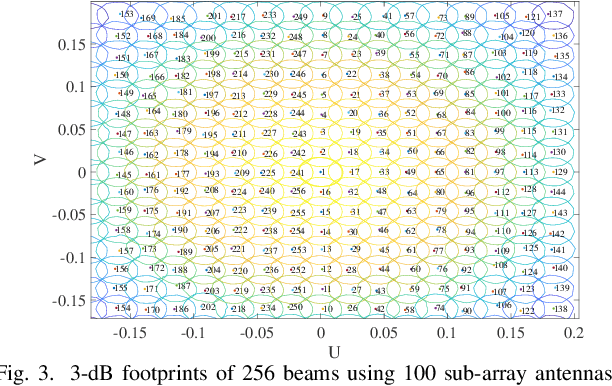
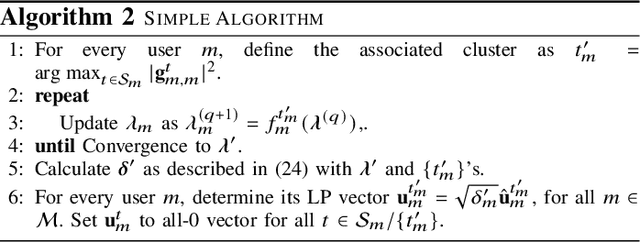
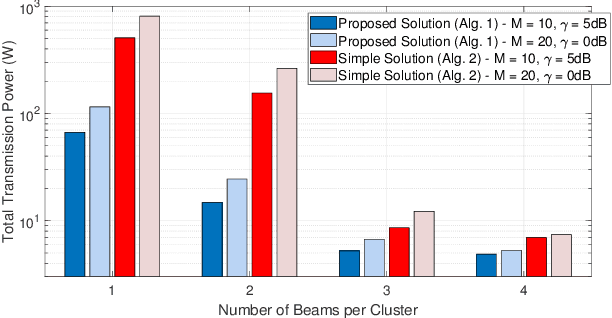
Abstract:This paper introduces a joint optimization framework for user-centric beam selection and linear precoding (LP) design in a coordinated multiple-satellite (CoMSat) system, employing a Digital-Fourier-Transform-based (DFT) beamforming (BF) technique. Regarding serving users at their target SINRs and minimizing the total transmit power, the scheme aims to efficiently determine satellites for users to associate with and activate the best cluster of beams together with optimizing LP for every satellite-to-user transmission. These technical objectives are first framed as a complex mixed-integer programming (MIP) challenge. To tackle this, we reformulate it into a joint cluster association and LP design problem. Then, by theoretically analyzing the duality relationship between downlink and uplink transmissions, we develop an efficient iterative method to identify the optimal solution. Additionally, a simpler duality approach for rapid beam selection and LP design is presented for comparison purposes. Simulation results underscore the effectiveness of our proposed schemes across various settings.
Harnessing the Power of Swarm Satellite Networks with Wideband Distributed Beamforming
Jul 10, 2023
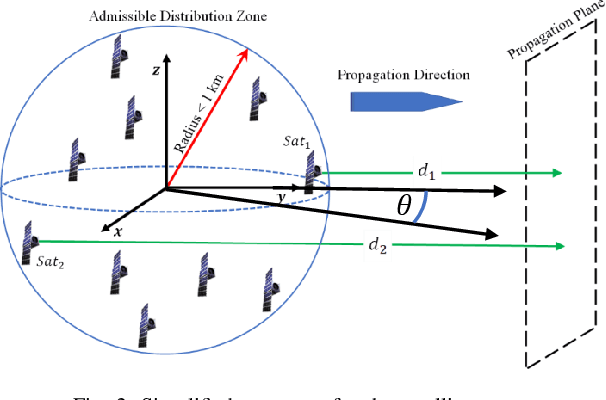
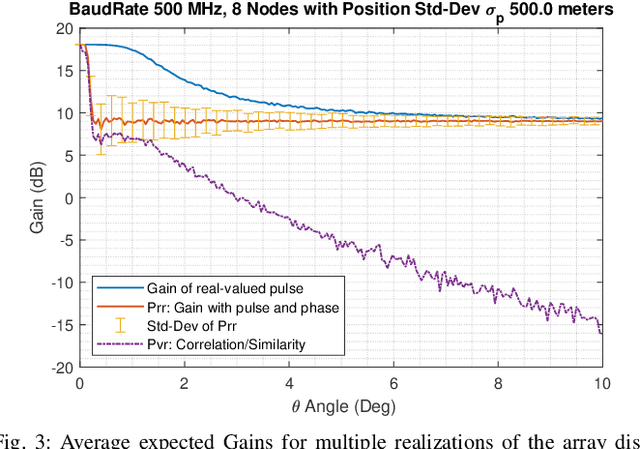
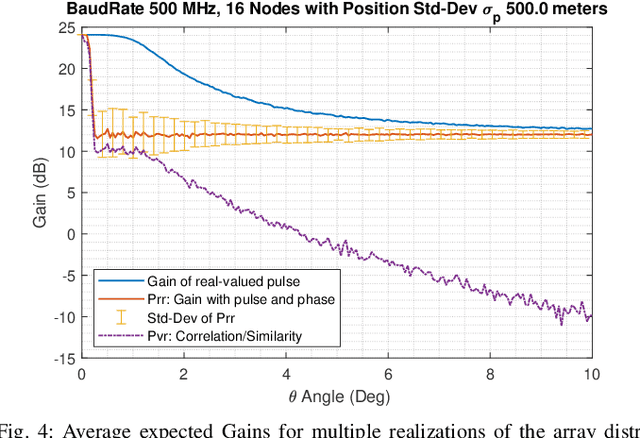
Abstract:The space communications industry is challenged to develop a technology that can deliver broadband services to user terminals equipped with miniature antennas, such as handheld devices. One potential solution to establish links with ground users is the deployment of massive antennas in one single spacecraft. However, this is not cost-effective. Aligning with recent \emph{NewSpace} activities directed toward miniaturization, mass production, and a significant reduction in spacecraft launch costs, an alternative could be distributed beamforming from multiple satellites. In this context, we propose a distributed beamforming modeling technique for wideband signals. We also consider the statistical behavior of the relative geometry of the swarm nodes. The paper assesses the proposed technique via computer simulations, providing interesting results on the beamforming gains in terms of power and the security of the communication against potential eavesdroppers at non-intended pointing angles. This approach paves the way for further exploration of wideband distributed beamforming from satellite swarms in several future communication applications.
Joint Linear Precoding and DFT Beamforming Design for Massive MIMO Satellite Communication
Nov 16, 2022



Abstract:This paper jointly designs linear precoding (LP) and codebook-based beamforming implemented in a satellite with massive multiple-input multiple-output (mMIMO) antenna technology. The codebook of beamforming weights is built using the columns of the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) matrix, and the resulting joint design maximizes the achievable throughput under limited transmission power. The corresponding optimization problem is first formulated as a mixed integer non-linear programming (MINP). To adequately address this challenging problem, an efficient LP and DFT-based beamforming algorithm are developed by utilizing several optimization tools, such as the weighted minimum mean square error transformation, duality method, and Hungarian algorithm. In addition, a greedy algorithm is proposed for benchmarking. A complexity analysis of these solutions is provided along with a comprehensive set of Monte Carlo simulations demonstrating the efficiency of our proposed algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge