Jonathan Thomm
Terminating Differentiable Tree Experts
Jul 02, 2024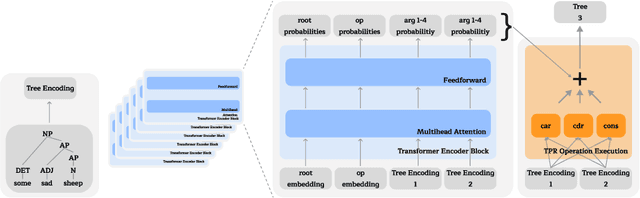

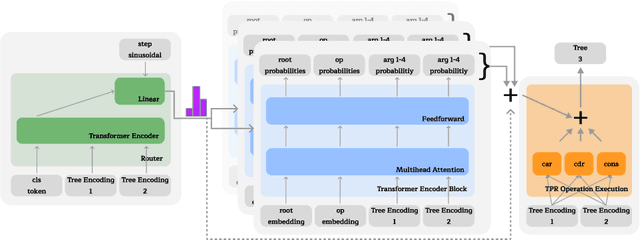

Abstract:We advance the recently proposed neuro-symbolic Differentiable Tree Machine, which learns tree operations using a combination of transformers and Tensor Product Representations. We investigate the architecture and propose two key components. We first remove a series of different transformer layers that are used in every step by introducing a mixture of experts. This results in a Differentiable Tree Experts model with a constant number of parameters for any arbitrary number of steps in the computation, compared to the previous method in the Differentiable Tree Machine with a linear growth. Given this flexibility in the number of steps, we additionally propose a new termination algorithm to provide the model the power to choose how many steps to make automatically. The resulting Terminating Differentiable Tree Experts model sluggishly learns to predict the number of steps without an oracle. It can do so while maintaining the learning capabilities of the model, converging to the optimal amount of steps.
Object-Attribute Binding in Text-to-Image Generation: Evaluation and Control
Apr 21, 2024Abstract:Current diffusion models create photorealistic images given a text prompt as input but struggle to correctly bind attributes mentioned in the text to the right objects in the image. This is evidenced by our novel image-graph alignment model called EPViT (Edge Prediction Vision Transformer) for the evaluation of image-text alignment. To alleviate the above problem, we propose focused cross-attention (FCA) that controls the visual attention maps by syntactic constraints found in the input sentence. Additionally, the syntax structure of the prompt helps to disentangle the multimodal CLIP embeddings that are commonly used in T2I generation. The resulting DisCLIP embeddings and FCA are easily integrated in state-of-the-art diffusion models without additional training of these models. We show substantial improvements in T2I generation and especially its attribute-object binding on several datasets.\footnote{Code and data will be made available upon acceptance.
Limits of Transformer Language Models on Learning Algorithmic Compositions
Feb 13, 2024



Abstract:We analyze the capabilities of Transformer language models on learning discrete algorithms. To this end, we introduce two new tasks demanding the composition of several discrete sub-tasks. On both training LLaMA models from scratch and prompting on GPT-4 and Gemini we measure learning compositions of learned primitives. We observe that the compositional capabilities of state-of-the-art Transformer language models are very limited and sample-wise scale worse than relearning all sub-tasks for a new algorithmic composition. We also present a theorem in complexity theory, showing that gradient descent on memorizing feedforward models can be exponentially data inefficient.
FABRIC: Personalizing Diffusion Models with Iterative Feedback
Jul 19, 2023Abstract:In an era where visual content generation is increasingly driven by machine learning, the integration of human feedback into generative models presents significant opportunities for enhancing user experience and output quality. This study explores strategies for incorporating iterative human feedback into the generative process of diffusion-based text-to-image models. We propose FABRIC, a training-free approach applicable to a wide range of popular diffusion models, which exploits the self-attention layer present in the most widely used architectures to condition the diffusion process on a set of feedback images. To ensure a rigorous assessment of our approach, we introduce a comprehensive evaluation methodology, offering a robust mechanism to quantify the performance of generative visual models that integrate human feedback. We show that generation results improve over multiple rounds of iterative feedback through exhaustive analysis, implicitly optimizing arbitrary user preferences. The potential applications of these findings extend to fields such as personalized content creation and customization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge