Geethan Karunaratne
IBM Research - Zurich
On the Role of Noise in Factorizers for Disentangling Distributed Representations
Nov 30, 2024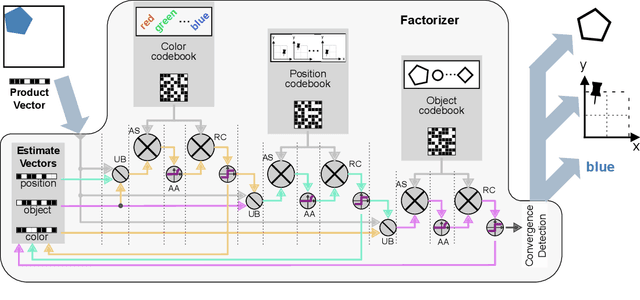
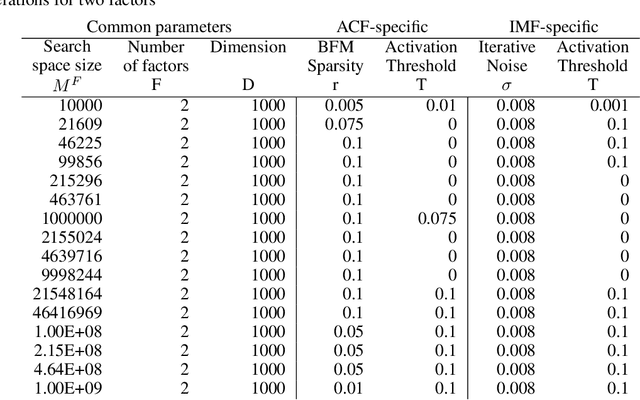
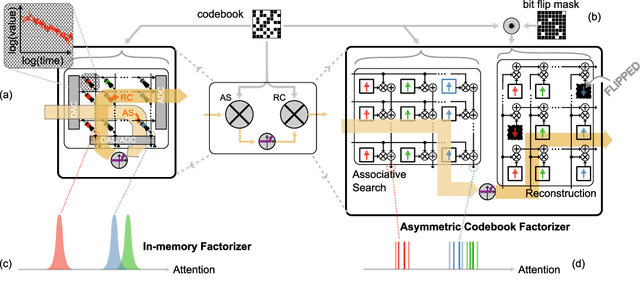
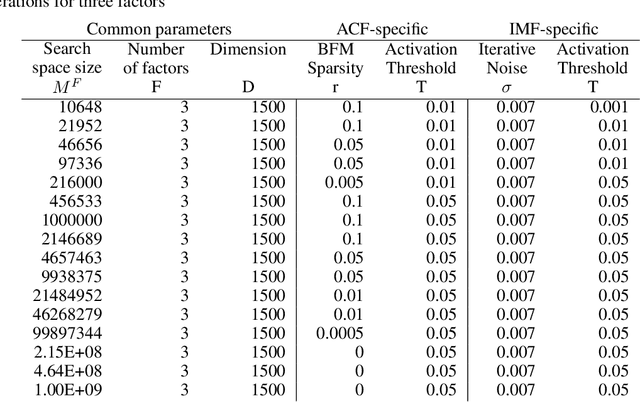
Abstract:To efficiently factorize high-dimensional distributed representations to the constituent atomic vectors, one can exploit the compute-in-superposition capabilities of vector-symbolic architectures (VSA). Such factorizers however suffer from the phenomenon of limit cycles. Applying noise during the iterative decoding is one mechanism to address this issue. In this paper, we explore ways to further relax the noise requirement by applying noise only at the time of VSA's reconstruction codebook initialization. While the need for noise during iterations proves analog in-memory computing systems to be a natural choice as an implementation media, the adequacy of initialization noise allows digital hardware to remain equally indispensable. This broadens the implementation possibilities of factorizers. Our study finds that while the best performance shifts from initialization noise to iterative noise as the number of factors increases from 2 to 4, both extend the operational capacity by at least 50 times compared to the baseline factorizer resonator networks. Our code is available at: https://github.com/IBM/in-memory-factorizer
Limits of Transformer Language Models on Learning Algorithmic Compositions
Feb 13, 2024



Abstract:We analyze the capabilities of Transformer language models on learning discrete algorithms. To this end, we introduce two new tasks demanding the composition of several discrete sub-tasks. On both training LLaMA models from scratch and prompting on GPT-4 and Gemini we measure learning compositions of learned primitives. We observe that the compositional capabilities of state-of-the-art Transformer language models are very limited and sample-wise scale worse than relearning all sub-tasks for a new algorithmic composition. We also present a theorem in complexity theory, showing that gradient descent on memorizing feedforward models can be exponentially data inefficient.
Zero-shot Classification using Hyperdimensional Computing
Jan 30, 2024Abstract:Classification based on Zero-shot Learning (ZSL) is the ability of a model to classify inputs into novel classes on which the model has not previously seen any training examples. Providing an auxiliary descriptor in the form of a set of attributes describing the new classes involved in the ZSL-based classification is one of the favored approaches to solving this challenging task. In this work, inspired by Hyperdimensional Computing (HDC), we propose the use of stationary binary codebooks of symbol-like distributed representations inside an attribute encoder to compactly represent a computationally simple end-to-end trainable model, which we name Hyperdimensional Computing Zero-shot Classifier~(HDC-ZSC). It consists of a trainable image encoder, an attribute encoder based on HDC, and a similarity kernel. We show that HDC-ZSC can be used to first perform zero-shot attribute extraction tasks and, can later be repurposed for Zero-shot Classification tasks with minimal architectural changes and minimal model retraining. HDC-ZSC achieves Pareto optimal results with a 63.8% top-1 classification accuracy on the CUB-200 dataset by having only 26.6 million trainable parameters. Compared to two other state-of-the-art non-generative approaches, HDC-ZSC achieves 4.3% and 9.9% better accuracy, while they require more than 1.85x and 1.72x parameters compared to HDC-ZSC, respectively.
TCNCA: Temporal Convolution Network with Chunked Attention for Scalable Sequence Processing
Dec 09, 2023



Abstract:MEGA is a recent transformer-based architecture, which utilizes a linear recurrent operator whose parallel computation, based on the FFT, scales as $O(LlogL)$, with $L$ being the sequence length. We build upon their approach by replacing the linear recurrence with a special temporal convolutional network which permits larger receptive field size with shallower networks, and reduces the computational complexity to $O(L)$. The resulting model is called TCNCA, a Temporal Convolutional Network with Chunked Attention. We evaluate TCNCA on EnWik8 language modeling, long-range-arena (LRA) sequence classification, as well as a synthetic reasoning benchmark associative recall. On EnWik8, TCNCA outperforms MEGA, reaching a lower loss with $1.37\times$/$1.24\times$ faster forward/backward pass during training. The dilated convolutions used in TCNCA are consistently and significantly faster operations than the FFT-based parallelized recurrence in GPUs, making them a scalable candidate for handling very large sequence lengths: they are up to $7.07\times$/$2.86\times$ faster in the forward/backward pass for sequences up to 131k. Further on LRA, TCNCA achieves, on average, $1.28\times$ speed-up during inference with similar accuracy to what MEGA achieves. On associative recall, we find that even a simplified version of TCNCA, without excessive multiplicative and additive interactions, remains superior or competitive to MEGA on a range of sequence lengths and vocabulary sizes.
MIMONets: Multiple-Input-Multiple-Output Neural Networks Exploiting Computation in Superposition
Dec 05, 2023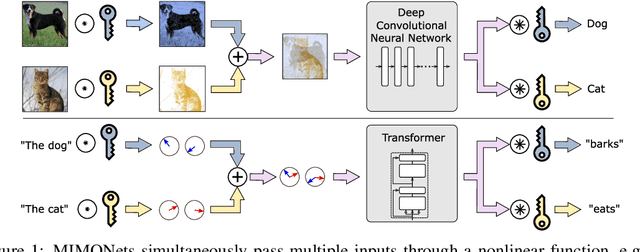
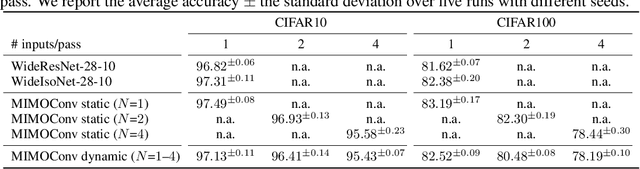
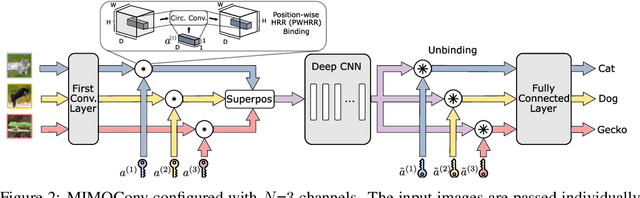
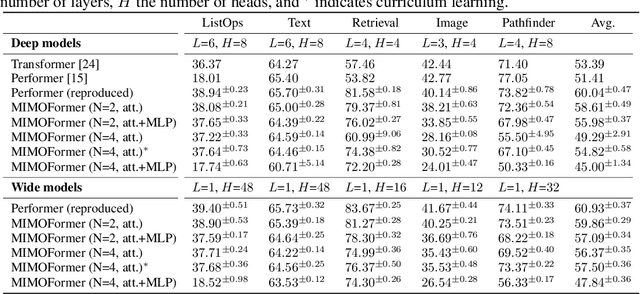
Abstract:With the advent of deep learning, progressively larger neural networks have been designed to solve complex tasks. We take advantage of these capacity-rich models to lower the cost of inference by exploiting computation in superposition. To reduce the computational burden per input, we propose Multiple-Input-Multiple-Output Neural Networks (MIMONets) capable of handling many inputs at once. MIMONets augment various deep neural network architectures with variable binding mechanisms to represent an arbitrary number of inputs in a compositional data structure via fixed-width distributed representations. Accordingly, MIMONets adapt nonlinear neural transformations to process the data structure holistically, leading to a speedup nearly proportional to the number of superposed input items in the data structure. After processing in superposition, an unbinding mechanism recovers each transformed input of interest. MIMONets also provide a dynamic trade-off between accuracy and throughput by an instantaneous on-demand switching between a set of accuracy-throughput operating points, yet within a single set of fixed parameters. We apply the concept of MIMONets to both CNN and Transformer architectures resulting in MIMOConv and MIMOFormer, respectively. Empirical evaluations show that MIMOConv achieves about 2-4 x speedup at an accuracy delta within [+0.68, -3.18]% compared to WideResNet CNNs on CIFAR10 and CIFAR100. Similarly, MIMOFormer can handle 2-4 inputs at once while maintaining a high average accuracy within a [-1.07, -3.43]% delta on the long range arena benchmark. Finally, we provide mathematical bounds on the interference between superposition channels in MIMOFormer. Our code is available at https://github.com/IBM/multiple-input-multiple-output-nets.
Factorizers for Distributed Sparse Block Codes
Mar 24, 2023Abstract:Distributed sparse block codes (SBCs) exhibit compact representations for encoding and manipulating symbolic data structures using fixed-with vectors. One major challenge however is to disentangle, or factorize, such data structures into their constituent elements without having to search through all possible combinations. This factorization becomes more challenging when queried by noisy SBCs wherein symbol representations are relaxed due to perceptual uncertainty and approximations made when modern neural networks are used to generate the query vectors. To address these challenges, we first propose a fast and highly accurate method for factorizing a more flexible and hence generalized form of SBCs, dubbed GSBCs. Our iterative factorizer introduces a threshold-based nonlinear activation, a conditional random sampling, and an $\ell_\infty$-based similarity metric. Its random sampling mechanism in combination with the search in superposition allows to analytically determine the expected number of decoding iterations, which matches the empirical observations up to the GSBC's bundling capacity. Secondly, the proposed factorizer maintains its high accuracy when queried by noisy product vectors generated using deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs). This facilitates its application in replacing the large fully connected layer (FCL) in CNNs, whereby C trainable class vectors, or attribute combinations, can be implicitly represented by our factorizer having F-factor codebooks, each with $\sqrt[\leftroot{-2}\uproot{2}F]{C}$ fixed codevectors. We provide a methodology to flexibly integrate our factorizer in the classification layer of CNNs with a novel loss function. We demonstrate the feasibility of our method on four deep CNN architectures over CIFAR-100, ImageNet-1K, and RAVEN datasets. In all use cases, the number of parameters and operations are significantly reduced compared to the FCL.
In-memory factorization of holographic perceptual representations
Nov 09, 2022Abstract:Disentanglement of constituent factors of a sensory signal is central to perception and cognition and hence is a critical task for future artificial intelligence systems. In this paper, we present a compute engine capable of efficiently factorizing holographic perceptual representations by exploiting the computation-in-superposition capability of brain-inspired hyperdimensional computing and the intrinsic stochasticity associated with analog in-memory computing based on nanoscale memristive devices. Such an iterative in-memory factorizer is shown to solve at least five orders of magnitude larger problems that cannot be solved otherwise, while also significantly lowering the computational time and space complexity. We present a large-scale experimental demonstration of the factorizer by employing two in-memory compute chips based on phase-change memristive devices. The dominant matrix-vector multiply operations are executed at O(1) thus reducing the computational time complexity to merely the number of iterations. Moreover, we experimentally demonstrate the ability to factorize visual perceptual representations reliably and efficiently.
In-memory Realization of In-situ Few-shot Continual Learning with a Dynamically Evolving Explicit Memory
Jul 14, 2022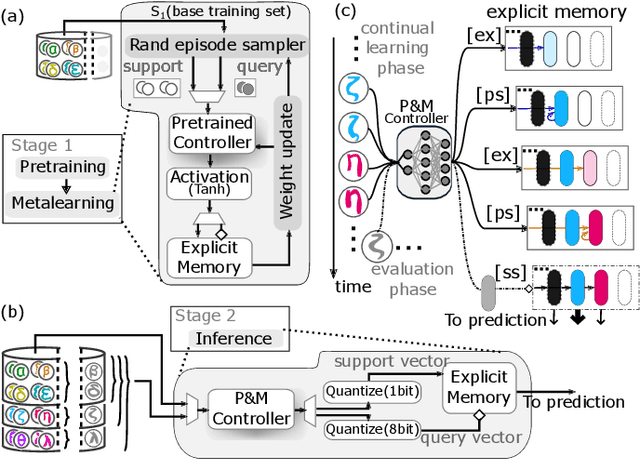
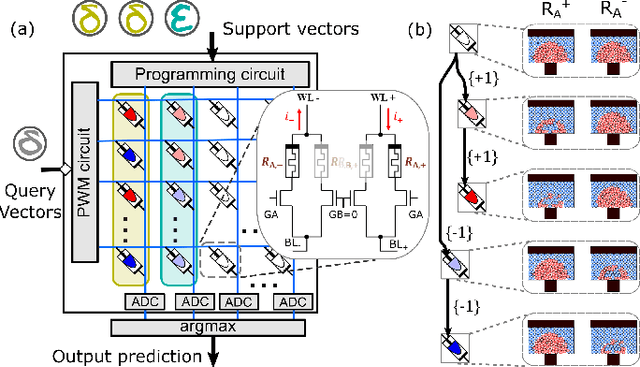
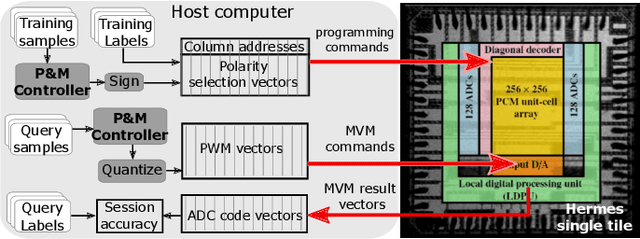
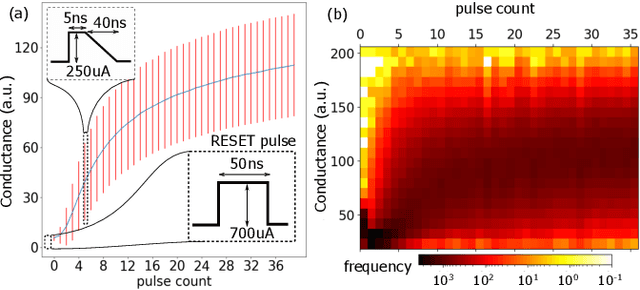
Abstract:Continually learning new classes from a few training examples without forgetting previous old classes demands a flexible architecture with an inevitably growing portion of storage, in which new examples and classes can be incrementally stored and efficiently retrieved. One viable architectural solution is to tightly couple a stationary deep neural network to a dynamically evolving explicit memory (EM). As the centerpiece of this architecture, we propose an EM unit that leverages energy-efficient in-memory compute (IMC) cores during the course of continual learning operations. We demonstrate for the first time how the EM unit can physically superpose multiple training examples, expand to accommodate unseen classes, and perform similarity search during inference, using operations on an IMC core based on phase-change memory (PCM). Specifically, the physical superposition of a few encoded training examples is realized via in-situ progressive crystallization of PCM devices. The classification accuracy achieved on the IMC core remains within a range of 1.28%--2.5% compared to that of the state-of-the-art full-precision baseline software model on both the CIFAR-100 and miniImageNet datasets when continually learning 40 novel classes (from only five examples per class) on top of 60 old classes.
Constrained Few-shot Class-incremental Learning
Mar 30, 2022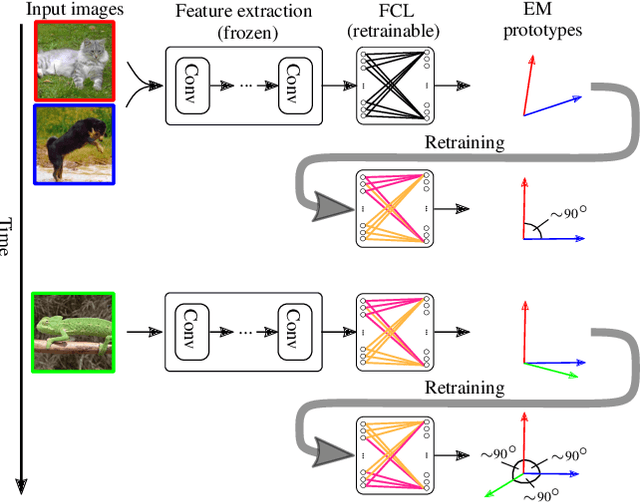
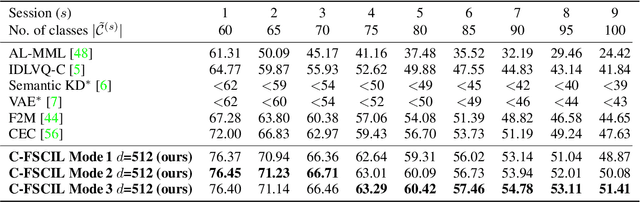
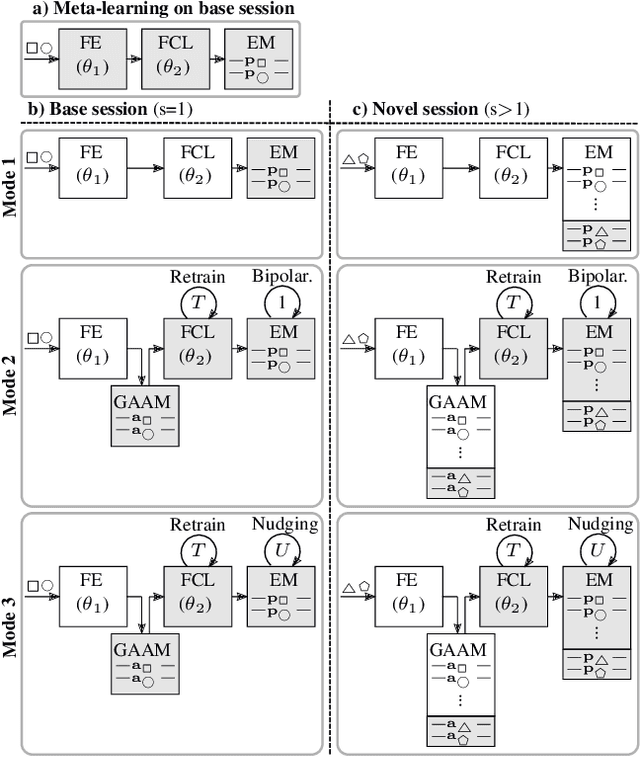
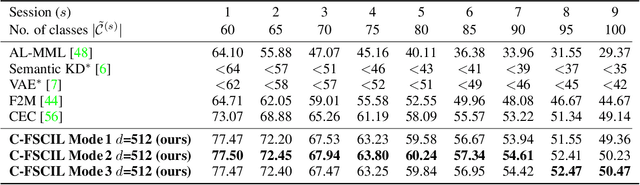
Abstract:Continually learning new classes from fresh data without forgetting previous knowledge of old classes is a very challenging research problem. Moreover, it is imperative that such learning must respect certain memory and computational constraints such as (i) training samples are limited to only a few per class, (ii) the computational cost of learning a novel class remains constant, and (iii) the memory footprint of the model grows at most linearly with the number of classes observed. To meet the above constraints, we propose C-FSCIL, which is architecturally composed of a frozen meta-learned feature extractor, a trainable fixed-size fully connected layer, and a rewritable dynamically growing memory that stores as many vectors as the number of encountered classes. C-FSCIL provides three update modes that offer a trade-off between accuracy and compute-memory cost of learning novel classes. C-FSCIL exploits hyperdimensional embedding that allows to continually express many more classes than the fixed dimensions in the vector space, with minimal interference. The quality of class vector representations is further improved by aligning them quasi-orthogonally to each other by means of novel loss functions. Experiments on the CIFAR100, miniImageNet, and Omniglot datasets show that C-FSCIL outperforms the baselines with remarkable accuracy and compression. It also scales up to the largest problem size ever tried in this few-shot setting by learning 423 novel classes on top of 1200 base classes with less than 1.6% accuracy drop. Our code is available at https://github.com/IBM/constrained-FSCIL.
Generalized Key-Value Memory to Flexibly Adjust Redundancy in Memory-Augmented Networks
Mar 11, 2022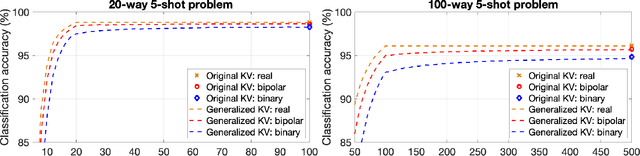
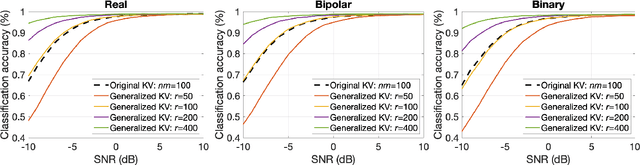
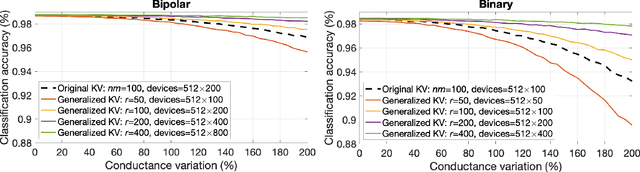
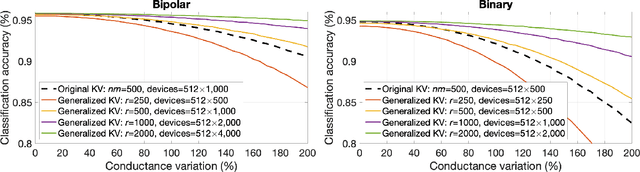
Abstract:Memory-augmented neural networks enhance a neural network with an external key-value memory whose complexity is typically dominated by the number of support vectors in the key memory. We propose a generalized key-value memory that decouples its dimension from the number of support vectors by introducing a free parameter that can arbitrarily add or remove redundancy to the key memory representation. In effect, it provides an additional degree of freedom to flexibly control the trade-off between robustness and the resources required to store and compute the generalized key-value memory. This is particularly useful for realizing the key memory on in-memory computing hardware where it exploits nonideal, but extremely efficient non-volatile memory devices for dense storage and computation. Experimental results show that adapting this parameter on demand effectively mitigates up to 44% nonidealities, at equal accuracy and number of devices, without any need for neural network retraining.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge