Generalized Key-Value Memory to Flexibly Adjust Redundancy in Memory-Augmented Networks
Paper and Code
Mar 11, 2022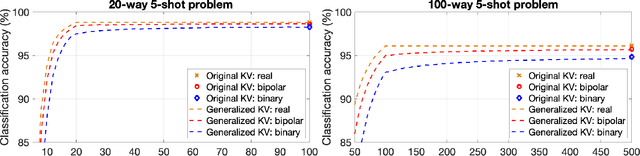
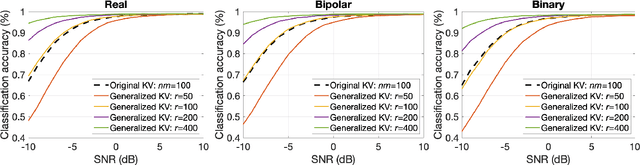
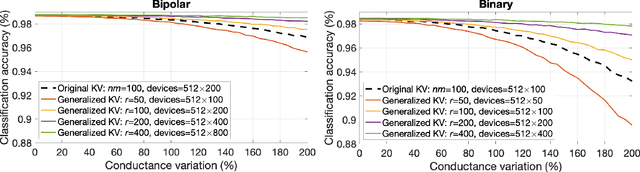
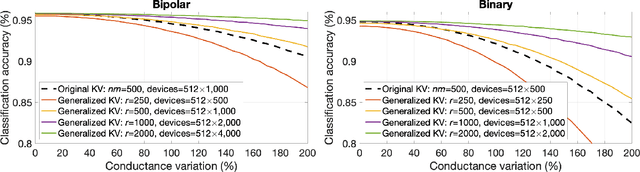
Memory-augmented neural networks enhance a neural network with an external key-value memory whose complexity is typically dominated by the number of support vectors in the key memory. We propose a generalized key-value memory that decouples its dimension from the number of support vectors by introducing a free parameter that can arbitrarily add or remove redundancy to the key memory representation. In effect, it provides an additional degree of freedom to flexibly control the trade-off between robustness and the resources required to store and compute the generalized key-value memory. This is particularly useful for realizing the key memory on in-memory computing hardware where it exploits nonideal, but extremely efficient non-volatile memory devices for dense storage and computation. Experimental results show that adapting this parameter on demand effectively mitigates up to 44% nonidealities, at equal accuracy and number of devices, without any need for neural network retraining.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge