John Schultz
Code World Models for General Game Playing
Oct 06, 2025
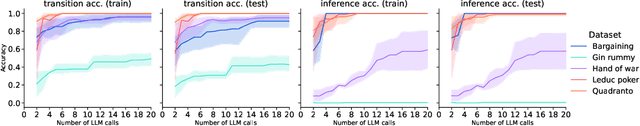
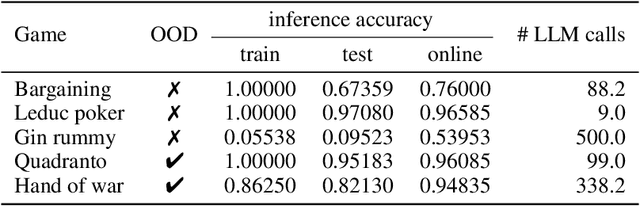
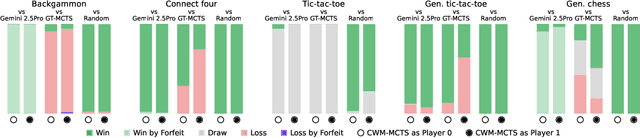
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) reasoning abilities are increasingly being applied to classical board and card games, but the dominant approach -- involving prompting for direct move generation -- has significant drawbacks. It relies on the model's implicit fragile pattern-matching capabilities, leading to frequent illegal moves and strategically shallow play. Here we introduce an alternative approach: We use the LLM to translate natural language rules and game trajectories into a formal, executable world model represented as Python code. This generated model -- comprising functions for state transition, legal move enumeration, and termination checks -- serves as a verifiable simulation engine for high-performance planning algorithms like Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS). In addition, we prompt the LLM to generate heuristic value functions (to make MCTS more efficient), and inference functions (to estimate hidden states in imperfect information games). Our method offers three distinct advantages compared to directly using the LLM as a policy: (1) Verifiability: The generated CWM serves as a formal specification of the game's rules, allowing planners to algorithmically enumerate valid actions and avoid illegal moves, contingent on the correctness of the synthesized model; (2) Strategic Depth: We combine LLM semantic understanding with the deep search power of classical planners; and (3) Generalization: We direct the LLM to focus on the meta-task of data-to-code translation, enabling it to adapt to new games more easily. We evaluate our agent on 10 different games, of which 4 are novel and created for this paper. 5 of the games are fully observed (perfect information), and 5 are partially observed (imperfect information). We find that our method outperforms or matches Gemini 2.5 Pro in 9 out of the 10 considered games.
Population-based Evaluation in Repeated Rock-Paper-Scissors as a Benchmark for Multiagent Reinforcement Learning
Mar 02, 2023



Abstract:Progress in fields of machine learning and adversarial planning has benefited significantly from benchmark domains, from checkers and the classic UCI data sets to Go and Diplomacy. In sequential decision-making, agent evaluation has largely been restricted to few interactions against experts, with the aim to reach some desired level of performance (e.g. beating a human professional player). We propose a benchmark for multiagent learning based on repeated play of the simple game Rock, Paper, Scissors along with a population of forty-three tournament entries, some of which are intentionally sub-optimal. We describe metrics to measure the quality of agents based both on average returns and exploitability. We then show that several RL, online learning, and language model approaches can learn good counter-strategies and generalize well, but ultimately lose to the top-performing bots, creating an opportunity for research in multiagent learning.
Learning to Navigate Wikipedia by Taking Random Walks
Oct 31, 2022Abstract:A fundamental ability of an intelligent web-based agent is seeking out and acquiring new information. Internet search engines reliably find the correct vicinity but the top results may be a few links away from the desired target. A complementary approach is navigation via hyperlinks, employing a policy that comprehends local content and selects a link that moves it closer to the target. In this paper, we show that behavioral cloning of randomly sampled trajectories is sufficient to learn an effective link selection policy. We demonstrate the approach on a graph version of Wikipedia with 38M nodes and 387M edges. The model is able to efficiently navigate between nodes 5 and 20 steps apart 96% and 92% of the time, respectively. We then use the resulting embeddings and policy in downstream fact verification and question answering tasks where, in combination with basic TF-IDF search and ranking methods, they are competitive results to the state-of-the-art methods.
The Advantage Regret-Matching Actor-Critic
Aug 27, 2020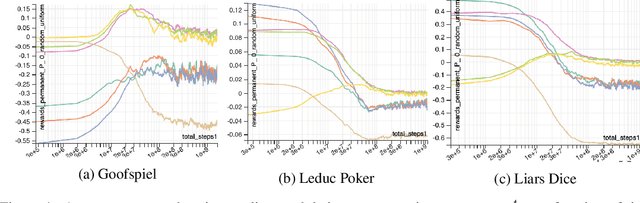
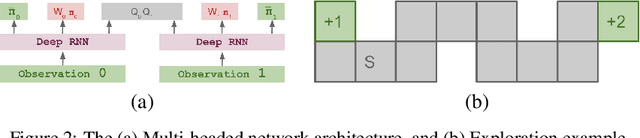

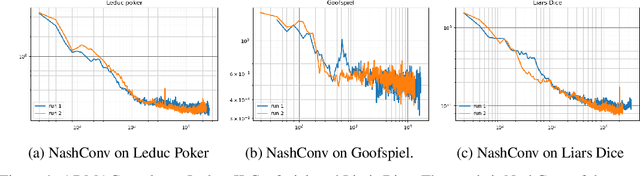
Abstract:Regret minimization has played a key role in online learning, equilibrium computation in games, and reinforcement learning (RL). In this paper, we describe a general model-free RL method for no-regret learning based on repeated reconsideration of past behavior. We propose a model-free RL algorithm, the AdvantageRegret-Matching Actor-Critic (ARMAC): rather than saving past state-action data, ARMAC saves a buffer of past policies, replaying through them to reconstruct hindsight assessments of past behavior. These retrospective value estimates are used to predict conditional advantages which, combined with regret matching, produces a new policy. In particular, ARMAC learns from sampled trajectories in a centralized training setting, without requiring the application of importance sampling commonly used in Monte Carlo counterfactual regret (CFR) minimization; hence, it does not suffer from excessive variance in large environments. In the single-agent setting, ARMAC shows an interesting form of exploration by keeping past policies intact. In the multiagent setting, ARMAC in self-play approaches Nash equilibria on some partially-observable zero-sum benchmarks. We provide exploitability estimates in the significantly larger game of betting-abstracted no-limit Texas Hold'em.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge