John Pavlopoulos
Archimedes, Athena Research Center, Greece, Department of Informatics, Athens University of Economics and Business, Greece
RAG-E: Quantifying Retriever-Generator Alignment and Failure Modes
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems combine dense retrievers and language models to ground LLM outputs in retrieved documents. However, the opacity of how these components interact creates challenges for deployment in high-stakes domains. We present RAG-E, an end-to-end explainability framework that quantifies retriever-generator alignment through mathematically grounded attribution methods. Our approach adapts Integrated Gradients for retriever analysis, introduces PMCSHAP, a Monte Carlo-stabilized Shapley Value approximation, for generator attribution, and introduces the Weighted Attribution-Relevance Gap (WARG) metric to measure how well a generator's document usage aligns with a retriever's ranking. Empirical analysis on TREC CAsT and FoodSafeSum reveals critical misalignments: for 47.4% to 66.7% of queries, generators ignore the retriever's top-ranked documents, while 48.1% to 65.9% rely on documents ranked as less relevant. These failure modes demonstrate that RAG output quality depends not solely on individual component performance but on their interplay, which can be audited via RAG-E.
TopClustRAG at SIGIR 2025 LiveRAG Challenge
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:We present TopClustRAG, a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) system developed for the LiveRAG Challenge, which evaluates end-to-end question answering over large-scale web corpora. Our system employs a hybrid retrieval strategy combining sparse and dense indices, followed by K-Means clustering to group semantically similar passages. Representative passages from each cluster are used to construct cluster-specific prompts for a large language model (LLM), generating intermediate answers that are filtered, reranked, and finally synthesized into a single, comprehensive response. This multi-stage pipeline enhances answer diversity, relevance, and faithfulness to retrieved evidence. Evaluated on the FineWeb Sample-10BT dataset, TopClustRAG ranked 2nd in faithfulness and 7th in correctness on the official leaderboard, demonstrating the effectiveness of clustering-based context filtering and prompt aggregation in large-scale RAG systems.
Silhouette-Guided Instance-Weighted k-means
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Clustering is a fundamental unsupervised learning task with numerous applications across diverse fields. Popular algorithms such as k-means often struggle with outliers or imbalances, leading to distorted centroids and suboptimal partitions. We introduce K-Sil, a silhouette-guided refinement of the k-means algorithm that weights points based on their silhouette scores, prioritizing well-clustered instances while suppressing borderline or noisy regions. The algorithm emphasizes user-specified silhouette aggregation metrics: macro-, micro-averaged or a combination, through self-tuning weighting schemes, supported by appropriate sampling strategies and scalable approximations. These components ensure computational efficiency and adaptability to diverse dataset geometries. Theoretical guarantees establish centroid convergence, and empirical validation on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrates statistically significant improvements in silhouette scores over k-means and two other instance-weighted k-means variants. These results establish K-Sil as a principled alternative for applications demanding high-quality, well-separated clusters.
Learning to Align: Addressing Character Frequency Distribution Shifts in Handwritten Text Recognition
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Handwritten text recognition aims to convert visual input into machine-readable text, and it remains challenging due to the evolving and context-dependent nature of handwriting. Character sets change over time, and character frequency distributions shift across historical periods or regions, often causing models trained on broad, heterogeneous corpora to underperform on specific subsets. To tackle this, we propose a novel loss function that incorporates the Wasserstein distance between the character frequency distribution of the predicted text and a target distribution empirically derived from training data. By penalizing divergence from expected distributions, our approach enhances both accuracy and robustness under temporal and contextual intra-dataset shifts. Furthermore, we demonstrate that character distribution alignment can also improve existing models at inference time without requiring retraining by integrating it as a scoring function in a guided decoding scheme. Experimental results across multiple datasets and architectures confirm the effectiveness of our method in boosting generalization and performance. We open source our code at https://github.com/pkaliosis/fada.
Dialect Normalization using Large Language Models and Morphological Rules
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Natural language understanding systems struggle with low-resource languages, including many dialects of high-resource ones. Dialect-to-standard normalization attempts to tackle this issue by transforming dialectal text so that it can be used by standard-language tools downstream. In this study, we tackle this task by introducing a new normalization method that combines rule-based linguistically informed transformations and large language models (LLMs) with targeted few-shot prompting, without requiring any parallel data. We implement our method for Greek dialects and apply it on a dataset of regional proverbs, evaluating the outputs using human annotators. We then use this dataset to conduct downstream experiments, finding that previous results regarding these proverbs relied solely on superficial linguistic information, including orthographic artifacts, while new observations can still be made through the remaining semantics.
SemEval-2025 Task 9: The Food Hazard Detection Challenge
Mar 25, 2025



Abstract:In this challenge, we explored text-based food hazard prediction with long tail distributed classes. The task was divided into two subtasks: (1) predicting whether a web text implies one of ten food-hazard categories and identifying the associated food category, and (2) providing a more fine-grained classification by assigning a specific label to both the hazard and the product. Our findings highlight that large language model-generated synthetic data can be highly effective for oversampling long-tail distributions. Furthermore, we find that fine-tuned encoder-only, encoder-decoder, and decoder-only systems achieve comparable maximum performance across both subtasks. During this challenge, we gradually released (under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) a novel set of 6,644 manually labeled food-incident reports.
Evaluation and Facilitation of Online Discussions in the LLM Era: A Survey
Mar 03, 2025
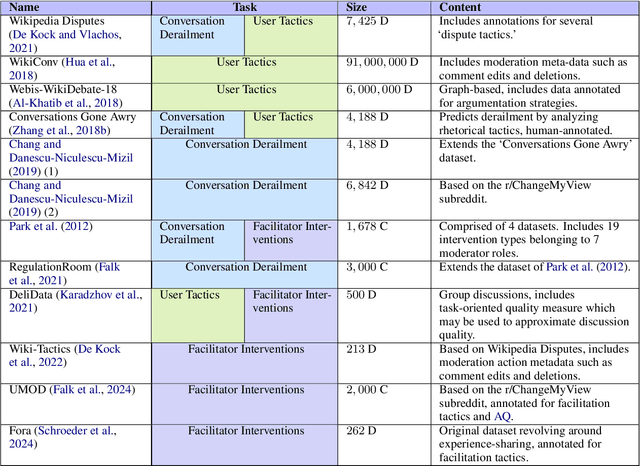

Abstract:We present a survey of methods for assessing and enhancing the quality of online discussions, focusing on the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs). While online discourses aim, at least in theory, to foster mutual understanding, they often devolve into harmful exchanges, such as hate speech, threatening social cohesion and democratic values. Recent advancements in LLMs enable facilitation agents that not only moderate content, but also actively improve the quality of interactions. Our survey synthesizes ideas from Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Social Sciences to provide (a) a new taxonomy on discussion quality evaluation, (b) an overview of intervention and facilitation strategies, along with a new taxonomy on conversation facilitation datasets, (c) an LLM-oriented roadmap of good practices and future research directions, from technological and societal perspectives.
GR-NLP-TOOLKIT: An Open-Source NLP Toolkit for Modern Greek
Dec 11, 2024
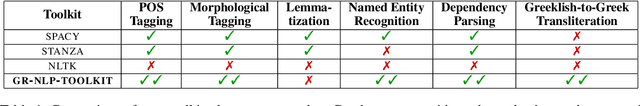
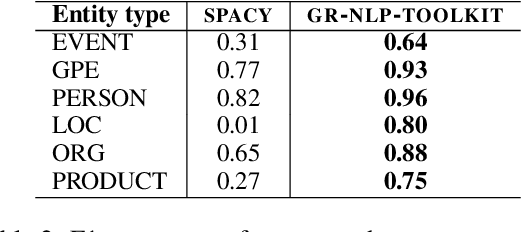
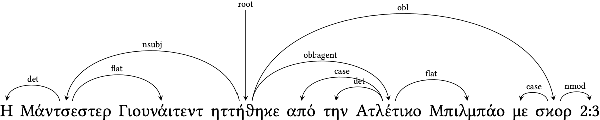
Abstract:We present GR-NLP-TOOLKIT, an open-source natural language processing (NLP) toolkit developed specifically for modern Greek. The toolkit provides state-of-the-art performance in five core NLP tasks, namely part-of-speech tagging, morphological tagging, dependency parsing, named entity recognition, and Greeklishto-Greek transliteration. The toolkit is based on pre-trained Transformers, it is freely available, and can be easily installed in Python (pip install gr-nlp-toolkit). It is also accessible through a demonstration platform on HuggingFace, along with a publicly available API for non-commercial use. We discuss the functionality provided for each task, the underlying methods, experiments against comparable open-source toolkits, and future possible enhancements. The toolkit is available at: https://github.com/nlpaueb/gr-nlp-toolkit
Hate Speech According to the Law: An Analysis for Effective Detection
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:The issue of hate speech extends beyond the confines of the online realm. It is a problem with real-life repercussions, prompting most nations to formulate legal frameworks that classify hate speech as a punishable offence. These legal frameworks differ from one country to another, contributing to the big chaos that online platforms have to face when addressing reported instances of hate speech. With the definitions of hate speech falling short in introducing a robust framework, we turn our gaze onto hate speech laws. We consult the opinion of legal experts on a hate speech dataset and we experiment by employing various approaches such as pretrained models both on hate speech and legal data, as well as exploiting two large language models (Qwen2-7B-Instruct and Meta-Llama-3-70B). Due to the time-consuming nature of data acquisition for prosecutable hate speech, we use pseudo-labeling to improve our pretrained models. This study highlights the importance of amplifying research on prosecutable hate speech and provides insights into effective strategies for combating hate speech within the parameters of legal frameworks. Our findings show that legal knowledge in the form of annotations can be useful when classifying prosecutable hate speech, yet more focus should be paid on the differences between the laws.
Leveraging LLMs for Translating and Classifying Mental Health Data
Oct 16, 2024
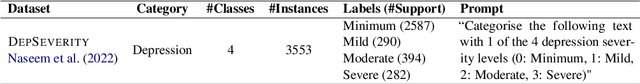
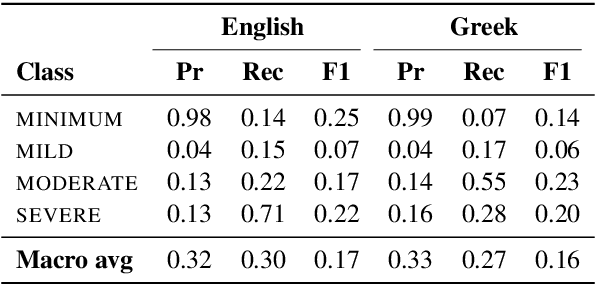

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used in medical fields. In mental health support, the early identification of linguistic markers associated with mental health conditions can provide valuable support to mental health professionals, and reduce long waiting times for patients. Despite the benefits of LLMs for mental health support, there is limited research on their application in mental health systems for languages other than English. Our study addresses this gap by focusing on the detection of depression severity in Greek through user-generated posts which are automatically translated from English. Our results show that GPT3.5-turbo is not very successful in identifying the severity of depression in English, and it has a varying performance in Greek as well. Our study underscores the necessity for further research, especially in languages with less resources. Also, careful implementation is necessary to ensure that LLMs are used effectively in mental health platforms, and human supervision remains crucial to avoid misdiagnosis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge