Tony Lindgren
RAG-E: Quantifying Retriever-Generator Alignment and Failure Modes
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems combine dense retrievers and language models to ground LLM outputs in retrieved documents. However, the opacity of how these components interact creates challenges for deployment in high-stakes domains. We present RAG-E, an end-to-end explainability framework that quantifies retriever-generator alignment through mathematically grounded attribution methods. Our approach adapts Integrated Gradients for retriever analysis, introduces PMCSHAP, a Monte Carlo-stabilized Shapley Value approximation, for generator attribution, and introduces the Weighted Attribution-Relevance Gap (WARG) metric to measure how well a generator's document usage aligns with a retriever's ranking. Empirical analysis on TREC CAsT and FoodSafeSum reveals critical misalignments: for 47.4% to 66.7% of queries, generators ignore the retriever's top-ranked documents, while 48.1% to 65.9% rely on documents ranked as less relevant. These failure modes demonstrate that RAG output quality depends not solely on individual component performance but on their interplay, which can be audited via RAG-E.
SemEval-2025 Task 9: The Food Hazard Detection Challenge
Mar 25, 2025



Abstract:In this challenge, we explored text-based food hazard prediction with long tail distributed classes. The task was divided into two subtasks: (1) predicting whether a web text implies one of ten food-hazard categories and identifying the associated food category, and (2) providing a more fine-grained classification by assigning a specific label to both the hazard and the product. Our findings highlight that large language model-generated synthetic data can be highly effective for oversampling long-tail distributions. Furthermore, we find that fine-tuned encoder-only, encoder-decoder, and decoder-only systems achieve comparable maximum performance across both subtasks. During this challenge, we gradually released (under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) a novel set of 6,644 manually labeled food-incident reports.
Evaluating the Reliability of Self-Explanations in Large Language Models
Jul 19, 2024Abstract:This paper investigates the reliability of explanations generated by large language models (LLMs) when prompted to explain their previous output. We evaluate two kinds of such self-explanations - extractive and counterfactual - using three state-of-the-art LLMs (2B to 8B parameters) on two different classification tasks (objective and subjective). Our findings reveal, that, while these self-explanations can correlate with human judgement, they do not fully and accurately follow the model's decision process, indicating a gap between perceived and actual model reasoning. We show that this gap can be bridged because prompting LLMs for counterfactual explanations can produce faithful, informative, and easy-to-verify results. These counterfactuals offer a promising alternative to traditional explainability methods (e.g. SHAP, LIME), provided that prompts are tailored to specific tasks and checked for validity.
CICLe: Conformal In-Context Learning for Largescale Multi-Class Food Risk Classification
Mar 18, 2024



Abstract:Contaminated or adulterated food poses a substantial risk to human health. Given sets of labeled web texts for training, Machine Learning and Natural Language Processing can be applied to automatically detect such risks. We publish a dataset of 7,546 short texts describing public food recall announcements. Each text is manually labeled, on two granularity levels (coarse and fine), for food products and hazards that the recall corresponds to. We describe the dataset and benchmark naive, traditional, and Transformer models. Based on our analysis, Logistic Regression based on a tf-idf representation outperforms RoBERTa and XLM-R on classes with low support. Finally, we discuss different prompting strategies and present an LLM-in-the-loop framework, based on Conformal Prediction, which boosts the performance of the base classifier while reducing energy consumption compared to normal prompting.
SCANIA Component X Dataset: A Real-World Multivariate Time Series Dataset for Predictive Maintenance
Jan 26, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a description of a real-world, multivariate time series dataset collected from an anonymized engine component (called Component X) of a fleet of trucks from SCANIA, Sweden. This dataset includes diverse variables capturing detailed operational data, repair records, and specifications of trucks while maintaining confidentiality by anonymization. It is well-suited for a range of machine learning applications, such as classification, regression, survival analysis, and anomaly detection, particularly when applied to predictive maintenance scenarios. The large population size and variety of features in the format of histograms and numerical counters, along with the inclusion of temporal information, make this real-world dataset unique in the field. The objective of releasing this dataset is to give a broad range of researchers the possibility of working with real-world data from an internationally well-known company and introduce a standard benchmark to the predictive maintenance field, fostering reproducible research.
Automotive Multilingual Fault Diagnosis
Oct 13, 2022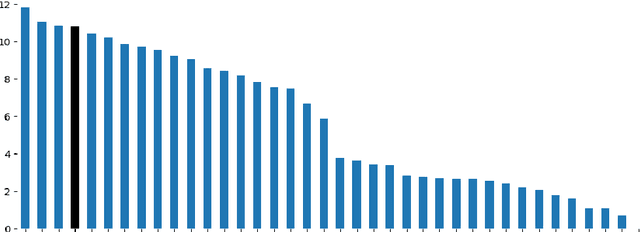

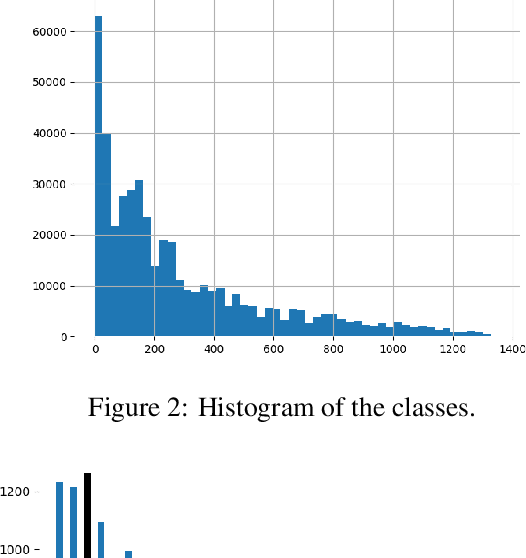
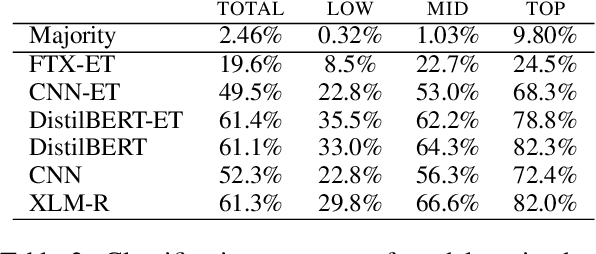
Abstract:Automated fault diagnosis can facilitate diagnostics assistance, speedier troubleshooting, and better-organised logistics. Currently, AI-based prognostics and health management in the automotive industry ignore the textual descriptions of the experienced problems or symptoms. With this study, however, we show that a multilingual pre-trained Transformer can effectively classify the textual claims from a large company with vehicle fleets, despite the task's challenging nature due to the 38 languages and 1,357 classes involved. Overall, we report an accuracy of more than 80% for high-frequency classes and above 60% for above-low-frequency classes, bringing novel evidence that multilingual classification can benefit automotive troubleshooting management.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge