Markus Borg
Code for Machines, Not Just Humans: Quantifying AI-Friendliness with Code Health Metrics
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:We are entering a hybrid era in which human developers and AI coding agents work in the same codebases. While industry practice has long optimized code for human comprehension, it is increasingly important to ensure that LLMs with different capabilities can edit code reliably. In this study, we investigate the concept of ``AI-friendly code'' via LLM-based refactoring on a dataset of 5,000 Python files from competitive programming. We find a meaningful association between CodeHealth, a quality metric calibrated for human comprehension, and semantic preservation after AI refactoring. Our findings confirm that human-friendly code is also more compatible with AI tooling. These results suggest that organizations can use CodeHealth to guide where AI interventions are lower risk and where additional human oversight is warranted. Investing in maintainability not only helps humans; it also prepares for large-scale AI adoption.
Trust Calibration in IDEs: Paving the Way for Widespread Adoption of AI Refactoring
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:In the software industry, the drive to add new features often overshadows the need to improve existing code. Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a new approach to improving codebases at an unprecedented scale through AI-assisted refactoring. However, LLMs come with inherent risks such as braking changes and the introduction of security vulnerabilities. We advocate for encapsulating the interaction with the models in IDEs and validating refactoring attempts using trustworthy safeguards. However, equally important for the uptake of AI refactoring is research on trust development. In this position paper, we position our future work based on established models from research on human factors in automation. We outline action research within CodeScene on development of 1) novel LLM safeguards and 2) user interaction that conveys an appropriate level of trust. The industry collaboration enables large-scale repository analysis and A/B testing to continuously guide the design of our research interventions.
Evaluation of Out-of-Distribution Detection Performance on Autonomous Driving Datasets
Jan 30, 2024



Abstract:Safety measures need to be systemically investigated to what extent they evaluate the intended performance of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) for critical applications. Due to a lack of verification methods for high-dimensional DNNs, a trade-off is needed between accepted performance and handling of out-of-distribution (OOD) samples. This work evaluates rejecting outputs from semantic segmentation DNNs by applying a Mahalanobis distance (MD) based on the most probable class-conditional Gaussian distribution for the predicted class as an OOD score. The evaluation follows three DNNs trained on the Cityscapes dataset and tested on four automotive datasets and finds that classification risk can drastically be reduced at the cost of pixel coverage, even when applied on unseen datasets. The applicability of our findings will support legitimizing safety measures and motivate their usage when arguing for safe usage of DNNs in automotive perception.
Automotive Perception Software Development: An Empirical Investigation into Data, Annotation, and Ecosystem Challenges
Mar 10, 2023Abstract:Software that contains machine learning algorithms is an integral part of automotive perception, for example, in driving automation systems. The development of such software, specifically the training and validation of the machine learning components, require large annotated datasets. An industry of data and annotation services has emerged to serve the development of such data-intensive automotive software components. Wide-spread difficulties to specify data and annotation needs challenge collaborations between OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) and their suppliers of software components, data, and annotations. This paper investigates the reasons for these difficulties for practitioners in the Swedish automotive industry to arrive at clear specifications for data and annotations. The results from an interview study show that a lack of effective metrics for data quality aspects, ambiguities in the way of working, unclear definitions of annotation quality, and deficits in the business ecosystems are causes for the difficulty in deriving the specifications. We provide a list of recommendations that can mitigate challenges when deriving specifications and we propose future research opportunities to overcome these challenges. Our work contributes towards the on-going research on accountability of machine learning as applied to complex software systems, especially for high-stake applications such as automated driving.
Automotive Multilingual Fault Diagnosis
Oct 13, 2022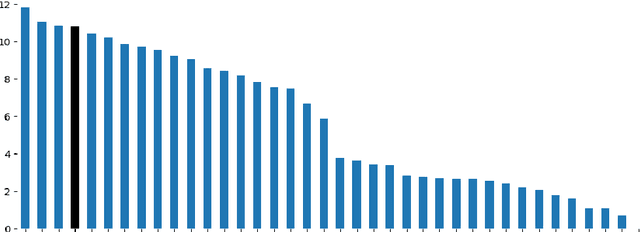

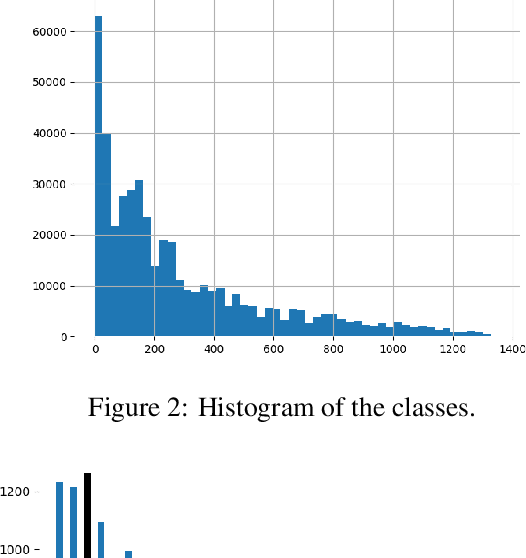
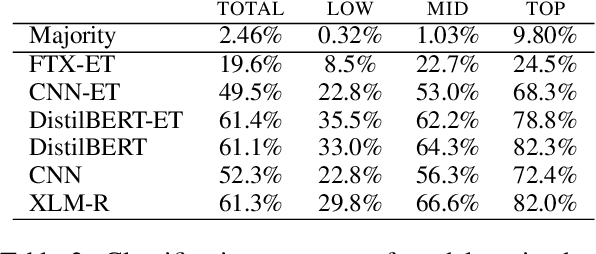
Abstract:Automated fault diagnosis can facilitate diagnostics assistance, speedier troubleshooting, and better-organised logistics. Currently, AI-based prognostics and health management in the automotive industry ignore the textual descriptions of the experienced problems or symptoms. With this study, however, we show that a multilingual pre-trained Transformer can effectively classify the textual claims from a large company with vehicle fleets, despite the task's challenging nature due to the 38 languages and 1,357 classes involved. Overall, we report an accuracy of more than 80% for high-frequency classes and above 60% for above-low-frequency classes, bringing novel evidence that multilingual classification can benefit automotive troubleshooting management.
Performance Analysis of Out-of-Distribution Detection on Trained Neural Networks
Apr 26, 2022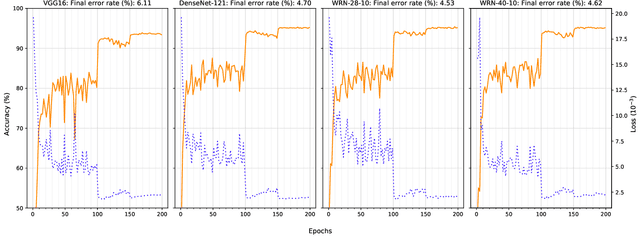
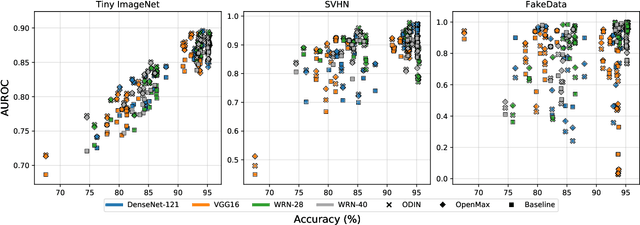
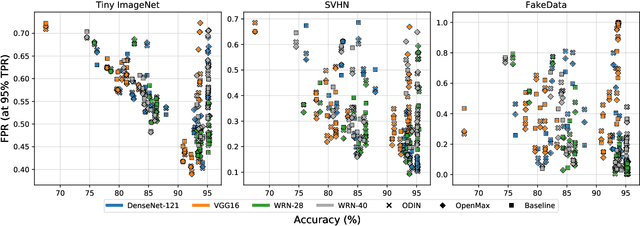
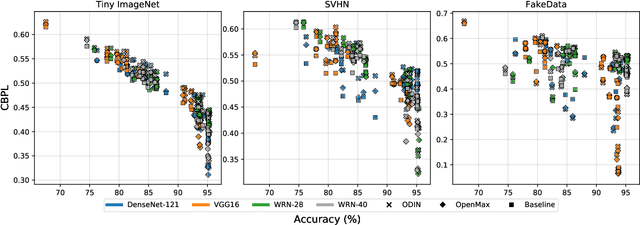
Abstract:Several areas have been improved with Deep Learning during the past years. Implementing Deep Neural Networks (DNN) for non-safety related applications have shown remarkable achievements over the past years; however, for using DNNs in safety critical applications, we are missing approaches for verifying the robustness of such models. A common challenge for DNNs occurs when exposed to out-of-distribution samples that are outside of the scope of a DNN, but which result in high confidence outputs despite no prior knowledge of such input. In this paper, we analyze three methods that separate between in- and out-of-distribution data, called supervisors, on four well-known DNN architectures. We find that the outlier detection performance improves with the quality of the model. We also analyse the performance of the particular supervisors during the training procedure by applying the supervisor at a predefined interval to investigate its performance as the training proceeds. We observe that understanding the relationship between training results and supervisor performance is crucial to improve the model's robustness and to indicate, what input samples require further measures to improve the robustness of a DNN. In addition, our work paves the road towards an instrument for safety argumentation for safety critical applications. This paper is an extended version of our previous work presented at 2019 SEAA (cf. [1]); here, we elaborate on the used metrics, add an additional supervisor and test them on two additional datasets.
Ergo, SMIRK is Safe: A Safety Case for a Machine Learning Component in a Pedestrian Automatic Emergency Brake System
Apr 16, 2022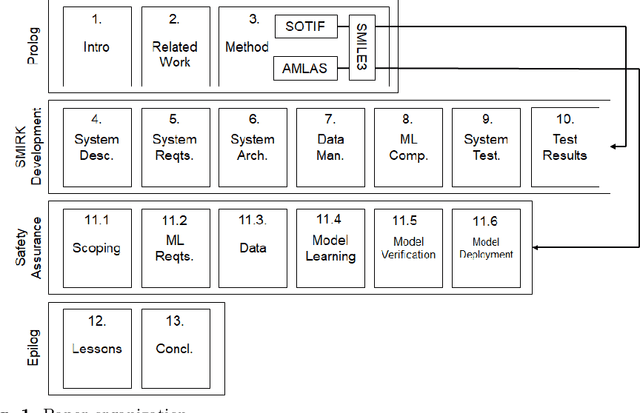
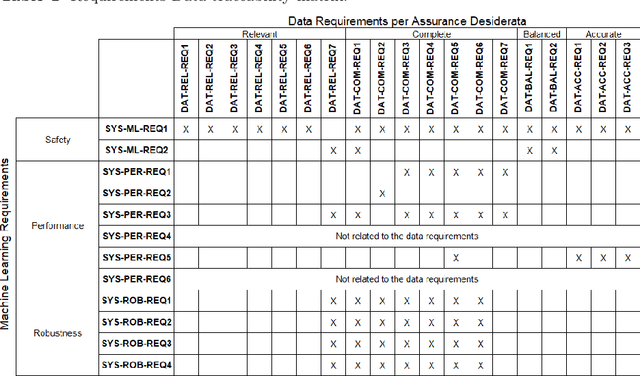
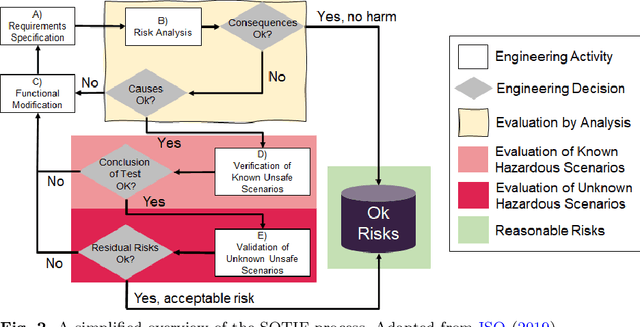
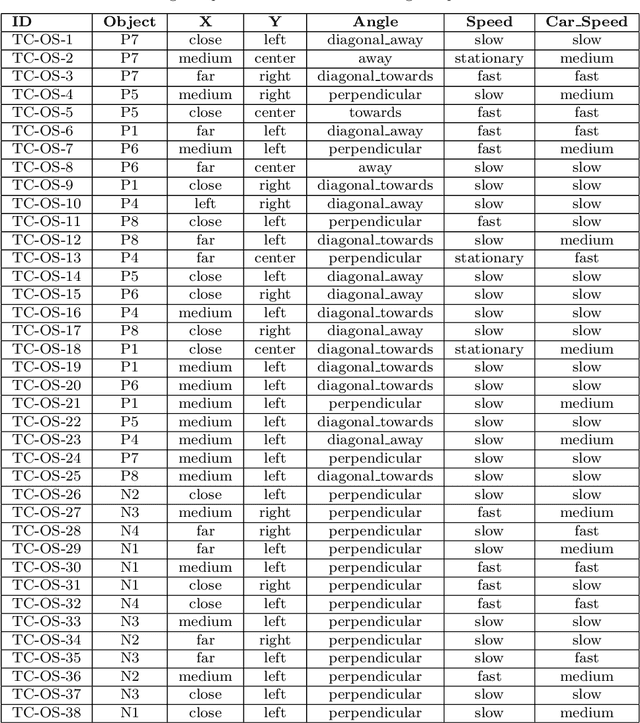
Abstract:Integration of Machine Learning (ML) components in critical applications introduces novel challenges for software certification and verification. New safety standards and technical guidelines are under development to support the safety of ML-based systems, e.g., ISO 21448 SOTIF for the automotive domain and the Assurance of Machine Learning for use in Autonomous Systems (AMLAS) framework. SOTIF and AMLAS provide high-level guidance but the details must be chiseled out for each specific case. We report results from an industry-academia collaboration on safety assurance of SMIRK, an ML-based pedestrian automatic emergency braking demonstrator running in an industry-grade simulator. We present the outcome of applying AMLAS on SMIRK for a minimalistic operational design domain, i.e., a complete safety case for its integrated ML-based component. Finally, we report lessons learned and provide both SMIRK and the safety case under an open-source licence for the research community to reuse.
Exploring ML testing in practice -- Lessons learned from an interactive rapid review with Axis Communications
Mar 30, 2022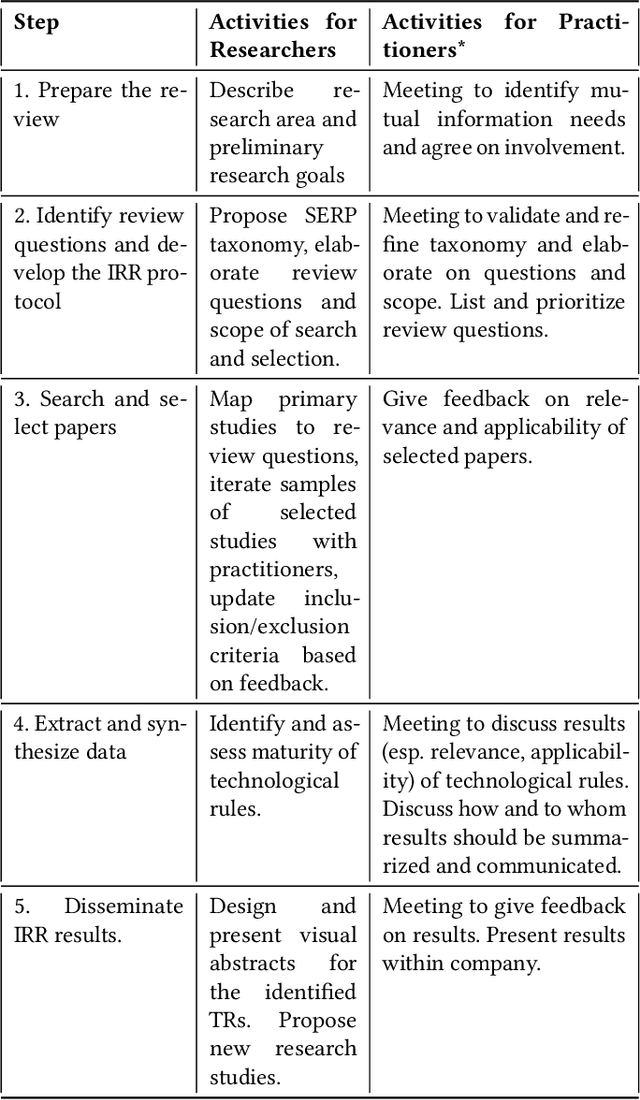
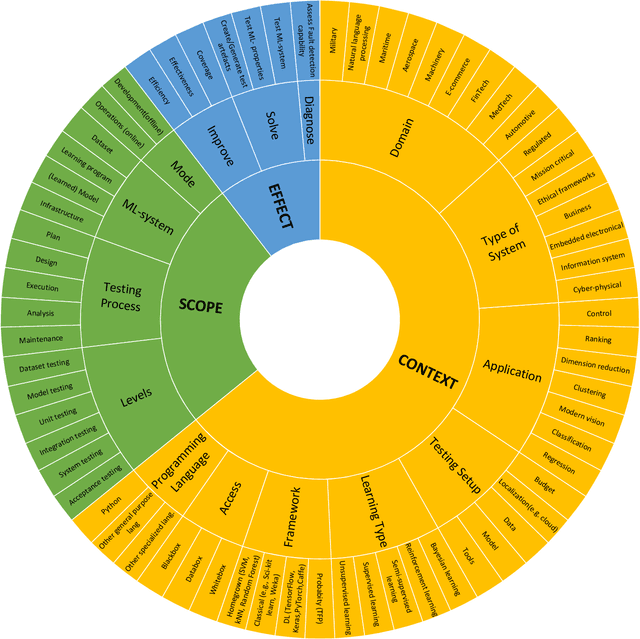
Abstract:There is a growing interest in industry and academia in machine learning (ML) testing. We believe that industry and academia need to learn together to produce rigorous and relevant knowledge. In this study, we initiate a collaboration between stakeholders from one case company, one research institute, and one university. To establish a common view of the problem domain, we applied an interactive rapid review of the state of the art. Four researchers from Lund University and RISE Research Institutes and four practitioners from Axis Communications reviewed a set of 180 primary studies on ML testing. We developed a taxonomy for the communication around ML testing challenges and results and identified a list of 12 review questions relevant for Axis Communications. The three most important questions (data testing, metrics for assessment, and test generation) were mapped to the literature, and an in-depth analysis of the 35 primary studies matching the most important question (data testing) was made. A final set of the five best matches were analysed and we reflect on the criteria for applicability and relevance for the industry. The taxonomies are helpful for communication but not final. Furthermore, there was no perfect match to the case company's investigated review question (data testing). However, we extracted relevant approaches from the five studies on a conceptual level to support later context-specific improvements. We found the interactive rapid review approach useful for triggering and aligning communication between the different stakeholders.
Quality Assurance of Generative Dialog Models in an Evolving Conversational Agent Used for Swedish Language Practice
Mar 29, 2022



Abstract:Due to the migration megatrend, efficient and effective second-language acquisition is vital. One proposed solution involves AI-enabled conversational agents for person-centered interactive language practice. We present results from ongoing action research targeting quality assurance of proprietary generative dialog models trained for virtual job interviews. The action team elicited a set of 38 requirements for which we designed corresponding automated test cases for 15 of particular interest to the evolving solution. Our results show that six of the test case designs can detect meaningful differences between candidate models. While quality assurance of natural language processing applications is complex, we provide initial steps toward an automated framework for machine learning model selection in the context of an evolving conversational agent. Future work will focus on model selection in an MLOps setting.
Machine Learning Testing in an ADAS Case Study Using Simulation-Integrated Bio-Inspired Search-Based Testing
Mar 22, 2022
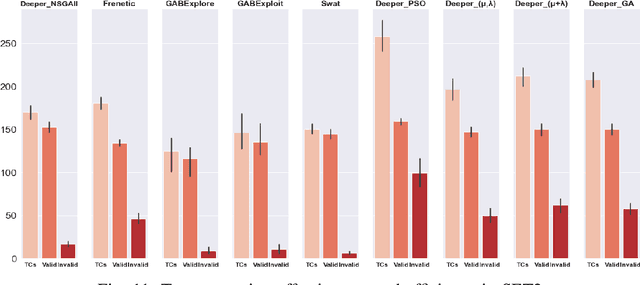


Abstract:This paper presents an extended version of Deeper, a search-based simulation-integrated test solution that generates failure-revealing test scenarios for testing a deep neural network-based lane-keeping system. In the newly proposed version, we utilize a new set of bio-inspired search algorithms, genetic algorithm (GA), $({\mu}+{\lambda})$ and $({\mu},{\lambda})$ evolution strategies (ES), and particle swarm optimization (PSO), that leverage a quality population seed and domain-specific cross-over and mutation operations tailored for the presentation model used for modeling the test scenarios. In order to demonstrate the capabilities of the new test generators within Deeper, we carry out an empirical evaluation and comparison with regard to the results of five participating tools in the cyber-physical systems testing competition at SBST 2021. Our evaluation shows the newly proposed test generators in Deeper not only represent a considerable improvement on the previous version but also prove to be effective and efficient in provoking a considerable number of diverse failure-revealing test scenarios for testing an ML-driven lane-keeping system. They can trigger several failures while promoting test scenario diversity, under a limited test time budget, high target failure severity, and strict speed limit constraints.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge