Katerina Korre
The CLEF-2025 CheckThat! Lab: Subjectivity, Fact-Checking, Claim Normalization, and Retrieval
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:The CheckThat! lab aims to advance the development of innovative technologies designed to identify and counteract online disinformation and manipulation efforts across various languages and platforms. The first five editions focused on key tasks in the information verification pipeline, including check-worthiness, evidence retrieval and pairing, and verification. Since the 2023 edition, the lab has expanded its scope to address auxiliary tasks that support research and decision-making in verification. In the 2025 edition, the lab revisits core verification tasks while also considering auxiliary challenges. Task 1 focuses on the identification of subjectivity (a follow-up from CheckThat! 2024), Task 2 addresses claim normalization, Task 3 targets fact-checking numerical claims, and Task 4 explores scientific web discourse processing. These tasks present challenging classification and retrieval problems at both the document and span levels, including multilingual settings.
Evaluation and Facilitation of Online Discussions in the LLM Era: A Survey
Mar 03, 2025
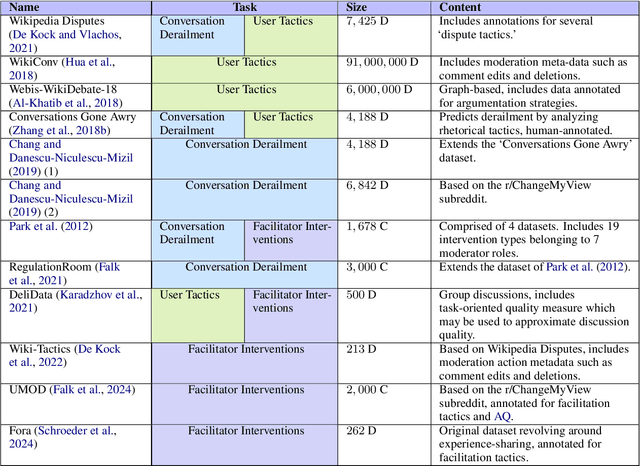

Abstract:We present a survey of methods for assessing and enhancing the quality of online discussions, focusing on the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs). While online discourses aim, at least in theory, to foster mutual understanding, they often devolve into harmful exchanges, such as hate speech, threatening social cohesion and democratic values. Recent advancements in LLMs enable facilitation agents that not only moderate content, but also actively improve the quality of interactions. Our survey synthesizes ideas from Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Social Sciences to provide (a) a new taxonomy on discussion quality evaluation, (b) an overview of intervention and facilitation strategies, along with a new taxonomy on conversation facilitation datasets, (c) an LLM-oriented roadmap of good practices and future research directions, from technological and societal perspectives.
Hate Speech According to the Law: An Analysis for Effective Detection
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:The issue of hate speech extends beyond the confines of the online realm. It is a problem with real-life repercussions, prompting most nations to formulate legal frameworks that classify hate speech as a punishable offence. These legal frameworks differ from one country to another, contributing to the big chaos that online platforms have to face when addressing reported instances of hate speech. With the definitions of hate speech falling short in introducing a robust framework, we turn our gaze onto hate speech laws. We consult the opinion of legal experts on a hate speech dataset and we experiment by employing various approaches such as pretrained models both on hate speech and legal data, as well as exploiting two large language models (Qwen2-7B-Instruct and Meta-Llama-3-70B). Due to the time-consuming nature of data acquisition for prosecutable hate speech, we use pseudo-labeling to improve our pretrained models. This study highlights the importance of amplifying research on prosecutable hate speech and provides insights into effective strategies for combating hate speech within the parameters of legal frameworks. Our findings show that legal knowledge in the form of annotations can be useful when classifying prosecutable hate speech, yet more focus should be paid on the differences between the laws.
Untangling Hate Speech Definitions: A Semantic Componential Analysis Across Cultures and Domains
Nov 11, 2024Abstract:Hate speech relies heavily on cultural influences, leading to varying individual interpretations. For that reason, we propose a Semantic Componential Analysis (SCA) framework for a cross-cultural and cross-domain analysis of hate speech definitions. We create the first dataset of definitions derived from five domains: online dictionaries, research papers, Wikipedia articles, legislation, and online platforms, which are later analyzed into semantic components. Our analysis reveals that the components differ from definition to definition, yet many domains borrow definitions from one another without taking into account the target culture. We conduct zero-shot model experiments using our proposed dataset, employing three popular open-sourced LLMs to understand the impact of different definitions on hate speech detection. Our findings indicate that LLMs are sensitive to definitions: responses for hate speech detection change according to the complexity of definitions used in the prompt.
Let Guidelines Guide You: A Prescriptive Guideline-Centered Data Annotation Methodology
Jun 20, 2024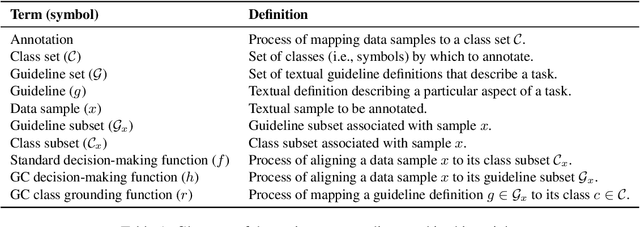
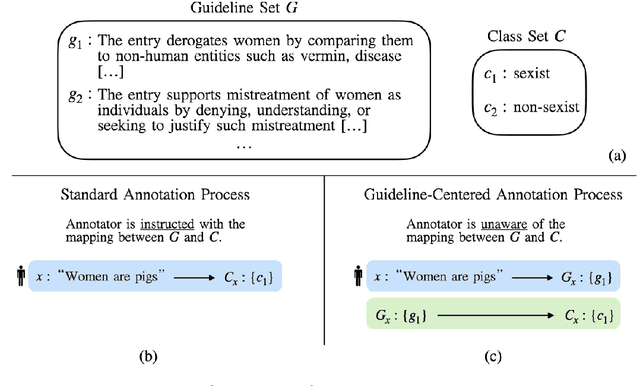
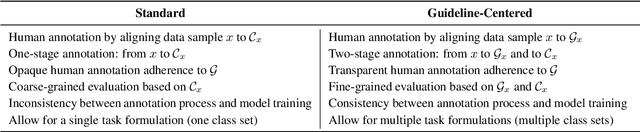
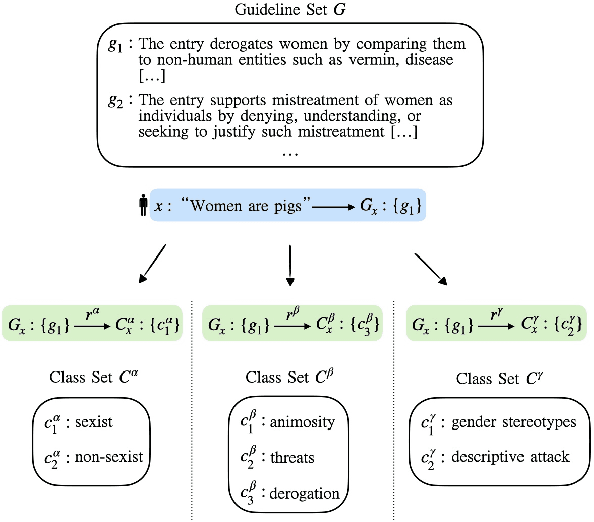
Abstract:We introduce the Guideline-Centered annotation process, a novel data annotation methodology focused on reporting the annotation guidelines associated with each data sample. We identify three main limitations of the standard prescriptive annotation process and describe how the Guideline-Centered methodology overcomes them by reducing the loss of information in the annotation process and ensuring adherence to guidelines. Additionally, we discuss how the Guideline-Centered enables the reuse of annotated data across multiple tasks at the cost of a single human-annotation process.
A Corpus for Sentence-level Subjectivity Detection on English News Articles
May 29, 2023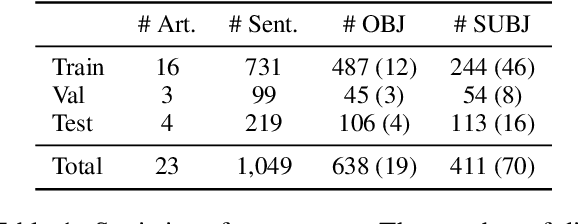
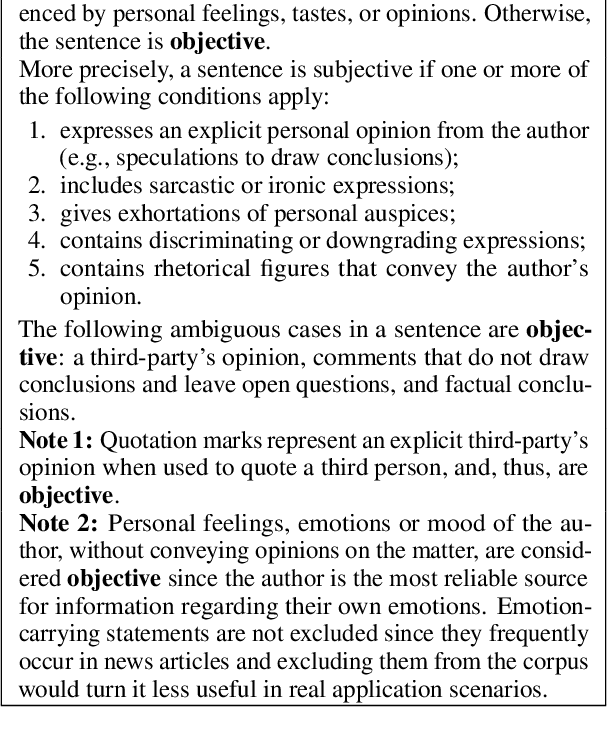
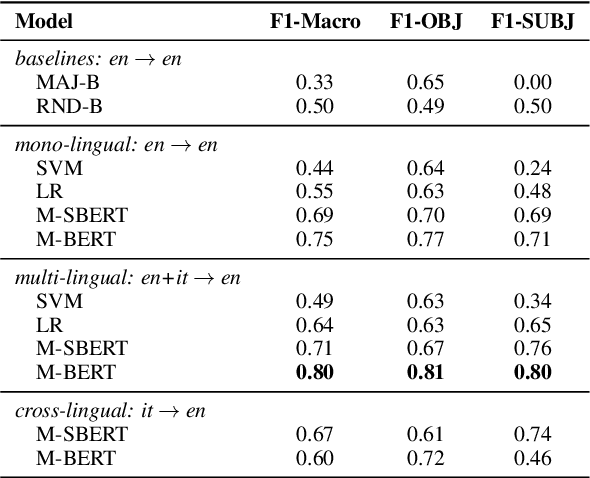
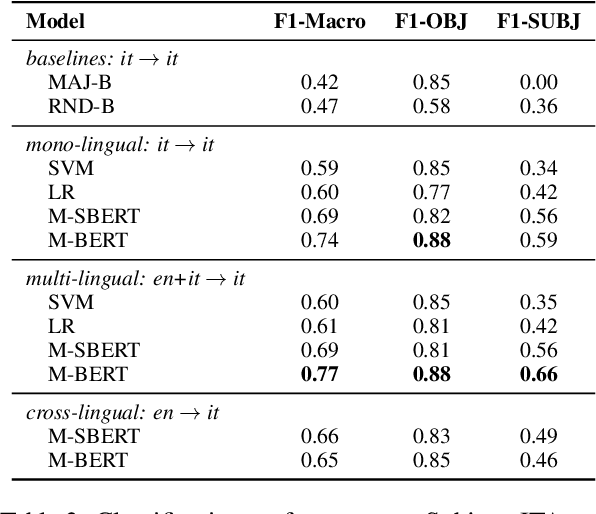
Abstract:We present a novel corpus for subjectivity detection at the sentence level. We develop new annotation guidelines for the task, which are not limited to language-specific cues, and apply them to produce a new corpus in English. The corpus consists of 411 subjective and 638 objective sentences extracted from ongoing coverage of political affairs from online news outlets. This new resource paves the way for the development of models for subjectivity detection in English and across other languages, without relying on language-specific tools like lexicons or machine translation. We evaluate state-of-the-art multilingual transformer-based models on the task, both in mono- and cross-lingual settings, the latter with a similar existing corpus in Italian language. We observe that enriching our corpus with resources in other languages improves the results on the task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge