Jivat Neet Kaur
Conformal Prediction Sets with Improved Conditional Coverage using Trust Scores
Jan 17, 2025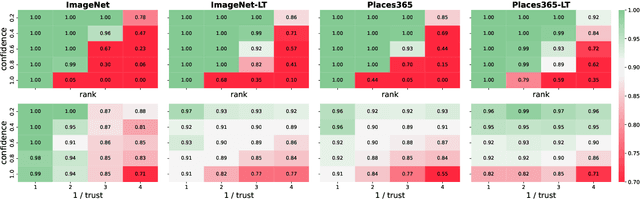
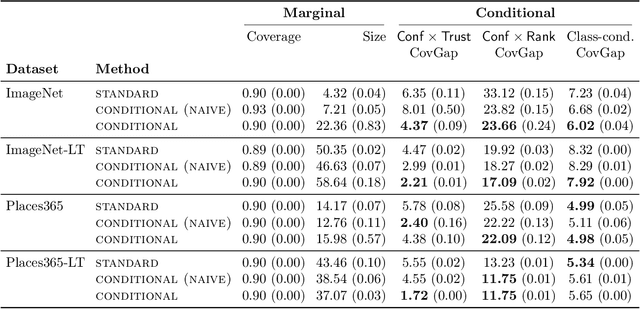
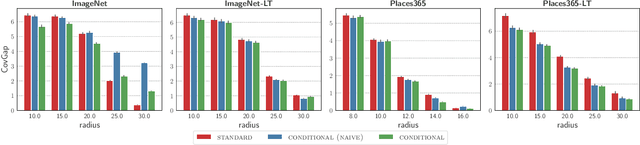
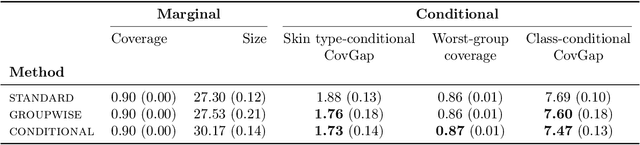
Abstract:Standard conformal prediction offers a marginal guarantee on coverage, but for prediction sets to be truly useful, they should ideally ensure coverage conditional on each test point. Unfortunately, it is impossible to achieve exact, distribution-free conditional coverage in finite samples. In this work, we propose an alternative conformal prediction algorithm that targets coverage where it matters most--in instances where a classifier is overconfident in its incorrect predictions. We start by dissecting miscoverage events in marginally-valid conformal prediction, and show that miscoverage rates vary based on the classifier's confidence and its deviation from the Bayes optimal classifier. Motivated by this insight, we develop a variant of conformal prediction that targets coverage conditional on a reduced set of two variables: the classifier's confidence in a prediction and a nonparametric trust score that measures its deviation from the Bayes classifier. Empirical evaluation on multiple image datasets shows that our method generally improves conditional coverage properties compared to standard conformal prediction, including class-conditional coverage, coverage over arbitrary subgroups, and coverage over demographic groups.
LM-CORE: Language Models with Contextually Relevant External Knowledge
Aug 12, 2022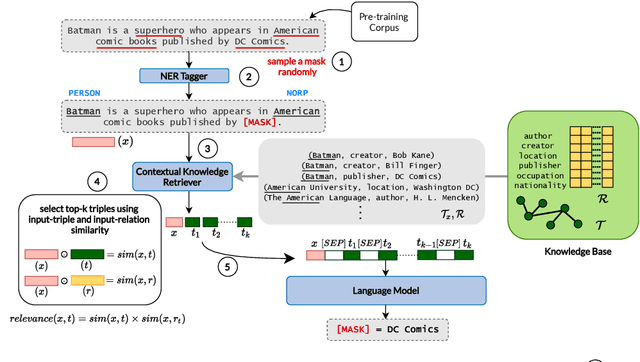
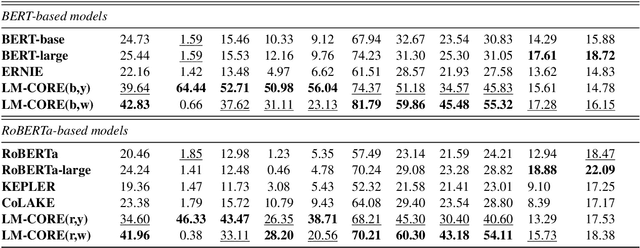

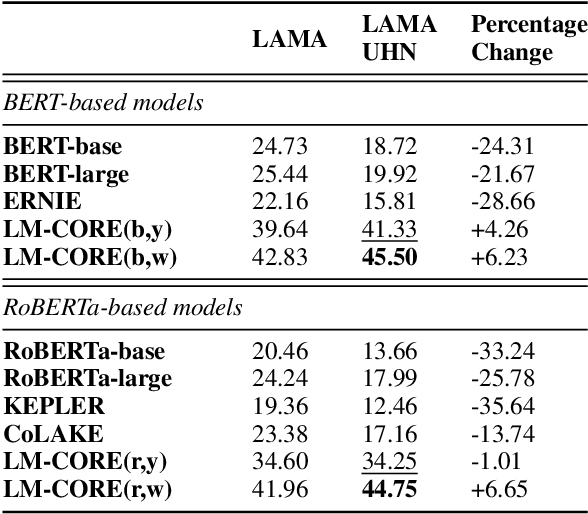
Abstract:Large transformer-based pre-trained language models have achieved impressive performance on a variety of knowledge-intensive tasks and can capture factual knowledge in their parameters. We argue that storing large amounts of knowledge in the model parameters is sub-optimal given the ever-growing amounts of knowledge and resource requirements. We posit that a more efficient alternative is to provide explicit access to contextually relevant structured knowledge to the model and train it to use that knowledge. We present LM-CORE -- a general framework to achieve this -- that allows \textit{decoupling} of the language model training from the external knowledge source and allows the latter to be updated without affecting the already trained model. Experimental results show that LM-CORE, having access to external knowledge, achieves significant and robust outperformance over state-of-the-art knowledge-enhanced language models on knowledge probing tasks; can effectively handle knowledge updates; and performs well on two downstream tasks. We also present a thorough error analysis highlighting the successes and failures of LM-CORE.
CoSe-Co: Text Conditioned Generative CommonSense Contextualizer
Jun 17, 2022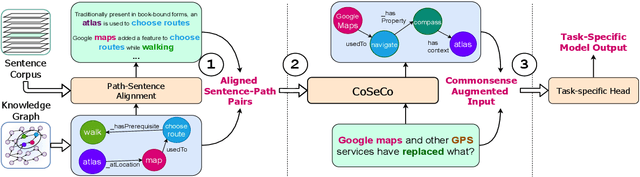

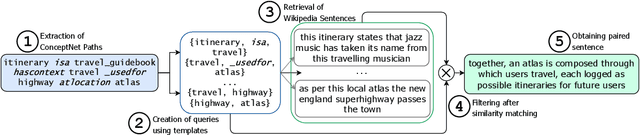
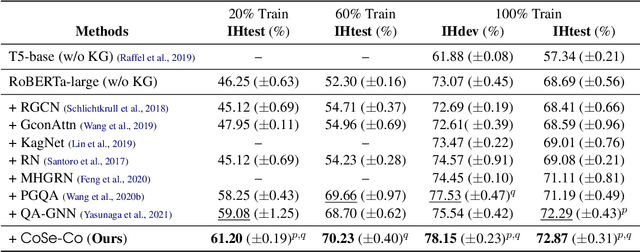
Abstract:Pre-trained Language Models (PTLMs) have been shown to perform well on natural language tasks. Many prior works have leveraged structured commonsense present in the form of entities linked through labeled relations in Knowledge Graphs (KGs) to assist PTLMs. Retrieval approaches use KG as a separate static module which limits coverage since KGs contain finite knowledge. Generative methods train PTLMs on KG triples to improve the scale at which knowledge can be obtained. However, training on symbolic KG entities limits their applicability in tasks involving natural language text where they ignore overall context. To mitigate this, we propose a CommonSense Contextualizer (CoSe-Co) conditioned on sentences as input to make it generically usable in tasks for generating knowledge relevant to the overall context of input text. To train CoSe-Co, we propose a novel dataset comprising of sentence and commonsense knowledge pairs. The knowledge inferred by CoSe-Co is diverse and contain novel entities not present in the underlying KG. We augment generated knowledge in Multi-Choice QA and Open-ended CommonSense Reasoning tasks leading to improvements over current best methods on CSQA, ARC, QASC and OBQA datasets. We also demonstrate its applicability in improving performance of a baseline model for paraphrase generation task.
Modeling the Data-Generating Process is Necessary for Out-of-Distribution Generalization
Jun 15, 2022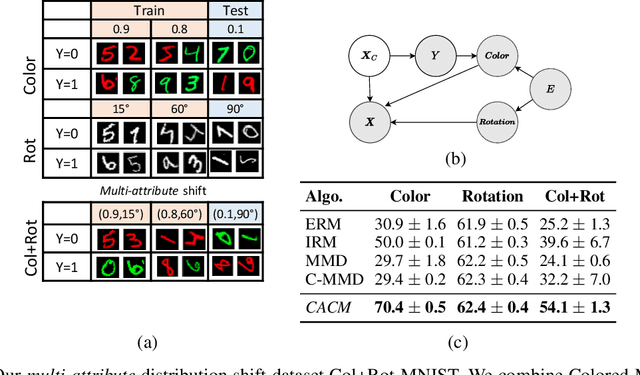
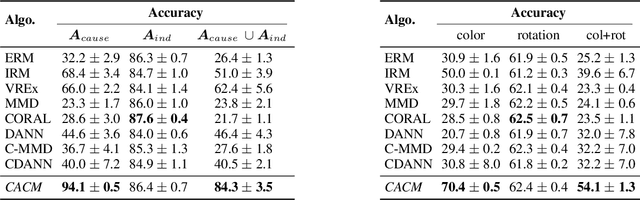
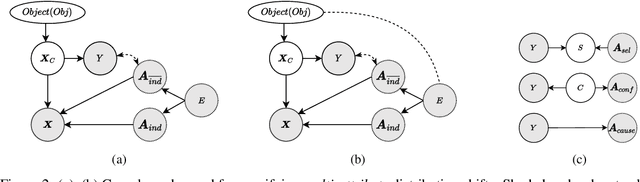
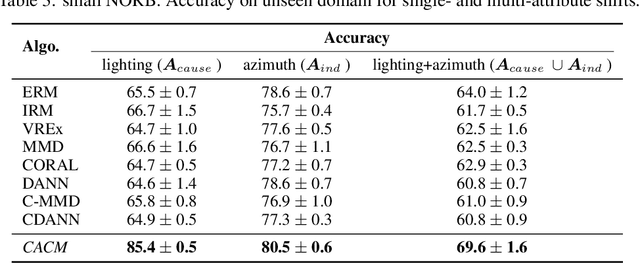
Abstract:Real-world data collected from multiple domains can have multiple, distinct distribution shifts over multiple attributes. However, state-of-the art advances in domain generalization (DG) algorithms focus only on specific shifts over a single attribute. We introduce datasets with multi-attribute distribution shifts and find that existing DG algorithms fail to generalize. To explain this, we use causal graphs to characterize the different types of shifts based on the relationship between spurious attributes and the classification label. Each multi-attribute causal graph entails different constraints over observed variables, and therefore any algorithm based on a single, fixed independence constraint cannot work well across all shifts. We present Causally Adaptive Constraint Minimization (CACM), a new algorithm for identifying the correct independence constraints for regularization. Results on fully synthetic, MNIST and small NORB datasets, covering binary and multi-valued attributes and labels, confirm our theoretical claim: correct independence constraints lead to the highest accuracy on unseen domains whereas incorrect constraints fail to do so. Our results demonstrate the importance of modeling the causal relationships inherent in the data-generating process: in many cases, it is impossible to know the correct regularization constraints without this information.
Modern Baselines for SPARQL Semantic Parsing
Apr 27, 2022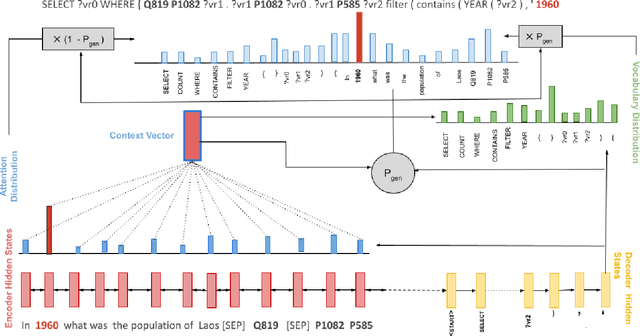
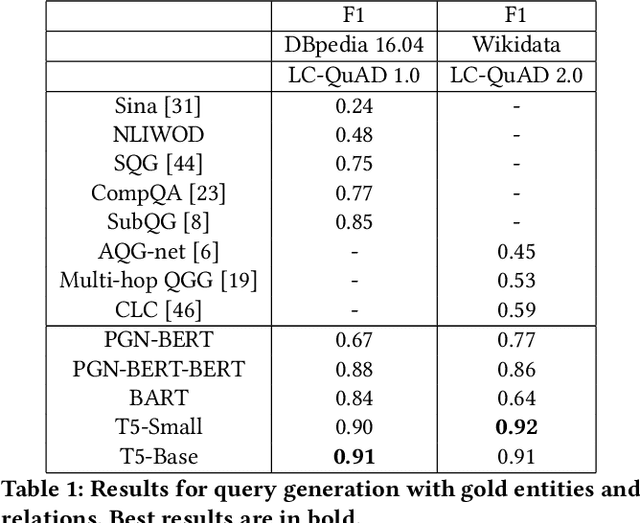
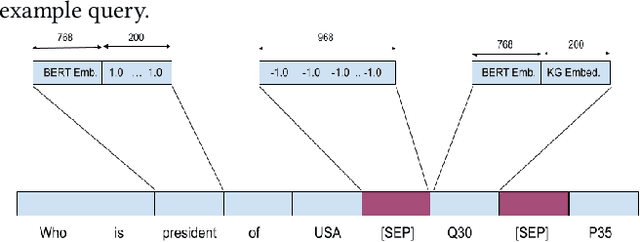
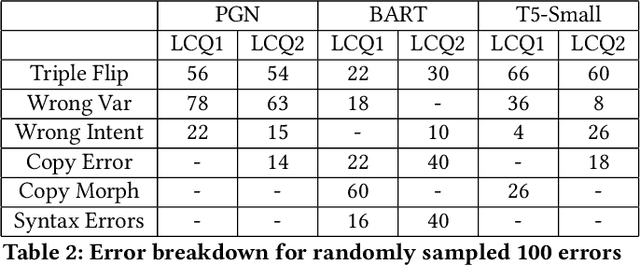
Abstract:In this work, we focus on the task of generating SPARQL queries from natural language questions, which can then be executed on Knowledge Graphs (KGs). We assume that gold entity and relations have been provided, and the remaining task is to arrange them in the right order along with SPARQL vocabulary, and input tokens to produce the correct SPARQL query. Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs) have not been explored in depth on this task so far, so we experiment with BART, T5 and PGNs (Pointer Generator Networks) with BERT embeddings, looking for new baselines in the PLM era for this task, on DBpedia and Wikidata KGs. We show that T5 requires special input tokenisation, but produces state of the art performance on LC-QuAD 1.0 and LC-QuAD 2.0 datasets, and outperforms task-specific models from previous works. Moreover, the methods enable semantic parsing for questions where a part of the input needs to be copied to the output query, thus enabling a new paradigm in KG semantic parsing.
Ask & Explore: Grounded Question Answering for Curiosity-Driven Exploration
Apr 24, 2021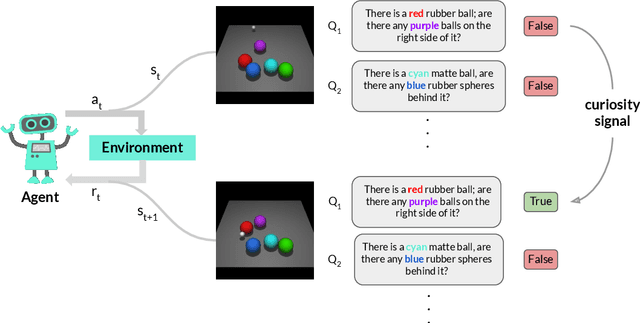
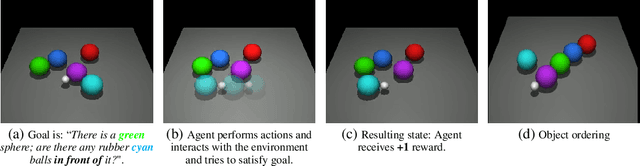
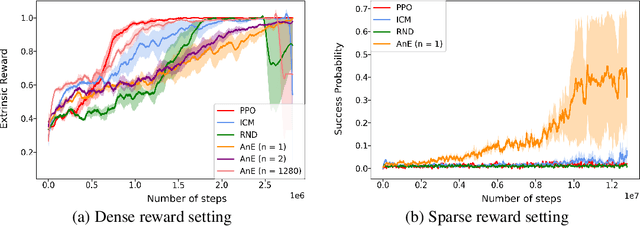
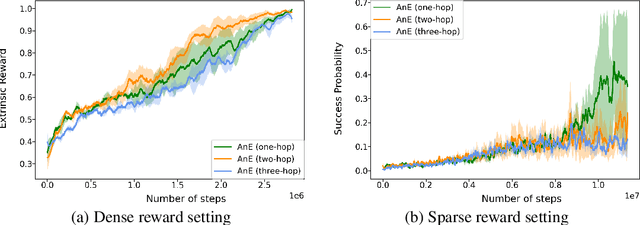
Abstract:In many real-world scenarios where extrinsic rewards to the agent are extremely sparse, curiosity has emerged as a useful concept providing intrinsic rewards that enable the agent to explore its environment and acquire information to achieve its goals. Despite their strong performance on many sparse-reward tasks, existing curiosity approaches rely on an overly holistic view of state transitions, and do not allow for a structured understanding of specific aspects of the environment. In this paper, we formulate curiosity based on grounded question answering by encouraging the agent to ask questions about the environment and be curious when the answers to these questions change. We show that natural language questions encourage the agent to uncover specific knowledge about their environment such as the physical properties of objects as well as their spatial relationships with other objects, which serve as valuable curiosity rewards to solve sparse-reward tasks more efficiently.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge