LM-CORE: Language Models with Contextually Relevant External Knowledge
Paper and Code
Aug 12, 2022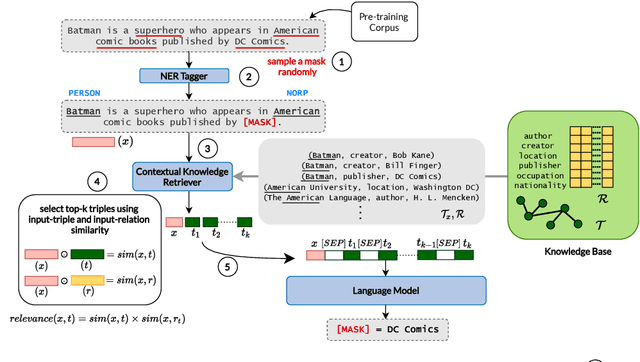
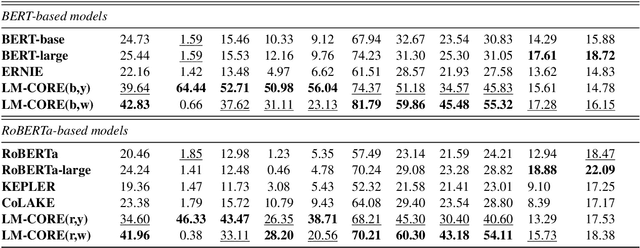

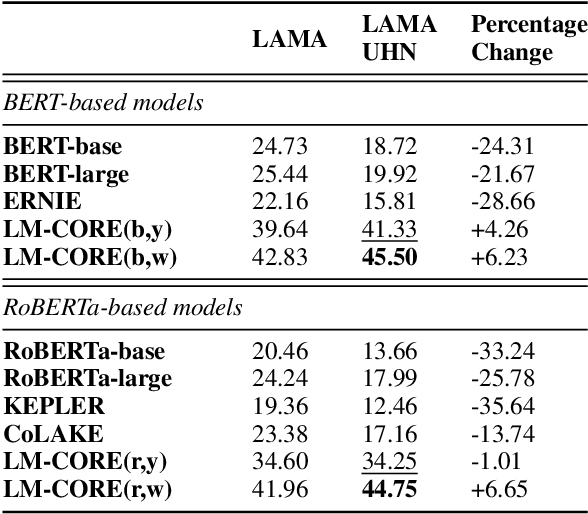
Large transformer-based pre-trained language models have achieved impressive performance on a variety of knowledge-intensive tasks and can capture factual knowledge in their parameters. We argue that storing large amounts of knowledge in the model parameters is sub-optimal given the ever-growing amounts of knowledge and resource requirements. We posit that a more efficient alternative is to provide explicit access to contextually relevant structured knowledge to the model and train it to use that knowledge. We present LM-CORE -- a general framework to achieve this -- that allows \textit{decoupling} of the language model training from the external knowledge source and allows the latter to be updated without affecting the already trained model. Experimental results show that LM-CORE, having access to external knowledge, achieves significant and robust outperformance over state-of-the-art knowledge-enhanced language models on knowledge probing tasks; can effectively handle knowledge updates; and performs well on two downstream tasks. We also present a thorough error analysis highlighting the successes and failures of LM-CORE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge