Jing Wei
The Tenth NTIRE 2025 Efficient Super-Resolution Challenge Report
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive review of the NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Single-Image Efficient Super-Resolution (ESR). The challenge aimed to advance the development of deep models that optimize key computational metrics, i.e., runtime, parameters, and FLOPs, while achieving a PSNR of at least 26.90 dB on the $\operatorname{DIV2K\_LSDIR\_valid}$ dataset and 26.99 dB on the $\operatorname{DIV2K\_LSDIR\_test}$ dataset. A robust participation saw \textbf{244} registered entrants, with \textbf{43} teams submitting valid entries. This report meticulously analyzes these methods and results, emphasizing groundbreaking advancements in state-of-the-art single-image ESR techniques. The analysis highlights innovative approaches and establishes benchmarks for future research in the field.
Few-shot Defect Image Generation based on Consistency Modeling
Aug 01, 2024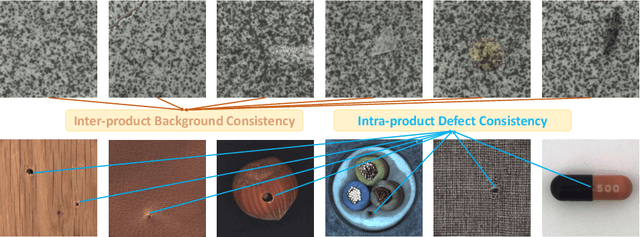
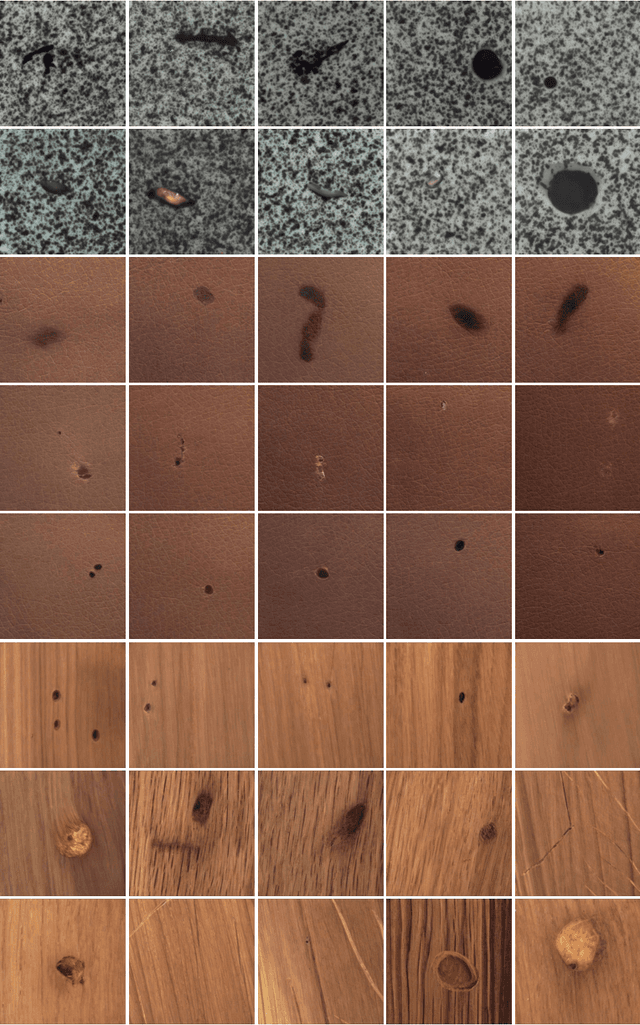
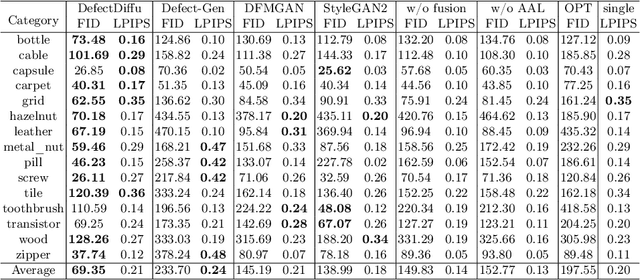

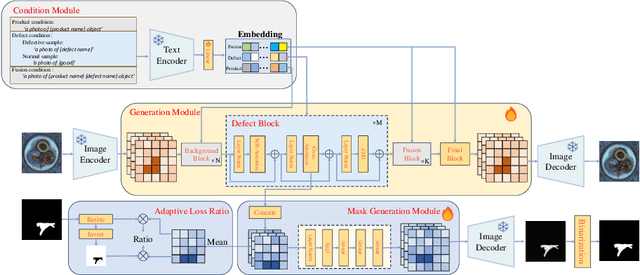
Abstract:Image generation can solve insufficient labeled data issues in defect detection. Most defect generation methods are only trained on a single product without considering the consistencies among multiple products, leading to poor quality and diversity of generated results. To address these issues, we propose DefectDiffu, a novel text-guided diffusion method to model both intra-product background consistency and inter-product defect consistency across multiple products and modulate the consistency perturbation directions to control product type and defect strength, achieving diversified defect image generation. Firstly, we leverage a text encoder to separately provide consistency prompts for background, defect, and fusion parts of the disentangled integrated architecture, thereby disentangling defects and normal backgrounds. Secondly, we propose the double-free strategy to generate defect images through two-stage perturbation of consistency direction, thereby controlling product type and defect strength by adjusting the perturbation scale. Besides, DefectDiffu can generate defect mask annotations utilizing cross-attention maps from the defect part. Finally, to improve the generation quality of small defects and masks, we propose the adaptive attention-enhance loss to increase the attention to defects. Experimental results demonstrate that DefectDiffu surpasses state-of-the-art methods in terms of generation quality and diversity, thus effectively improving downstream defection performance. Moreover, defect perturbation directions can be transferred among various products to achieve zero-shot defect generation, which is highly beneficial for addressing insufficient data issues. The code are available at https://github.com/FFDD-diffusion/DefectDiffu.
Generating Educational Materials with Different Levels of Readability using LLMs
Jun 18, 2024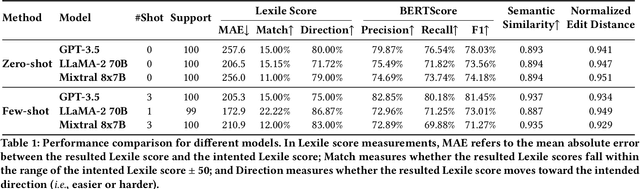
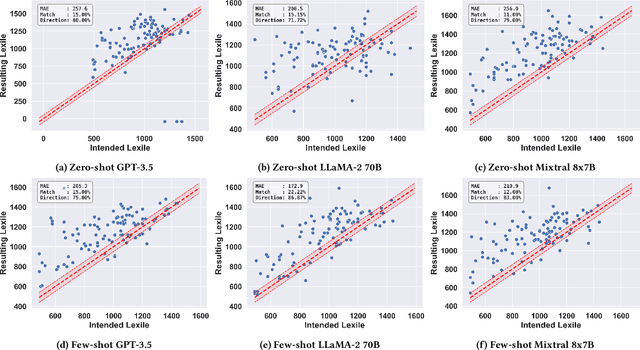
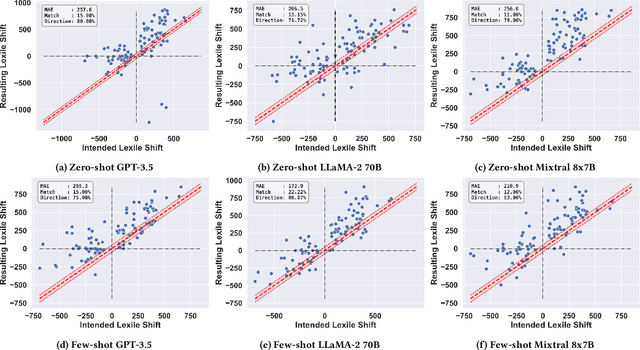
Abstract:This study introduces the leveled-text generation task, aiming to rewrite educational materials to specific readability levels while preserving meaning. We assess the capability of GPT-3.5, LLaMA-2 70B, and Mixtral 8x7B, to generate content at various readability levels through zero-shot and few-shot prompting. Evaluating 100 processed educational materials reveals that few-shot prompting significantly improves performance in readability manipulation and information preservation. LLaMA-2 70B performs better in achieving the desired difficulty range, while GPT-3.5 maintains original meaning. However, manual inspection highlights concerns such as misinformation introduction and inconsistent edit distribution. These findings emphasize the need for further research to ensure the quality of generated educational content.
Learning to Model Diverse Driving Behaviors in Highly Interactive Autonomous Driving Scenarios with Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Feb 21, 2024Abstract:Autonomous vehicles trained through Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) have shown impressive results in many driving scenarios. However, the performance of these trained policies can be impacted when faced with diverse driving styles and personalities, particularly in highly interactive situations. This is because conventional MARL algorithms usually operate under the assumption of fully cooperative behavior among all agents and focus on maximizing team rewards during training. To address this issue, we introduce the Personality Modeling Network (PeMN), which includes a cooperation value function and personality parameters to model the varied interactions in high-interactive scenarios. The PeMN also enables the training of a background traffic flow with diverse behaviors, thereby improving the performance and generalization of the ego vehicle. Our extensive experimental studies, which incorporate different personality parameters in high-interactive driving scenarios, demonstrate that the personality parameters effectively model diverse driving styles and that policies trained with PeMN demonstrate better generalization compared to traditional MARL methods.
Comparing Large Language Model AI and Human-Generated Coaching Messages for Behavioral Weight Loss
Dec 07, 2023Abstract:Automated coaching messages for weight control can save time and costs, but their repetitive, generic nature may limit their effectiveness compared to human coaching. Large language model (LLM) based artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots, like ChatGPT, could offer more personalized and novel messages to address repetition with their data-processing abilities. While LLM AI demonstrates promise to encourage healthier lifestyles, studies have yet to examine the feasibility and acceptability of LLM-based BWL coaching. 87 adults in a weight-loss trial rated ten coaching messages' helpfulness (five human-written, five ChatGPT-generated) using a 5-point Likert scale, providing additional open-ended feedback to justify their ratings. Participants also identified which messages they believed were AI-generated. The evaluation occurred in two phases: messages in Phase 1 were perceived as impersonal and negative, prompting revisions for Phase 2 messages. In Phase 1, AI-generated messages were rated less helpful than human-written ones, with 66 percent receiving a helpfulness rating of 3 or higher. However, in Phase 2, the AI messages matched the human-written ones regarding helpfulness, with 82% scoring three or above. Additionally, 50% were misidentified as human-written, suggesting AI's sophistication in mimicking human-generated content. A thematic analysis of open-ended feedback revealed that participants appreciated AI's empathy and personalized suggestions but found them more formulaic, less authentic, and too data-focused. This study reveals the preliminary feasibility and acceptability of LLM AIs, like ChatGPT, in crafting potentially effective weight control coaching messages. Our findings also underscore areas for future enhancement.
Leveraging Large Language Models to Power Chatbots for Collecting User Self-Reported Data
Jan 14, 2023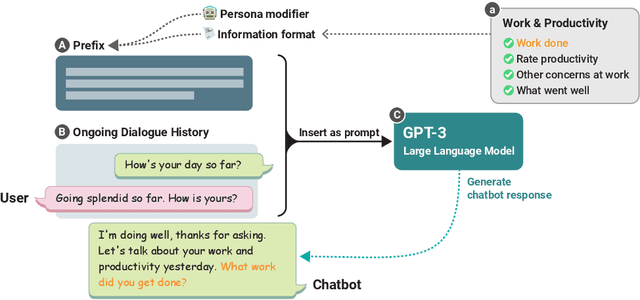
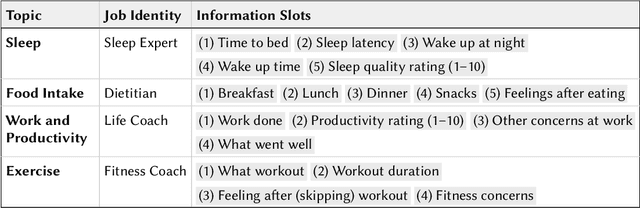
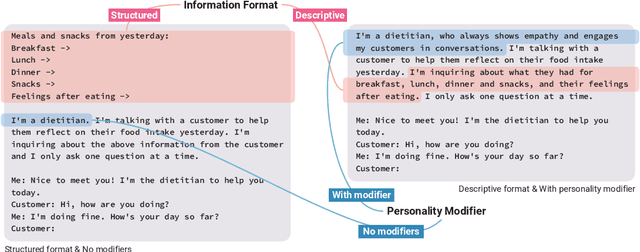
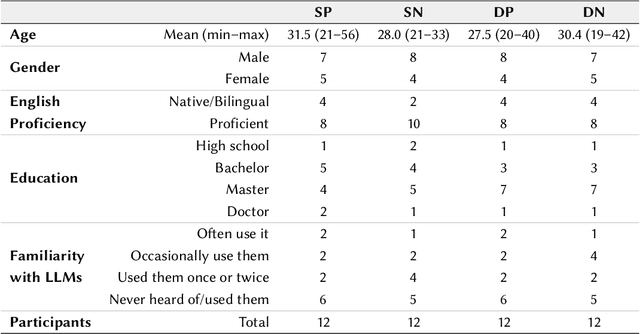
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) provide a new way to build chatbots by accepting natural language prompts. Yet, it is unclear how to design prompts to power chatbots to carry on naturalistic conversations while pursuing a given goal, such as collecting self-report data from users. We explore what design factors of prompts can help steer chatbots to talk naturally and collect data reliably. To this aim, we formulated four prompt designs with different structures and personas. Through an online study (N = 48) where participants conversed with chatbots driven by different designs of prompts, we assessed how prompt designs and conversation topics affected the conversation flows and users' perceptions of chatbots. Our chatbots covered 79% of the desired information slots during conversations, and the designs of prompts and topics significantly influenced the conversation flows and the data collection performance. We discuss the opportunities and challenges of building chatbots with LLMs.
$Radar^2$: Passive Spy Radar Detection and Localization using COTS mmWave Radar
Jan 10, 2022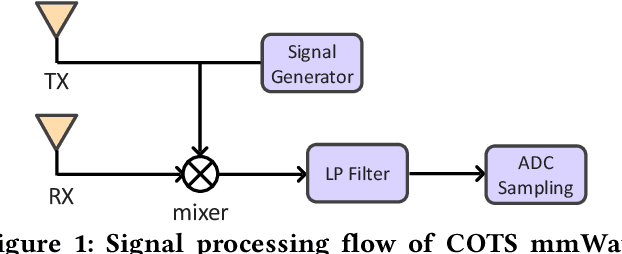

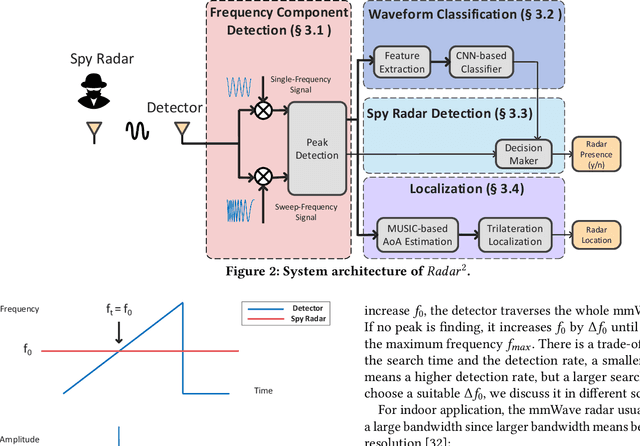
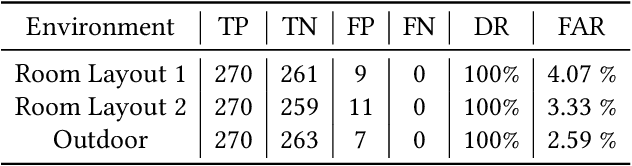
Abstract:Millimeter-wave (mmWave) radars have found applications in a wide range of domains, including human tracking, health monitoring, and autonomous driving, for its unobtrusive nature and high range accuracy. These capabilities, however, if used for malicious purposes, could also lead to serious security and privacy issues. For example, a user's daily life could be secretly monitored by a spy radar. Hence, there is a strong urge to develop systems that can detect and localize such spy radars. In this paper, we propose $Radar^2$, a practical passive spy radar detection and localization system using a single commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) mmWave radar. Specifically, we propose a novel \textit{Frequency Component Detection} method to detect the existence of mmWave signal, distinguish between mmWave radar and WiGig signals using a convolutional neural network (CNN) based waveform classifier, and localize spy radars using the trilateration method based on the detector's observations at multiple anchor points. Not only does $Radar^2$ work for different types of mmWave radar, but it can also detect and localize multiple radars simultaneously. Finally, we perform extensive experiments to evaluate the effectiveness and robustness of $Radar^2$ in various settings. Our evaluation shows that the radar detection rate is constantly above 96$\%$ and the localization error is within 0.3m. The results also reveal that $Radar^2$ is robust against various factors (room layout, human activities, etc.).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge