Jaeseok Kim
Evaluating Visual and Cultural Interpretation: The K-Viscuit Benchmark with Human-VLM Collaboration
Jun 24, 2024Abstract:To create culturally inclusive vision-language models (VLMs), the foremost requirement is developing a test benchmark that can diagnose the models' ability to respond to questions reflecting cultural elements. This paper addresses the necessity for such benchmarks, noting that existing research has relied on human annotators' manual efforts, which impedes diversity and efficiency. We propose a semi-automated pipeline for constructing cultural VLM benchmarks to enhance diversity and efficiency. This pipeline leverages human-VLM collaboration, where VLMs generate questions based on guidelines, human-annotated examples, and image-wise relevant knowledge, which are then reviewed by native speakers for quality and cultural relevance. The effectiveness of our adaptable pipeline is demonstrated through a specific application: creating a dataset tailored to Korean culture, dubbed K-Viscuit. The resulting benchmark features two types of questions: Type 1 questions measure visual recognition abilities, while Type 2 assess fine-grained visual reasoning skills. This ensures a thorough diagnosis of VLM models across various aspects. Our evaluation using K-Viscuit revealed that open-source models notably lag behind proprietary models in understanding Korean culture, highlighting areas for improvement. We provided diverse analyses of VLM performance across different cultural aspects. Besides, we explored the potential of incorporating external knowledge retrieval to enhance the generation process, suggesting future directions for improving cultural interpretation ability of VLMs. Our dataset and code will be made publicly available.
Translation Deserves Better: Analyzing Translation Artifacts in Cross-lingual Visual Question Answering
Jun 04, 2024
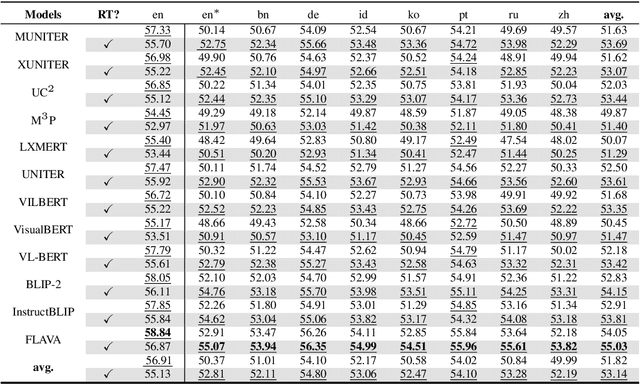
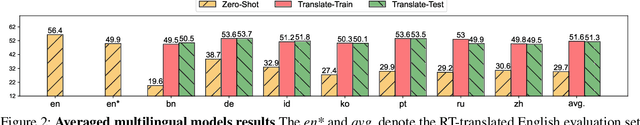

Abstract:Building a reliable visual question answering~(VQA) system across different languages is a challenging problem, primarily due to the lack of abundant samples for training. To address this challenge, recent studies have employed machine translation systems for the cross-lingual VQA task. This involves translating the evaluation samples into a source language (usually English) and using monolingual models (i.e., translate-test). However, our analysis reveals that translated texts contain unique characteristics distinct from human-written ones, referred to as translation artifacts. We find that these artifacts can significantly affect the models, confirmed by extensive experiments across diverse models, languages, and translation processes. In light of this, we present a simple data augmentation strategy that can alleviate the adverse impacts of translation artifacts.
Cleaning tasks knowledge transfer between heterogeneous robots: a deep learning approach
Mar 13, 2019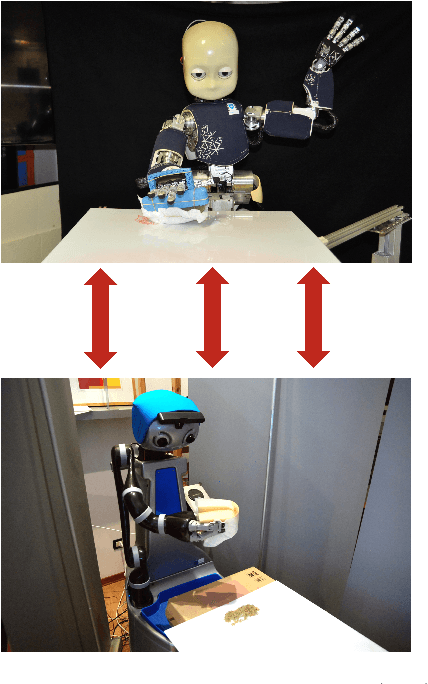
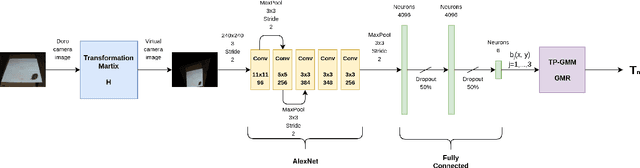

Abstract:Nowadays, autonomous service robots are becoming an important topic in robotic research. Differently from typical industrial scenarios, with highly controlled environments, service robots must show an additional robustness to task perturbations and changes in the characteristics of their sensory feedback. In this paper a robot is taught to perform two different cleaning tasks over a table, using a learning from demonstration paradigm. However, differently from other approaches, a convolutional neural network is used to generalize the demonstrations to different, not yet seen dirt or stain patterns on the same table using only visual feedback, and to perform cleaning movements accordingly. Robustness to robot posture and illumination changes is achieved using data augmentation techniques and camera images transformation. This robustness allows the transfer of knowledge regarding execution of cleaning tasks between heterogeneous robots operating in different environmental settings. To demonstrate the viability of the proposed approach, a network trained in Lisbon to perform cleaning tasks, using the iCub robot, is successfully employed by the DoRo robot in Peccioli, Italy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge